关键词 > 02831/Acc代写
07 02831 Accounting for Managers 2016
发布时间:2022-01-12
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MBA
Accounting for Managers
07 02831
2016
Section A
1. Several years ago, on leaving university, Bean, Pip and Saffy set up a business, BPS, designing and manufacturing furniture for sale to retailers. When BPS was established, Bean and Pip each took 45% of the share capital, with Saffy holding the remaining 10%. This arrangement has remained unchanged. Bean and Pip have always worked full-time in the business and remain its sole directors. Saffy’s role was initially part-time, but after the first two years she transferred to full-time work in her own consultancy business. Her contribution to BPS in recent years has been limited to occasionally providing advice. The relationship between the three shareholders has remained good, but all three are so busy that Saffy rarely meets the others. BPS has been successful, and in February of each year, with the exception of 2015, has paid a substantial dividend to its three shareholders.
Saffy’s consultancy business has also been successful and she now employs 20 staff. You are Saffy’s financial adviser.
During 2013, the two directors decided to expand BPS’s international sales, by establishing sales forces in two neighbouring countries. By early 2014, orders were starting to come in from the new countries. The expansion strategy has been very successful. Last week, Saffy attended a meeting with Bean and Pip, to discuss the future of BPS. Bean and Pip explained that the business now requires more capital in order to fund further expansion, and the purpose of the meeting with Saffy was to request her to inject capital of £250,000 into the business.
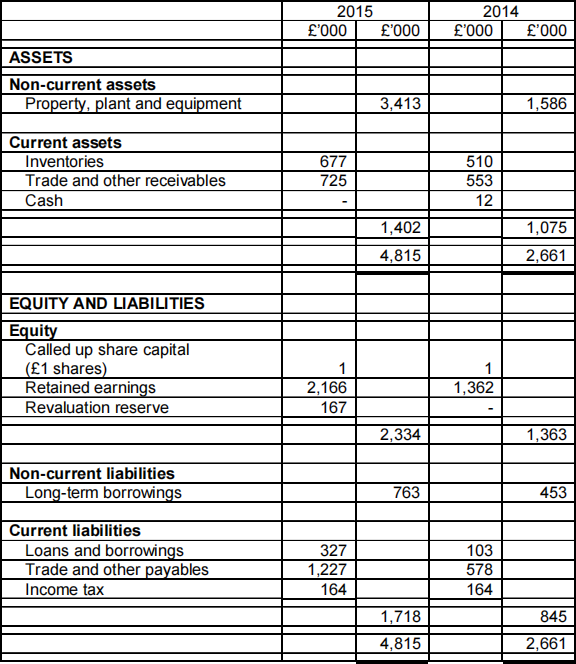
Saffy was provided with a draft Statement of profit or loss for the year ended 31 March 2015 and a Statement of financial position at that date (both given below). The draft statements are unaudited, but the figures are not expected to change, except for the income tax expense figure for 2015. BPS’s accountant has not yet completed a tax calculation and so the 2014 figure of £164,000 has been used as an estimate. No statement of changes in equity has been provided, but the only movements on it would be in respect of a revaluation of property, plant and equipment that took place during the year and the movement on retained earnings in respect of the profit for the period.
Saffy, who has a reasonably good understanding of financial statements, is impressed by the revenue and profit growth. However, she has asked you, as her financial adviser, to look at the figures, in order to identify possible risks and problem areas.![]()
![]()
![]()
BPS: Draft Statement of profit or loss for the year ended 31 March 2015
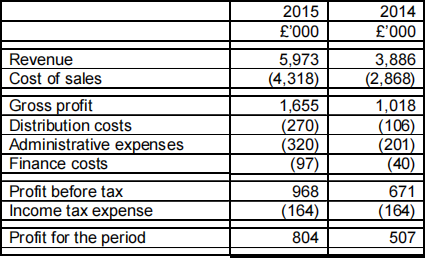
BPS: Draft Statement of financial position at 31 March 2015
Required:
Prepare a report for Saffy that:
a) Analyses and interprets the draft financial statements and discusses BPS’s performance and position.
(Up to 18 marks are available for the calculation of relevant accounting
ratios). [35]
b) Discuss any possible risks and problem areas revealed by the financial statements and the actions that the directors could take to address these
risks and problems. [5]
Total marks [40]
Section B![]()
![]()
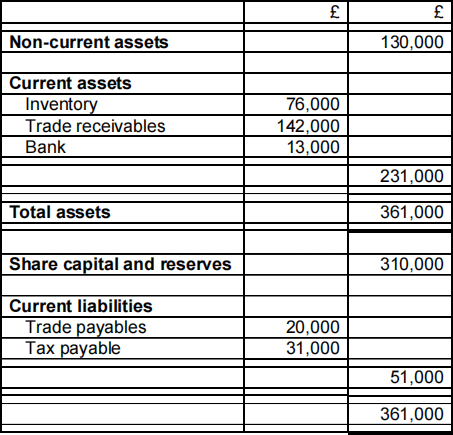
2. Midlands International Ltd is in the process of preparing its budget for the three months ending 30 September 2015. The company’s Statement of financial position as at 30 June 2015 is provided below:
Statement of financial position as at 30 June 2015:
The following revenue and expenses have been estimated for the three- month period:
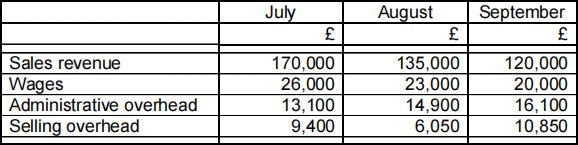
Material costs are 60% of sales for each month and are purchased in the month of sale.
Additional information:
1. Non-current assets amounting to £103,000 will be bought and paid
for in August and amounting to £50,000 will be bought and paid for in September. A non-current asset with a written down value of £1,000 will be sold for £2,000 in cash in July.
2. Corporation tax of £31,000 in respect of last year’s profit will be payable in September.
3. 10% of sales are paid in cash. Of the credit customers, 70% pay in the month after sale; 30% two months after sale. Trade receivables shown in the opening Statement of financial position are expected to pay: 70% in July and 30% in August.
4. Materials are paid for 50% in the month of purchase, the remainder in the month after purchase. Trade payables at the beginning of the year will be paid in July.
5. Wages, administrative and selling overheads are paid in the month in which they are incurred.
6. Administrative overhead estimates shown above include the following amounts for depreciation:
July £5,000: August £6,800: September £8,000.
7. The bank charges overdraft interest at a rate of 12% per annum. The interest is calculated on the bank balance at the end of each month and is added to the bank balance in the following month. No interest is paid by the bank on debit bank balances.
Required:
a) Prepare a monthly cash budget for the three months to 30 September
b) Prepare a statement of profit or loss for the three-month period ending 30 September 2015 and a statement of financial position as at that date. [10]
c) Evaluate the liquidity and the profitability of the company. Your analysis should include the benefits that the company could derive from preparing a
cash budget. [5]
Total marks [30]
3. It has been suggested that, in addition to being business-planning tools, budgets are widely perceived as motivational devices aimed at obtaining desired levels of performance by the company through its management.
Required:
Discuss the factors motivational devices.
that influence the effectiveness of budgets as
[30] Total marks [30]
4. Albatross Limited manufactures two versions of the same product - basic
and deluxe, and in recent months they have been trying to persuade customers who buy the basic version to purchase the deluxe version instead. Overheads have, in the past been absorbed using the labour hour basis.
Details of the two products are given below.
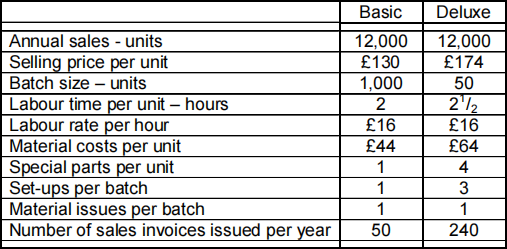
An analysis of overhead costs for Albatross Limited has provided the following information:
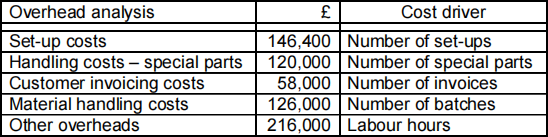
Required:
a) Calculate the profit per unit for the basic and deluxe models using:
i) The traditional absorption approach, and [5]
ii) activity-based costing methods. [15]
b) Write a brief report to the management of Albatross that:
i) Recommends managerial action in light of the information calculated in a) above, and [5]
![]() ii) explains how activity-based techniques can be used to improve
ii) explains how activity-based techniques can be used to improve
Total marks [30]

