关键词 > MTH6141/MTH6141P
MTH6141/MTH6141P: Random Processes 2020
发布时间:2022-01-05
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MTH6141/MTH6141P: Random Processes
Question 1 [13 marks]. This question is about a Markov chain (X0 , X1 , X2 , . . .) with finite state space S .
(a) State what is meant by the Markov property.
(b) For states i, j e S, define what is meant by the transition probability pi,j .
(c) Let 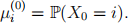 Prove that
Prove that
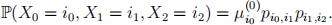
State any standard results used.
Question 2 [24 marks]. Daily weather is modelled by a Markov chain Xn on state space S = {1, 2, 3} where 1 corresponds to a sunny day, 2 corresponds to a rainy day, and 3 corresponds to a snowy day. The transition matrix of Xn is
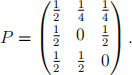
(a) Draw the transition graph for this Markov chain.
(b) If it is sunny on a given day, then what is the probability that it is rainy two days later?
(c) (i) For a general Markov chain with transition matrix P , define what it means for a probability distribution on state space S to be an equilibrium
|
distribution. (ii) For a general Markov chain with transition matrix P , define what it means for a probability distribution on state space S to be a limiting distribution. (d) (i) Explain why the transition matrix is regular. (ii) Determine the limiting probability distribution. |
|
Question 3 [20 marks]. This question is about a gambler. The gambler starts with an initial fortune of e2. He gambles once per day until he quits. He quits when either he loses all his money or he increases his fortune to e4. On a day when he has 戈j, where j e {1, 2, 3}, he gambles on the outcome of a game, and wins e1 with probability (4 - j)/10, but loses e1 with probability (6 + j)/10.
|
(a) The gambler’s changing fortune can be modelled as a Markov chain with five states. Define the five states and say to what situations they correspond. (b) Draw a transition graph for this Markov chain. (c) Write down a transition matrix for the Markov chain. (Indicate clearly which rows of the matrix correspond to which states.) (d) Using first-step analysis, or otherwise, find the expected number of gambles the gambler makes until he quits. Show your working. |
Question 4 [18 marks].
(a) State the Thinning Lemma for Poisson processes.
Parts (b)-(e) of this question are about a bus stop at which buses arrive according to a Poisson process of rate 6 per hour. Your answers to the following questions should be expressed in powers of e (where appropriate), but they should be simplified in all other ways.
|
(b) What is the probability that two buses arrive between 8:00 am and 8:30 am? (c) Given that no bus arrives between 8:00 am and 8:30 am, what is the probability that at least two buses arrive between 8:30 am and 9:00 am? |
(d) Each bus which arrives at the bus stop is ‘out of service’ with probability 1/4, independently of all the other buses. What is the probability that at least two ‘in service’ buses arrive between 9:00 am and 11:00 am?
(e) Determine the expected arrival time of the second bus to arrive after 8:00 am.
Question 5 [25 marks]. A continuous time Markov chain X(t) on state space S = {1, 2, 3} has the following generator matrix:
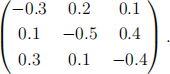
Initially, X(0) = 1.
(a) Draw a transition graph for this random process.
(b) State Kolmogorov’s forward equations for 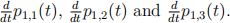
(c) Calculate the probability that the process remains in state 1 throughout the period 0 s t s 2. Your answer should be expressed in powers of e (if appropriate),
|
but should be simplified in all other ways. (d) Determine the probability that the second jump of the process is into state 1. (e) Write down the equations satisfied by the limiting distribution of this continuous time Markov chain. You do not need to solve them. |

