关键词 > Econ400
Econ 400 HW 4 Spring 2024
发布时间:2024-05-30
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Econ 400 HW 4 Spring 2024
1. In this problem you are asked to compare the outcomes of monopoly and perfect competition in one market. We are going to assume very simple functional forms in order to simplify the algebra. We assume that the firm has a very simple cost function: c(q) = cq, with c > 0. The marginal cost of production therefore is constant. As for the inverse market demand, we assume that it takes the simple linear form PD(Q) = a − bQ, with a > c > 0, and b > 0, where Q is the total market quantity, the sum of each firms individual output q.
(a) Consider first the case of perfect competition. Derive the marginal and average cost curves. How does the supply curve look like for each firm? What about in the industry? (aggregate the indi- vidual supply curve over J firms). (4 points)
(b) Equate supply and demand to obtain the industry-level produc- tion under perfect competition Q*,well as the price level under perfect competition P* . (3 points)
(c) How do perfect competition price and quantity vary as the marginal cost of production c increases? How do they vary if there is a positive demand shock (a increases)? (3 points)
(d) We consider now the monopoly case. Write down the profit maximization problem and the first order conditions with re- spect to q [In the case of monopoly, q = Q]
(e) 5. Solve for Pm and Qm How does PM vary as a increases? Why is this comparative statics different from the one under perfect competition? (2 points)
(f) Compare the total output and prices of perfect competition and monopoly. Compute the monopoly profits and compare them to the profits under perfect competition. (3 points)
2. Consider a market with inverse demand PD(Q) = a−bQ, served by J competitive firms who each have cost function c(q) = 2/c q 2 + F, where F is fixed costs.
(a) Derive the marginal and average cost curves. How does the sup- ply curve look like for each firm? What about in the industry? (aggregate the individual supply curve over J firms). (4 points)
(b) Equate supply and demand to obtain the industry-level produc- tion under perfect competition Q*,well as the price level under perfect competition P* . (3 points)
(c) What will the long run competitive price PLR be in this indus- try? What is the shape of the long-run competitive supply curve? (3 points)
(d) How many firms will operate in the long run of this industry? Derive an expression for J as a function of a, b, c and F. (3 points)
(e) Under what conditions on F will the J you found above be larger than 1? (2 points)
(f) Suppose that F is above the level you found above; is it still pos- sible that a firm could sell to these consumers and turn a profit? Explain how, in words. (2 points).
3. Consider an economy with two consumers, Adalia and Briana and two goods: bicycles, x1, and flowers, x2 . Adalia’s initial endowment of the commodities is bundle A = (40, 60) and Brianna’s endowment is bundle B = (60, 40). Adalia and Briana’s utility functions are given by, for i = A, B
Ui(x1, x2) = 4log x1 + 4log x2
(a) Sketch an Edgeworth box and mark the point that corresponds to initial endowments. 3 points.
(b) Is this current allocation an efficient allocation? Explain why or why not. 5 points.
(c) What is the value of each consumer’s endowment, as a function of p1 and p2 ? 2 points.
(d) Calculate each consumer’s demand functions for x1 and x2. 3 points.
(e) Normalize p2 = 1, and using each consumer’s endowed “in- come,” the resource constraint for good 1, calculate the competi- tive price p1 . 5 points.
(f) Using the prices you found, calculate the competitive equilib- rium, and sketch it. 5 points.
(g) Is this outcome on the contract curve? Explain. 5 points.
4. Consider two firms that can produce goods X and Y using only labor according to the following production functions.
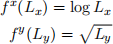
There are 20 units of labor available.
(a) Write out the maximization problem of output of firm y with firm x output fixed at 2. 5 points.
(b) With the solution Lx(*) found above, calculate the maximum out-put of firm y. 2 points.
(c) Treating firm x output as a parameter, solve for the production possibilities frontier in this economy. 5 points.
(d) Suppose that the Marginal rate of substitution for the consumer who will consume the output of the two firms is 2/1; what is the efficient level of output of each good? How much labor will each firm use? 3 points.

