关键词 > BEEM012
BEEM012 – Practice Questions for Dynamic Causal Effects
发布时间:2024-05-27
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
BEEM012 – Practice Questions for Dynamic Causal Effects
1 Dynamic Causal Effects
1. What is the name of this model (remember to include the order of the model)
Yt = β0 + β1Xt + β2Xt-1 + β3Xt-2 ··· + βr+1Xt-r + ut
. Explain, in terms of the model coefficients, what the dynamic multi- pliers are
. If we want to understand the cumulative impact of a change in X on Y over the next three periods, how would we compute this from parame- ters in this model?
. What are the two conditions required for us to estimate this model?
. Explain intuitively why serial correlation of errors might be present in the model above.
. Explain whether this statement is True or False: “If we estimate our model on data with serially correlated errors, our estimated coefficients may be biased but our standard errors will be correct. ”
. Explain the distinction between the assumptions described by the fol- lowing two error conditions:
i) E[ut |Xt, Xt-1 , . . .] = 0 and
ii) E[ut | ..., Xt+1, Xt, Xt-1 , . . .] = 0
2. Exogeneity v. Strict Exogeneity
. Question 1 A friend is asking you how to estimate Dynamic Causal E↵ects for a project they are working on. Their outcome variable is the price of staple crops which can be consumed or stored., and they want to understand how climate shocks impact prices. In their context, reliable climate forecasts are widely available. Is it reasonable to assume strict exogeneity in this case?
. Question 2 A friend is asking you how to estimate Dynamic Causal E↵ects for a project they are working on. Their outcome variable is the price of staple crops which can be consumed or stored., and they want to understand how climate shocks impact prices. In their context, reliable climate forecasts are not widely available and people have no way to predict next period’s climate shocks this period. Is it reasonable to assume strict exogeneity in this case?
3. In what circumstance is computing HAC errors the best method available to to deal with serial correlation of errors when estimating Dynamic Causal E↵ects? Give an intuitive explanation of how it deals with serial correlation of errors.
. Explain what type of exogeneity is reasonable to assume in this case. . If we begin with homoskedasticity-only errors
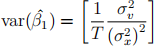
how do we adjust to account for serially correlated errors?
. Explain the issue with estimating the exact value of fT and discuss the role of the truncation parameter. Why can’t we just include estimates of all lags of autocorrelation?
. Write down the formula for f(ˆ)T using the truncation parameter m
4. Topic: Dynamic E↵ects under Strict Exogeneity
. If we can assume that our errors follow strict exogeneity, explain how modelling our error as ![]() t = ut − φ1ut-1 allows us to derive models without autocorrelated errors.
t = ut − φ1ut-1 allows us to derive models without autocorrelated errors.
– Explain why this condition is only true under strict exogeneity:
E[![]() t | X(-)t , X(-)t-1 , . . .] = 0
t | X(-)t , X(-)t-1 , . . .] = 0
– How do we recover our dnamic multipliers from the estimated co- efficients from this model?
Y(ˆ)t =ˆ(↵)0 +φ(ˆ)1 Yt-1 +δ0(ˆ)Xt + δˆ1Xt-1 +δ2(ˆ)Xt-2
– Write the expression for the dynamic multiplier on Yt from being treated one period ago in terms of these coefficients
5. Topic: Cochrane-Orcutt Estimator
. Now, we consider the second model for estimating dynamic causal ef- fects under strict exogeneity. Describe the procedure for computing the feasible GLS estimator.
. Explain how we use the final outcome of the Cochrane-Orcutt estimator to repeat this process for the iterated Cochrane-Orcutt.
6. Topic: Dynamic Effects Methods
. Which method should you use under the assumption of exogeneity?
. If your priority is having no bias at all, and you don’t mind having a higher-variance estimator, which method should you use under the assumption of strict exogeneity?
. If your priority is having a low variance estimator, and you don’t mind having some bias in your estimator, which method should you use under the assumption of strict exogeneity?

