关键词 > QF5202A
QF5202A Structured Products Homework One
发布时间:2024-05-20
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
QF5202A
Structured Products
Homework One
1. The optimal policy adopted by the holder of a flexible notional currency forward is to exercise either (i) the whole notional, (ii) zero amount on each preset exercise date. Use your own words to justify the above claim. Suppose differential transaction costs are charged according to the amount transacted, say, 0.1% on the first $10, 000 and 0.12% on the next $10, 000, would optimality of the above exercise policy remain to hold? Explain your answer. [1]
2. Consider the three-jump process for the approximation of the jump ratio of the asset price process over one period as in the lecture note. The governing equations for the parameters p1, p2, p3, u, m and d can be obtained by
(i) setting the sum of probabilities to be 1
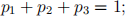
(ii) equating the first two moments of the approximating discrete distribution and the corresponding continuous lognormal distribution
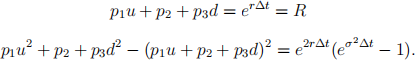
The last equation can be simplified as
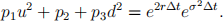
The remaining two conditions can be chosen freely. They are chosen to be
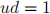
and
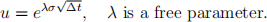
By solving the five equations together, show that
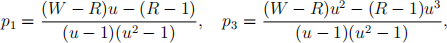
where 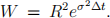 Also, show that the trinomial model reduces to the usual binomial scheme when λ = 1. [2]
Also, show that the trinomial model reduces to the usual binomial scheme when λ = 1. [2]
3. Consider the window Parisian feature, associated with each time point, a moving window is defined with 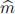 consecutive monitoring instants before and including that time point. The option is knocked out at a given time when the asset price has already stayed within the knock-out region exactly m time, m ≤
consecutive monitoring instants before and including that time point. The option is knocked out at a given time when the asset price has already stayed within the knock-out region exactly m time, m ≤ 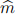 , within the moving window. Under what condition does the window Parisian feature reduce to the consecutive Parisian feature? How to construct the corresponding discrete grid function gwin in the forward shooting grid (FSG) algorithm? [2]
, within the moving window. Under what condition does the window Parisian feature reduce to the consecutive Parisian feature? How to construct the corresponding discrete grid function gwin in the forward shooting grid (FSG) algorithm? [2]
Hint: We define a binary string A = a1a2 · · · a m to represent the history of asset price path falling inside or outside the knock-out region within the moving window. The augmented path dependence state vector has binary strings as elements. For example, the binary string a1 assumes the value 1 (or 0) if the asset price path falls inside (or outside) the knock-out region on one day earlier. Explain how to update A when the calendar time moves one day forward.
4. Let Ft denote the exchange rate process that gives the time-t domestic currency price of one unit of foreign currency. Let Qd and Qf denote the risk neutral measure in the domestic currency world and foreign currency world, respectively. Let rd and rf denote the domestic and foreign riskless interest rate, respectively.
Let FS/U denote the Singaporean currency price of one unit of US currency and FH/S denote the Hong Kong currency price of one unit of Singaporean currency. Assume FS/U to be governed by the following dynamics under the risk neutral measure QS in the Singaporean currency world:
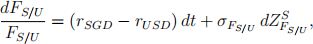
where rSGD and rUSD are the Singaporean and US riskless interest rates, respectively. The quanto option pays FH/S Hong Kong dollars if FS/U is above the strike level X. Find the value of the quanto option in Hong Kong currency in terms of the riskless interest rates of the different currency worlds and volatility values σFS/U and σFH/S . [2]
5. Suppose we would like to replicate the discrete realized variance as proxied by
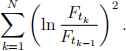
Here, Ftk is the closing price of the tN -maturity futures at time tk, k = 1, 2, . . . , N. Similar to the replication of VIX, we use traded call options and put options in the replicating portfolio. Let rk be the daily rate of return of the tN -maturity futures defined by
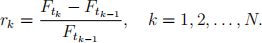
Using basic calculus, one can easily obtain the following approximations:
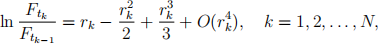
and
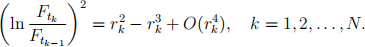
You are not required to prove these approximations.
(a) Using the above results, show that
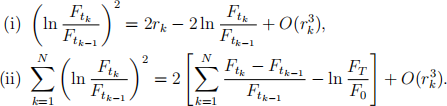
(b) Show that the approximate replication of the discrete realized variance is given by
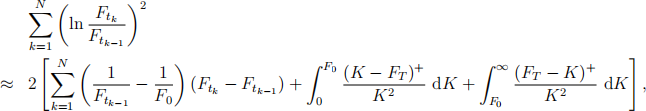
where FT = FtN . Explain how to implement the replication using the dynamic position of futures (derived from the first term) and the static positions of the out-of-the-money put options and call options on the T-maturity futures (derived from the second and third integral terms). [3]
Hint: Recall the Taylor expansion formula for ln 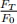 :
:
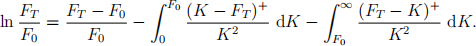
Take note of the dynamic position of futures required.

