关键词 > SESM6050
SESM6050 Tribology for Future Mobility SEMESTER 2 MOCK EXAM
发布时间:2024-05-18
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
SESM6050 Tribology for Future Mobility
SEMESTER 2 MOCK EXAM
Question 1
(a) With illustrated notes describe the bath tub curve. [10 marks]
(b) What are the laws of friction? Comment on the applicability for polymer and metal contacts. [6 marks]
(c) Describe the similarities and differences between abrasive and adhesive wear? [9 marks]
Question 2
(a) What are the differences between hydrodynamic and elastohydrodynamic lubrications? [4 marks]
(b) Explain why applied load in elastohydrodynamic lubrication has little effect on the minimum film thickness? [4 marks]
(c) A hydrodynamic plain journal bearing has a diameter of 200 mm and a width of 50 mm and supports a radial load of 10 kN, while the shaft rotates at 300 rpm. Calculate the oil viscosity if the maximum pressure (pmax) obtained in the bearing is 5 MPa and the coefficient of friction is 0.003. [8 marks]
(d) A cylindrical roller bearing is used to support an 8 kN load for 1200 h at 600 rpm. Calculate the load carrying capacity of this bearing for 95% reliability. What size bearing would you recommend? [9 marks]
Question 3
(a) In analysing heat flow in a sliding contact a dimensionless group known as the Péclet number J can be defined by J = ua⁄2KB where u is the sliding speed, a is the radius of the circular contact patch and KB is the thermal diffusivity of the body over which the contact is moving.
How can the value of J be interpreted in physical terms? [4 marks]
Discuss qualitatively how the distribution of heat flux between the two bodies and the resulting temperature distributions will vary as the Péclet number is varied between very low (J ≪ 1) and very high (J ≫ 1) values. [6 marks]
(b) A machine brake assembly consists of a fixed ball sliding against the rim of a rotating disc. Two different designs are proposed: one with a nylon ball and a steel disc, and the other with a steel ball and a nylon disc. In both designs the coefficient of sliding friction between the nylon and the steel can be assumed to be 0.5, and the contact patch to be circular with a diameter of 1 mm. The load pressing the ball against the disc is 10 N and the disc rotates at a maximum surface speed of 1 m s−1. The material properties are as follows:
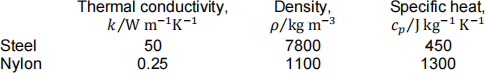
Calculate for each brake design:
i. the maximum power dissipated in friction;
ii. the value of the Péclet number J;
iii. the maximum flash temperature rise at the sliding interface. [10 marks]
Explain in qualitative terms why the interfacial temperature rise is considerably greater for one design than for the other. Discuss the proposed design of brake critically. What further information would you need in order to optimize the design of the brake? [5 marks]
Question 4
(a) What are the advantages of ball bearings when utilised for deep-groove and angular-contact ball bearings? [8 marks]
(b) What are the advantages of cylindrical rollers compared with ball bearings? [3 marks]
(c) Consider a single-row, deep-groove ball bearing (6209) with the following dimensions and operational conditions:

Calculate the maximum ball load (Wz)max and pressure pmax, as well as the total elastic compression on the load line (δmax). [9 marks]
Determine the ball inner- and outer-race film parameters (Λ) and comment on the suitability of the bearing design. [5 marks]

