关键词 > MATH3333
MATH 3333 3.0 Section A Test
发布时间:2024-05-17
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MATH 3333 3.0 Section A
Test
February 29, 2024
Question 1: (15 marks)
1) 15 pt Consider the linear model yi = β0 +β1 xi,1+β2 xi,2+ϵ. Given the current data set with
10 observations, we obtain the least square estimates of the regression coefficients β(ˆ)0 = 3,
β(ˆ)1 = 2, and β(ˆ)2 = 1. Now one additional data point is available. They are x11,1 = 5, and
x11,2 = 3, y11 = 19.5. Please use the online algorithm (stochastic gradient descent method) to update the linear model using the new observations. Provide all of the work of your calculation. Use the learning rate 0.001.
Question 2: (25pt) Logistic regression is a popular classification algorithm. In logistic regression, we assume Y = (Y1 ,..., Yn )T are a collection of n binary observations. For each Yi , we observe Xi = (Xi1, Xi2, Xi3)T predictors. Let pi = P(Yi = 1). We assume
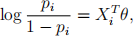
where θ = (θ1 ,θ2 ,θ3 )T is the vector of regression coefficients. The probability function of
any binary random outcome is given as P(Yi ) = pi(Y)i (1 − pi )(1 −Yi) .
5pt) Derive the derivative of the overal loglikelihood of the dataset ∂l(Y)/∂θ1 using chain rule, where l(Y) =:i Yi log pi + (1 − Yi )log(1 − pi ).
5pt) Derive the second order partial derivative of the overal loglikelihood of the dataset ∂2 l(Y)/∂θ1 ∂θ3 .
5pt) Ifθ(ˆ) = (0.5, 0.2, 0.1)T , and we observe a new observation xn+1 = (1, 4, 5)T . Please predict
the probability pn+1 = P(Yn+1 = 1).
5pt) Suppose Yn+1 = 1, calculate the first derivative vector ∂l(Yn+1)/∂θ .
5pt) If instead of using Newton’s method, we decide to use stochastic gradient accent algo- rithm, which updates the parameter in the following manner:
θ(ˆ)new =θ(ˆ)current + λ∂l(Yn+1)/∂θ .
Please update the estimate for θ. Use the learning rate λ = 0.001.
Question 3: 5 pt) Suppose we use the logistic regression to predict whether or not a mortgage application will be defaulted. We build a classification model based on the training data and we apply the algorithm on the testing data set. Here are the classification results on the testing data using the cutting-off probability equal to 1/2 : fp = 20, tp = 80, fn = 30, tn = 90. (fp: the true status is negative, but falsely identifed as positive; tp: the true status is positive and is correctly identifed as postive; fn: the true status is positive, but falsely identified as negative; tn: the true status is negative, and is correctly identified as negative.) 2pt) Calculate the sensitivity (the proportion of correctly identified positive outcomes) and specificity (the proportion of correctly identified negative outcomes) of the algorithm on the testing data set.
1pt) If the negative is probability
bank wishes to further decrease the fn number as the loss associated with false more costly compared to the false positive cases. Should we increase the cut-off value?
1pt) Calculate the sensitivity and specificity of the algorithm when the cut off probability is 0.
1pt) Calculate the sensitivity and specificity of the algorithm when the cut off probability is 1.
Question 4: (8pt) In maximum likelihood estimation, the estimator is obtained by maxi- mizing the log likelihood function. However, most of the log likelihood has to be optimized by Newton-Raphson algorithm. In this question, we use Newton-Raphson algorithm to find a local maximum of a univariate function. Consider the function f(θ) = 3θ3 − 2θ + 6,θ > 0. Suppose the initial estimate is θ(0) = 1.5. Use Newton-Raphson algorithm to update the estimate and compute the updated parameter θ(1) .
Question 5: (3pt) Based on a data set, we perform a ridge regression with λ = 0.1. It is
given that
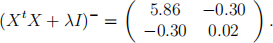
We also have
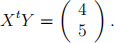
3 pt) Based on all the results above, compute the ridge regression estimate for the regression coefficients.
Question 6:
In the following, we provide the output of lasso program on the fish toxicity data. The
predictors are the original 6 measurements (V1-V6) collected by biologists and 100 irrelevant measurements (X7 -X106) I simulated from normal distributions. In total, we have 106 candidate predictors.
Sequence of LASSO moves:
Var V6 V2 V3 V4 V5 V1 X94 X104 X56 X106 X86 X28 X51 X17 X50 . . .
Step 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 . . .
a) 2 pt. According to the outcome, please provide the sequence of the first six candidate models.
b) 2 pt Based on the output, more and more predictors are added into the linear model. Along this path of LASSO moves, is the penalty paraemter λ increased or decreased so that more predictors are included in the model?
Question 7: 10 pt We wish to maximize the following objective function Q(β). Please derive the first derivative of the objective function with respect to β, and solve the derivative equation. The objective function is as follows
Q(β) = (2Xβ − Y)T (5Xβ − Y),
Where X is a data matrix of dimension n × p, β is ap × 1 regression coefficient vector, Y is a n × 1 response vector.
a) 5 pt. Please derive the first derivative of the objective function with respect to β .
b) 5 pt Based on part a), set the first derivative equal to zero and solve for β .

