关键词 > MachineLearning
Machine Learning Intelligent Chip Design
发布时间:2024-05-16
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Machine Learning Intelligent Chip Design
[HW3] Implement NoC by SystemC
Description
NoC (Network-on-Chip) is a promising architecture that can help overcome communication bottlenecks and performance limitations in modern computer systems. It decouples computing resources from communication resources, allowing for large-scale parallel processing and highly flexible communication channel configurations that can be optimized based on specific application requirements.
Additionally, NoC is highly fault-tolerant and scalable, providing a powerful foundation for future integrated circuit and system architectures.
Implementation Details
In HW3, you are required to implement a 4x4 mesh-based NoC architecture as shown in Figure 1. The system architecture includes the following two types of modules:
• Router: The routers will be responsible for routing flits between different components within the network.
• Core: Each router will be connected to a core module, which includes the Processing Element (PE) and the Network Interface (NI). The PE generates data packets, while the NI manages communication between the PE and the router.
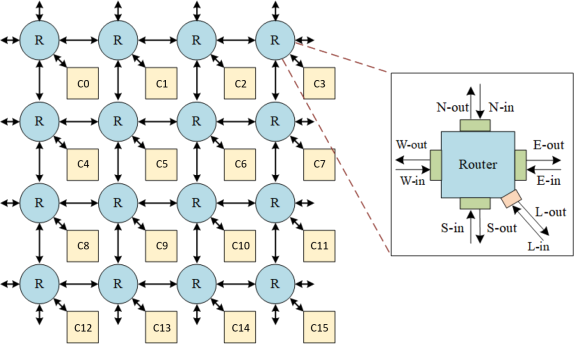
Figure1. 4x4 mesh-based NoC architecture
To simplify the complexity of system design for this assignment, TA will provide a pre-written PE. The PE will be encapsulated within the core module and mainly consists of three functions:
• void init(int pe_id)
You need to call this function at the beginning of the simulation. The pe_id is numbered sequentially, starting from 0 in the upper-left corner, as shown in Figure 1.
• Packet* get_packet()
Each time you call this function, you can obtain a send packet. If the PE has no more packets to send, this function will return nullptr.
The definition of a packet is shown in Figure 2, each packet contains a source_id and a dest_id, along with a floating-point vector datas. The length of the vector in each packet is different.
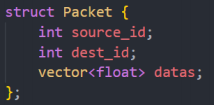
Figure 2. Packet structure
• void check_packet(Packet* p)
When all flits of a packet are received, you need to pack these flits into a packet and send it to the PE by calling this function. The PE will verify whether the packet is correct. When all PEs receive the correct packets, the simulation will stop immediately and display the following screen.
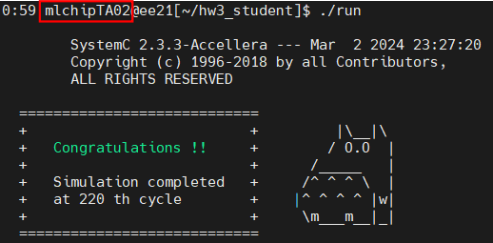
Figure 3. Screenshot of successful simulation
Please take a screenshot and place it in your report, ensuring that your workstation account is in the picture.
Additionally, TA also provides the port definitions of Core and Router modules (Figure 4). You need to connect the core to the router, and the router to the top, bottom, left, and right routers, as shown in the architecture in Figure 1. As a reminder, since the size of each flit is limited to 34 bits, the packet should be decomposed before it is sent to the router.
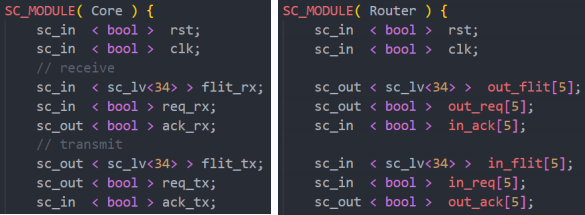
Figure 4. Port definitions of Core module and Router module
Figure 5 is an example of flit format definitions, the first two bits are used to identify the header, body or tail flit. You can reference the definition example or customize the flit format and even modify the port definition. Please explain your design considerations (such as latency, bandwidth, complexity, etc.) in detail in the report.
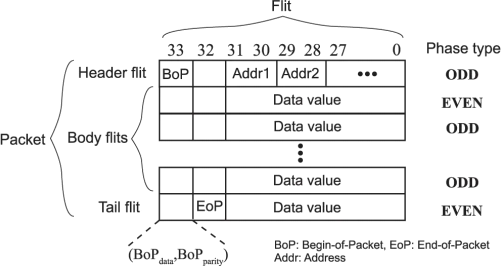
Figure 5. Example of flit format definitions
In the main function, there are three separate parts. The signals declaration, modules declaration and modules connection. You can reference Figure 4 to declare all the signal you need in the main function and interconnect these routers and cores to construct your network.
For the pattern files, the data format is “TO
Implement Notes
A key aspect of the implementation will be the choice of routing policy employed by the routers (e.g., XY routing, west-first adaptive routing, etc.). This policy will determine how data packets are transmitted through the network and affects simulation time.
It is important to note that in this assignment, only sc_in and sc_out can be used for ports. Channels and interfaces that were utilized in HW2 are not allowed.
Additionally, using pointer in port definition is also forbidden as it doesn't make sense in hardware design.
Submission Guidelines
• Please compress a folder named HW
• The folder should include:
o Report (Name: HW
o Codes
o Makefile
o pattern folder
• Example:
• Ensure that your code is well-commented and organized for clarity and understanding.
• Plagiarism is forbidden, otherwise you will get 0 point!!!
• SystemC Implementation:
Use SystemC to implement the 4x4 mesh-based NoC architecture.
• Report:
A brief report document containing
o Simulation results with your workstation account.
o How do you design the router and NI? What routing algorithm do you use? What is the depth of the buffer? Do you use virtual channels?
o Your implementation approach, challenges faced, and any observations or insights gained during the implementation and simulation process.

