关键词 > ECON20120
ECON20120 Mathematical Economics I 2022
发布时间:2024-05-16
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECON20120
Mathematical Economics I
Release Date: 6 June 2022 at 9:45am.
Submission Deadline: 8 June 2022 at 9:45am.
Section A
Answer all questions.
Question A.1 (Word Limit: 100 words)
Consider the following game in normal form:
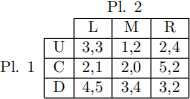
(i) If the game is played with simultaneous moves, identify all the pure strategy Nash equilibria (if any).
(ii) If the game is played with simultaneous moves, identify all the mixed strategy Nash equi- libria (if any).
(iii) If the game is played with sequential moves, where player 1 moves irst, identify all the subgame perfect Nash equilibria (if any).
(iv) If the game is played with sequential moves, where player 1 moves irst, identify all the Nash equilibria which involve empty threats (if any). [10 marks]
Question A.2 (Word Limit: 300 words)
For this exercise s=1+the fourth digit of your student number.
A research laboratory announces the discovery of a new refreshment. Immediately the public expresses a (linear) demand for the new product. There are two irms which have capacity to produce quantities q1 , q2 of the new product with constant marginal costs c1 , c2 respectively, where c2 = c1 + 4 根 s. You observe that before irms start to produce (i.e., q1 = q2 = 0) the market clears at p = 160 根 s. When supplies arrive at the market you observe that the equilib- rium price and quantity settle at ![]() = 60 根 s and Q(-) = 200 根 s respectively.
= 60 根 s and Q(-) = 200 根 s respectively.
(i) Suppose that you consider investing in irm 1 by inancing half of its production cost in exchange for half of its revenue. Compute the proit that irm 1 would retain after paying you of. [5 marks]
(ii) Alternatively you consider investing in this market and discover that, at a ixed cost F = 70000, you can buy a technology to produce the new product with constant marginal costs c = 60. Explain and justify whether or not you would invest in this market. [10 marks]
(iii) Explain whether or not the manager of irm 1 would rather accept your ofer in (i), or decline it and let you proceed with your alternative in (ii). [5 marks]
Question A.3 (Word Limit: 300 words)
In an industry there are two irms, R1 and R2, producing diferentiated products that engage in price setting competition. They both have constant marginal costs c1 and c2 and the demand functions of their respective products are
D1(p1 , p2 , p3 ) = 70 - 2p1 + p2
D2(p1 , p2 , p3 ) = 140 + p1 - 2p2
(i) Firm R1 chooses its price p1 irst, followed by irm R2 who sets its own price p2 after observ- ing the price set by its opponent. Compute the equilibrium prices in this market as a function of the marginal costs. [10 marks]
(ii) Suppose that marginal costs evolve over continuous time according to the system:
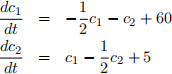
By studying the above system, compute the long run equilibrium prices in this market. [10 marks]
Section B
Answer either Question B.1 or Question B.2.
Each question is worth 50 marks.
Question B.1 (Word Limit: 300 words) In a market there are two identical irms, i = 1, 2 that supply a product. The total cost is given by Ci(qi) = 240qi, where qi is the output supplied by irm i = 1, 2. The inverse demand function in this market is given by:
p = 600 - 2Q (1)
where Q = q1 + q2 .
(i) If the managers of the two irms colluded to jointly produce total output and share the proits, show that the most proitable collusion agreement would be to produce the monopoly output. Demonstrate that in lack of some enforcement mechanism, such a collusion agreement would not be stable from a strategic point of view. [10 marks]
(ii) Find the equilibrium in this market if irms simultaneously and non-cooperatively choose the quantities they produce. Briely but clearly show your derivations. Compute the equilibrium proits of irms 1 and 2 respectively. [10 marks]
(iii) The manager of irm 2 faces the following situation: Before production decisions, irm 2 has the opportunity to invest in a new technology that will reduce its marginal cost to c2 = 160. This new technology requires payment of a ixed installation cost F = 600 根 s, where s=1+the fourth digit of your student number, so the total cost of irm 2 would become C2(q2 ) = 160q2 + 600 根 s.
The decision whether or not to install the new technology will be known by irm 1 before its output decision. If he does not invest in the new technology, irm 2 can move irst. If he invests, the installation of the new technology will cause delays in the output decision of irm 2 and meanwhile irm 1 will announce its output decision irst, i.e., irm 1 will move irst. Explain what you expect will happen in this strategic situation. [15 marks]
(iv) Knowing the facts of the situation in (iii), before the manager takes his decision, you ofer the following deal: invest in irm 2 by inancing half of the production costs. In return you will receive a fraction of the irm’s revenue, which would be negotiated via a bargaining game of alternating ofers (’split the pie’) where the manager will make the irst ofer and the game will last four rounds, after which none will receive anything. If both of you have a discount rate δ = 2/1, explain whether or not:
(a) This is a good deal for you if it is accepted.
(b) The manager would accept this deal. [15 marks]
Question B.2 (Word Limit: 300 words) In an industry there are three irms, R1 , R2 and R3, producing diferentiated products. They all have constant marginal costs c1 = c2 = 20, c3 = c. The demand functions of their respective products are
D1(p1 , p2 , p3 ) = 80 - 2p1 + p2 + p3
D2(p1 , p2 , p3 ) = 80 + p1 - 2p2 + p3
D3(p1 , p2 , p3 ) = 80 + p1 + p2 - 2p3
(i) Set up the proit functions of the three irms. [5 marks]
(ii) The three irms are in a two stage price setting competition. In the irst stage irms R1 and R2 set their prices p1 and p2 simultaneously. In the second stage, irm R3 once it observes the prices set by R1 and R2 sets its price p3 .
Compute the equilibrium prices in this two stage game, as a function of the cost parameter c. [20 marks]
(iii) Suppose that the game is repeated over time periods t = 1, 2, . . .. You have an invention that can reduce the cost parameter c over time, according to the equation
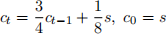
where s=1+the fourth digit of your student number.
(a) Compute the time path of the equilibrium price of irm R3 .
(b) Compute the long run equilibrium prices in this market as t → ∞. [15 marks]
(iv) Compute the additional proit that your invention will ofer irm R3 in the long run. Find the one time payment F you would ask for your invention if you split the extra proit with irm R3, according to the following alternating ofers game, where both you and irm R3 have a discount factor δ = 3/1: firm R3 will make the first offer and the negotiation will last for 4 periods, after which the deal is of and both get nothing. [10 marks]

