关键词 > LHPhysicalIIIb/0333681
LH Physical IIIb / 03 33681 Chemistry Summer Examinations 2023
发布时间:2024-05-15
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & PHYSICAL SCIENCES
SCHOOL OF CHEMISTRY
Year 3 Degree of MSci/BSc with Honours
Chemistry
Chemistry with Industrial Experience
Chemistry with Business Management
Chemistry with a Modern Language
Degree of B.A./BSc Liberal Arts & Sciences
LH Physical IIIb / 03 33681
Summer Examinations 2023
Time Allowed: 3 hours
1. (a) Giving full justification, suggest the best technique (or combination of
techniques) and experimental strategy that could be used to investigate each of the following situations (i) to (iii):
[Do not describe all the details of how the methods work from your notes.
Instead you should focus on the key features of the experiment that make it suitable for the situation and explain why other methods maybe less suited.]
(i) the nature of lattice defects in a crystal of barium phosphate; (2 marks)
(ii) the magnetic structure of Y3Fe5O12 ; (3 marks)
(iii) accurate details of the structural packing arrangement in a crystal of benzoic acid and whether this structure is representative of the bulk sample. (4 marks)
(b) Explain why, following exposure to gaseous carbon monoxide, the LEED
pattern for the (100) face of a single crystal of palladium remained the same, whereas the XPS spectrum of this surface contained additional peaks. (3 marks)
(c) Both XRF and XPS maybe used to gain insights into the composition of a solid. Describe, giving an explanation of the underlying reasons, the extent to which these techniques probe the bulk composition versus the surface composition of the solid. (4 marks)
2. (a) In a first experiment, the tip of a STM operated in constant height mode is
moved in direction x across the surface schematically depicted in Figure 1, where materials A and B are two metals with work functions ΦA and ΦB, respectively.
Sketch the dependence of the tunnelling current, I, on the lateral position,x, if
(i) ΦA > ΦB
(ii) ΦA = ΦB
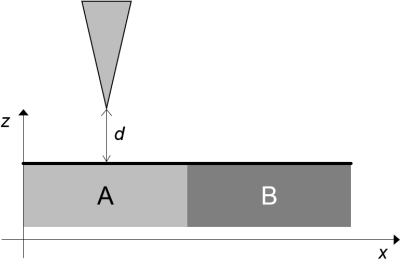
Figure 1 (4 marks)
(b) In a successive experiment, I is measured while the tip of the STM is positioned above metal A and the tip-surface separation, d, is increased, resulting in the data in Table 1.
Table 1
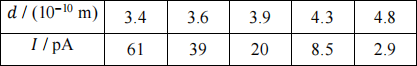
Determine the value of ΦA in eV, assuming that the STM tip is made of material A. Give all your working. (6 marks)
(c) XPS measurements are performed on thin films of two types of conjugated polymers (structures shown in Figure 2).
Sketch the expected C 1s and S 1s spectra, justifying the number, relative intensity and relative position of the peaks if:
(i) the polymer side chain is propyl;
(ii) the polymer side chain is ethoxy.
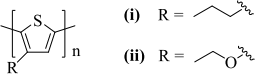
Figure 2
Hint: consider the values of the electronegativity and the binding energies of 1s core electrons for the elements in their natural form given in Table 2.
Table 2
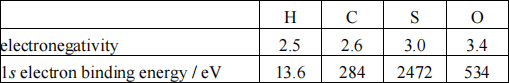 (6 marks)
(6 marks)
3. (a) A Ru/silica catalyst consists of 8 wt% Ru dispersed on a silica support. On
exposure of the catalyst to carbon monoxide, the CO is selectively chemisorbed onto the Ru only. Data recorded for the chemisorption of CO on a sample of 1.34 g of catalyst at 273 K are given in the table below. (The volume adsorbed has been corrected to STP, where 1 mole of gas occupies a volume of 22.414 dm3.)
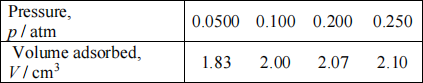
(i) Confirm that the data fit the Langmuir isotherm and find the Langmuir
constant Kand the number of molecules Nm corresponding to complete coverage. Given that the area occupied on the surface by each CO molecule is 1.65 x 10- 19 m2, calculate the accessible surface area of the ruthenium [in m2 (g Ru)- 1]. (6 marks)
(ii) Explain why the Langmuir isotherm model is more appropriate than the
BET isotherm to determine the accessible surface area of Ru using CO. (1 mark)
(b) The catalytic activity of the above Ru/silica catalyst, alongside a series of other second row transition metals supported on silica, was tested under a constant set of conditions for the removal of sulfur from sulfur-containing hydrocarbons.
The results arepresented in the table below (initial rate data normalised for surface area and given in arbitrary units):
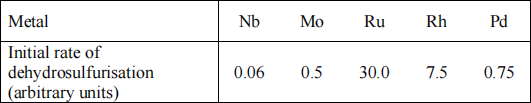
(i) Sketch (do not use graph paper) a plot of relative catalytic activity vs atomic number and name the type of plot that this graph represents.
Explain the pattern of activity observed, with clear reference to the rate determining step for hydrodesulfurisation reactions and how sulfur-containing molecules bind to the catalyst. Suggest how the activity of the Rh/silica sample could be increased. (6 marks)
(ii) Under the same conditions, a catalyst composed of molybdenum sulfide on
silica (MoS2/silica) showed substantially lower initial activity compared with both molybdenum metal particles on silica (Mo/silica) and ruthenium sulfide on silica (RuS2/silica). Discuss why catalysts based on MoS2/silica are preferred over both these other two catalysts. (3 marks)

