关键词 > FIN412
FIN 412 Assignment 1
发布时间:2024-05-10
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
FIN 412 Assignment 1
Due Date: May 12
INSTRUCTIONS:
❼ The total marks for this assignment are 100.
❼ Please work on this assignment in a group of at most 4 people, photocopy your work and submit one pdf version on eclass by 11:00 pm, May 12.
❼ Please write down the names and student ID’s of the group members.
❼ Please write your answers clearly, since 0 marks will be assigned to ambiguous answers.
❼ Partial credit will be given for showing logically correct reasoning, even if the final answer is not correct.
❼ If not otherwise specified, discount rates for bonds are quoted with the compounding frequency corresponding to the frequency of coupon payment (eg, semiannual APR for semiannual coupon payment).
❼ If not otherwise specified, an annuity or perpetuity is regular; ie, the first payment is located at the end of the first period.
❼ If not otherwise specified, put 2 decimal places in the final result for dollar amount (eg, ✩1.99) and rates (eg, 1.99%); therefore, you need to retain more decimal places in your intermediate calculation steps (6 decimal places recommended).
1. Time Value of Money I [10 marks]
(a) [5 marks] What is the present value of ✩5,000 to be received at the end of each year for the next 6 years if the interest rate is 5% EAR?
(b) [5 marks] What is the present value of ✩5,000 to be received at the beginning of every 6-month period for the next 6 years if the interest rate is 5% semiannual APR?
2. Time Value of Money II [10 marks]
Your 6% monthly APR, 36-month car loan requires monthly payments of $600 at the end of each month. The first payment will be made in 1 month. Immediately after making the 10th payment, you realize that you can’t afford the car. Your friend Justin offers to takeover making the payments if you, in return, give your friend the car.
(a) [5 marks] Calculate PV of your future payment, immediately after making the 10th payment.
(b) [5 marks] If the car is worth $15,000 on the open market, after you make the 10th payment, is this a good deal for you with Justin?
3. Statistics for Asset Returns [34 marks]
The returns for the shares of Firm X and Y for the next year are represented by the following joint probability distribution as the decimals in the middle of the table. (Please express the results in percentage and keep 4 decimal places for all the sub-questions, eg, 1.9999%)
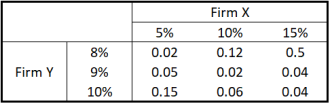
(a) [6 marks] Calculate the expected returns for Firm X and Y.
(b) [6 marks] Calculate the variances for the returns of X and Y.
(c) [6 marks] Calculate the standard deviations for the returns of X and Y.
(d) [6 marks] Calculate the covariance for the returns of X and Y.
(e) [6 marks] Calculate the correlation for the returns of X and Y.
(f) [4 marks] Briefly interpret your finding in (d) and (e), regarding the direction of the co-movement of the stock prices
4. Scenario Analaysis [16 marks]
The risk-free rate currently is 2% per year. You just paid ✩100 for a share of stock Y. You expect to hold the stock for 1 year. Your expectation regarding the stock is given in following table. The cash dividends will be paid just before the year end.
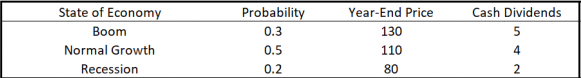
(a) [6 marks] What is the expected return of stock in percentage during your holding period?
(b) [6 marks] What is the standard deviation of stock return during your holding period?
(c) [4 marks] What is Sharpe ratio for your holding period?
5. Growth of $1: BRK vs S&P 500 (Excel Recommended) [12 marks]
Download “Growth of 1 dollar.xlsx”. It contains the net annual return of Berkshire Hathaway and S&P 500 from 1965 to 2022, with the raw data from the 2022 letter to shareholders from Warren Buffett. Note that all returns are expressed in percentage points (eg, 49.5 for BRK in 1965 should be understood as 49.5% ).
(a) [6 marks] Assume $1 was invested in 1965 in BRK and S&P 500, calculate the wealth index for BRK and S&P 500 for each year, plot the two paths of wealth index from 1965 to 2022 in the same graph. Name the two paths clearly.
(b) [6 marks] Calculate the annualized return (taking into account the compounding) for the period from 1965 to 2022 for BRK and S&P 500. Compare your result with that in the 2022 letter to shareholders from Warren Buffett. Do you have the similar result?
6. Explore the Market (Excel Recommended) [18 marks]
Download the Excel spreadsheet “Explore Market.xlsx”. It contains end-of-month adjusted closing prices from December 1990 to December 2020 for 4 companies: Apple, Microsoft, Coca-Cola and IBM. Adjusted closing prices take into account dividends and stock splits when used to calcu-late returns. The file also contains monthly risk free rate. Monthly data gives us better estimates of variance and covariance than annual data, by allowing us to observe the data at higher frequency.
(a) [4 marks] Calculate the monthly returns in percentage for each firm, based on the adjusted closing prices.
(b) [7 marks] Based on (a), use the Excel function “=CORREL( )” to obtain the correlation be- tween each pair from the 4 firms. Report it in the correlation matrix below. Explain why the return of Coca-Cola has relative low correlations with the returns of the other firms.

(c) [7 marks] Based on (a), complete the table below

Use Excel function “=AVERAGE( )” and “STDEV.S( )” to calculate mean and standard deviation
standard deviation: standard deviation of monthly returns
risk premium: average of monthly excess returns
sd of excess return: standard deviation of monthly excess returns
risk premium, annualized: risk premium × 12
sd of excess return, annualized: sd of excess return × 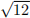
Sharpe ratio: 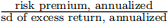
Note: the monthly excess return for each stock is the difference between the monthly return for each stock and the monthly risk-free rate, which is varying each month.

