关键词 > Physics1221
Physics 1221 Practice Quiz #4
发布时间:2024-05-05
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Physics 1221
Practice Quiz #4
April 15, 2024
Please complete on the separate answer sheets.
Long Answer Problems (10 pts each)
1. A block (m = 2.0 kg), sitting on a frictionless table, is attached on either side by springs, one with a spring constant k1 = 1250 N/m, the other with a spring constant k2 = 1950 N/m. The other ends of these springs are fixed to rigid walls, and, initially, neither spring is compressed nor stretched when the block is in its original position.
(a) If the block is displaced 5.0 cm to the right, stretching spring #1 and compressing spring #2, what is the net force of the springs on the block?
(b) The block is then released and begins to oscillate. What is the period of its oscillation?
(c) What is the speed of the block as it passes through its original (equilibrium) position?
(d) If, for some reason, spring #2 breaks just as the block moves through its equilibrium position, what is the amplitude of the oscillation of the block connected solely to spring #1? (Show all work to receive full credit.)

2. A plunger can be moved back and forth in a hollow tube that is L = 150 cm long with two open ends. A stretched wire is placed near the open end of the tube, as shown in the igure. The l = 50.0 cm long, 5.0 gram (5.0x 10—3 kg) wire isixed at both ends and oscillates in its fundamental mode. When the plunger in the tube is pulled downward a distance x = 34 cm from the top of the tube, the vibrating wire sets the air column in the tube into oscillation at the column’s fundamental frequency so that the vibrating wire and the oscillating air column in the tube are at resonance, i.e., they share the same frequency. Assume the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s.
(a) Find this fundamental frequency and
(b) the tension in the wire. Note, the open side of the tube would be considered a “free” boundary whereas the plunger side would be considered a “ixed” boundary.
(c) To the nearest tenth of a centimeter, what are the two locations (distances x from the top of the tube) nearest the x = 34 cm position the plunger should be moved such that audible beats, arising from the sounds produced by the wire and the air column having diferent pitches, with a frequency of 10 Hz can be heard?
(d) If the intensity of the sound generated by this pipe is 40 dB at a distance of 4.0 meters away, at what distance from the pipe is the intensity 34 dB?
(Show all work to receive full credit.)
Multiple Choice (2 pts each)
1. A simple pendulum has length L and period T. As it passes through its equilibrium position, the string is suddenly clamped at its midpoint. The period then becomes:
(A) 2T (B) T (C) T/2 (D) T/4 (E) none of these
2. An object attached to a spring exhibits simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 10.0 cm. How far from equilibrium will the object be when the system’s potential energy, deined as zero at the object’s equilibrium position, is equal to its kinetic energy?
(A) 3.00 cm (B) 5.00 cm (C) 7.07 cm (D) 9.00 cm
(E) The distance cannot be determined from the data given.
3. A wave on along string is represented by the equation y = 1.0 m sin[(0.5 m— 1 ) x — (1.5 s — 1 ) t]. The speed and the direction of motion of this wave is:
(A) 0.33 m/s in the +x direction. (B) 0.75 m/s in the +x direction.
(C) 3.00 m/s in the +x direction. (D) 0.33 m/s in the —x direction.
(E) 3.00 m/s in the —x direction.
4. A wave pulse (shown to the right) is traveling on a long rope to the left, toward a boundary with “open” boundary conditions. Which of the illustrations below could be a snapshot of the rope at a later time?

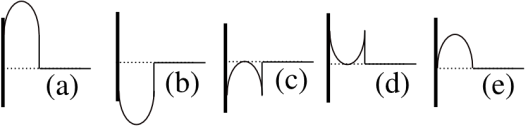
5. The frequency of a car’s horn is 1000 Hz. When this car approaches an observer, the observer hears a frequency of 1050 Hz. When the car is moving away from the observer at this same speed, the observer will hear a frequency of
(A) 950 Hz. (B) 955 Hz. (C) 970 Hz. (D) 1053 Hz.
(E) Not enough information.

