关键词 > ECE4122/6122
ECE 4122/6122 Final Project
发布时间:2021-11-08
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECE 4122/6122 Final Project
Submitting the Assignment:
All the files needed to compile your code including a CMakeLists.txt should be zipped up into a file called FinalProject.zip and uploaded to canvas. For the Final Project, you can choose between two types of submission:
1. You can develop your final project on your local machine. If you chose this type you will need to create a narrated video showing your program working and either upload it to canvas or provide a link its location.
2. You can develop your final project on pace-ice and just upload your code to canvas. You need to make sure it builds and runs on pace-ice.
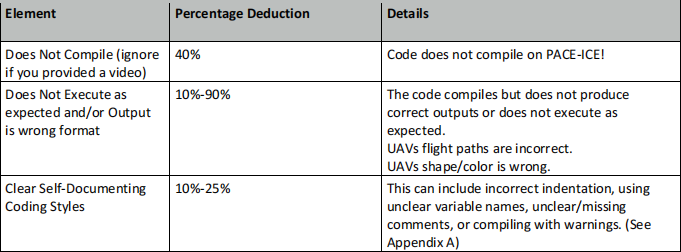
Grading Rubric
AUTOMATIC GRADING POINT DEDUCTIONS :
LATE POLICY
GaTech Buzzy Bowl
The company you work for has been selected to develop a half-time show using UAVs. You need to develop a 3D simulation using std::thread and OpenGL to demo the show to the game organizers for their approval.
Below is a description of the show that you will be creating with a 3D simulation.
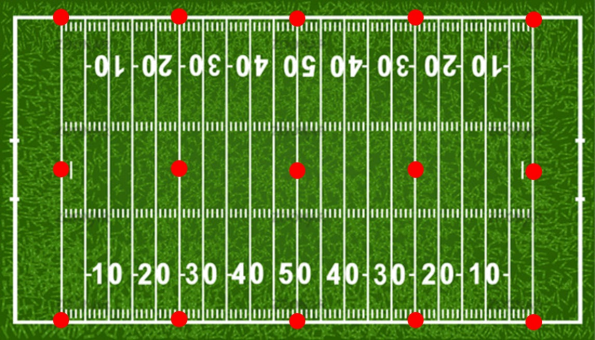
1) The show is made up of 15 UAVs that are placed on the football field at the 0, 25, 50, 25, 0 yard-lines as shown below by the red dots.
2) The UAVs remain on the ground for 5 seconds after the beginning of the simulation.
3) After the initial 5 seconds the UAVs then launch from the ground and go towards the point (0, 0, 50 m) above the ground with a maximum velocity of 2 m/s
4) As they approach the point, (0, 0, 50 m), they began to fly in random paths along the surface of a virtual sphere of radius 10 m while attempting to maintain a speed between 2 to 10 m/s.
5) The simulation ends once all of the UAV have come within 10 m of the point, (0, 0, 50 m), and the UAVs have flown along the surface for 60 seconds.
6) Each UAV has the following
a. Each UAV has a mass of 1 kg and is able to generate a single force vector with a total maximum magnitude of 20 N in any direction.
b. Scale each UAV so it is just small enough to fix in a 20-cm cube bounding box. Pick a UAV object from the attached zip file. There are lots of free 3D objects online and for an extra 20 extra bonus points place a texture map on a 3D object of your choosing or on one of the included 3D objects.
7) You must develop a multithread application using 16 threads. The main thread is responsible for rendering the 3D scene with the 15 UAVs and a green (RGB=(0,255,0)) rectangle representing the football field in a 400 x 400 window. You will get 10 extra bonus points for using a bitmap file called ff.bmp in the same location as the executable to apply a football field texture to the rectangle. The other 15 threads are each responsible for controlling the motion of a single UAV.
8) Create a class called ECE_UAV that has member variables to contain the mass, (x, y, z) position, (vx, vy, yz) velocities, and (ax, ay, az) accelerations of the UAV. The ECE_UAV class also contains a member variable of type std::thread. A member function start() causes the thread member variable to run an external function called threadFunction
void threadFunction(ECE_UAV* pUAV);
The threadFunction updates the kinematic information every 10 msec.
9) The main thread polls the UAV once every 30 msec to determine their current locations in order to update the 3D scene.
10) The coordinate system of the 3D simulation is defined as follows: The origin is located at the center of the football field at ground level. The positive z axis points straight up, and the x axis is along the width of the field and the y axis is along the length.
11) A camera location, orientation, and field of view should be used so that the whole football field and the virtual 10m sphere is in the view. You can display a semi-transparent representation of the virtual sphere
12) The flight of the UAV is controlled by the following kinematic rules
a. The force vector created by the UAV plus the force of gravity (10 N in the negative z direction) determine the direction of acceleration for the UAV.
b. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to determine the acceleration of the UAV in each direction.
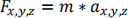
c. Use the equations of motion for constant acceleration in each direction (xyz) to determine the location and velocity of the UAV every 10 msec.
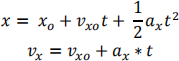
d. You can use any method you want to maintain the UAVs flight path along the surface of the 10m radius virtual sphere. One possible method to consider is to use a variation of Hooke’s Law simulating a virtual spring between the surface of the sphere and the radial distance of the UAV from the center of the sphere.
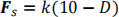
where D is the distance from the UAV to the center of the sphere. And the direction of
is along the normalized vector from the UAV to the sphere center. The value of k can be varied to bind the UAV tighter to the surface.
13) If the bounding boxes of two UAVs come within 1 cm of each other an elastic collision occurs. For simplicity we are going to model the UAVs as point objects and the UAVs will just swap velocity vectors for the next time step:
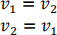
ECE6122 Students:
The magnitude of the color of your UAV should oscillate between full and half color throughout the simulation.
Appendix A: Coding Standards
Indentation:
When using if/for/while statements, make sure you indent 4 spaces for the content inside those. Also make sure that you use spaces to make the code more readable.
For example:
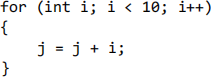
If you have nested statements, you should use multiple indentions. Each { should be on its own line (like the for loop) If you have else or else if statements after your if statement, they should be on their own line.
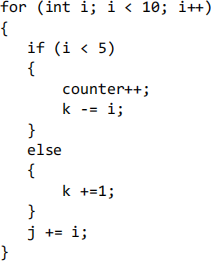
Camel Case:
This naming convention has the first letter of the variable be lower case, and the first letter in each new word be capitalized (e.g. firstSecondThird). This applies for functions and member functions as well! The main exception to this is class names, where the first letter should also be capitalized.
Variable and Function Names:
Your variable and function names should be clear about what that variable or function is. Do not use one letter variables, but use abbreviations when it is appropriate (for example: “imag" instead of “imaginary”). The more descriptive your variable and function names are, the more readable your code will be. This is the idea behind self documenting code.
File Headers:
Every file should have the following header at the top

Code Comments:
1. Every function must have a comment section describing the purpose of the function, the input and output parameters, the return value (if any).
2. Every class must have a comment section to describe the purpose of the class.
3. Comments need to be placed inside of functions/loops to assist in the understanding of the flow of the code.

