关键词 > Excel代写
Solve each problem using Excel Solver.
发布时间:2023-12-11
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Solve each problem using Excel Solver.
0) (Baker and Powell, 2013) The Diaz Coffee Company blends three types of coffee beans (Brazilian, Colombian, and Peruvian) into ground coffee to be sold at retail. Suppose that each kind of bean has a distinctive aroma and strength, and the company has a chief taster who can rate these features on a scale of 1 to 100. The features of the beans are tabulated as follows:
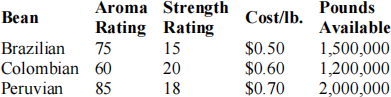
The company would like to create a blend that has an aroma rating of at least 78 and a strength rating of at least 16. Its supplies of the various beans are limited, however. The available quantities are specified above. All beans are delivered under a previously arranged purchase agreement. Diaz wants to make four million pounds of the blend at the lowest possible cost.
1) Write the mathematical formulation of the following problem:(Baker and Powell, 2013) Veerman Furniture Company makes three kinds of office furniture: chairs, desks, and tables. Each product requires some labor in the parts fabrication department, the assembly department, and the shipping department. The furniture is sold through a regional distributor, who has estimated the maximum potential sales for each product in the coming quarter. Finally, the accounting department has provided some data showing the profit contributions on each product. The decision problem is to determine the product mix—that is, to maximize Veerman’s profit for the quarter by choosing production quantities for the chairs, desks, and tables. The following data summarizes the parameters of the problem:
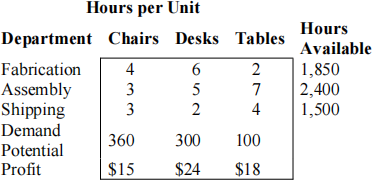
a) How much of each product should this firm produce to maximize profits?
b) Suppose now that the firm would like to ensure the total number of tables produced is at least 175. How much of each product should this firm produce to maximize profits?
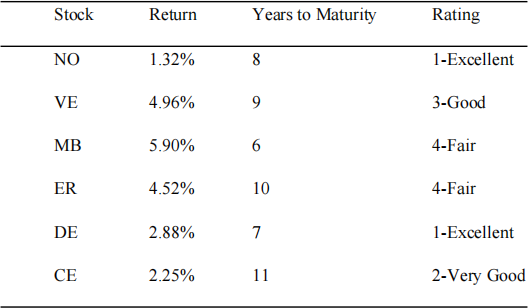
2) Let’s say you want to start building your investment portfolio. You have a list of six possible stocks in which you are interested and a budget of $50,000. You are risk-averse and do not want to invest more than 30% in any single investment. At least 60% of your budget should be invested in long-term bonds (maturing in 8 or more years). Finally, you do not want to invest more than 15% of your budget on stocks with a fair rating. How much should you invest to maximize your return? (Assume that you will invest all of your budget.)
3) (Baker and Powell, 2013, p262) The production planning problem has several formulations. In one version, a company has contracted to meet a certain demand schedule and faces constraints on production capacity. The problem is to find a least-cost production plan. In our example, a company produces two products (A and B) using two types of machines (X and Y) over a planning period of three months. The products can be produced on either machine, and the following table describes the machine hours required to make a single unit of each product:
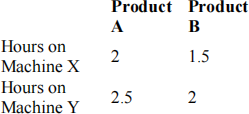
Machine capacities on X and Y are given for each of the three months. In addition, the quantities to be delivered each month, according to the contract, are also given:
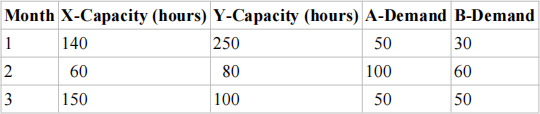
The relevant costs are labor on each machine ($30.00/hour) and inventory held ($10.00/unit/month, for either product). Assume that inventory holding costs are applied to the ending inventory.
4) (Baker and Powell, 2013, p273) You are the Director of the Computer Center for Gaillard College and responsible for scheduling the staffing of the center, which is open from 8 a.m. until midnight. You have monitored the usage of the center at various times of the day and determined that the following number of computer consultants are required:
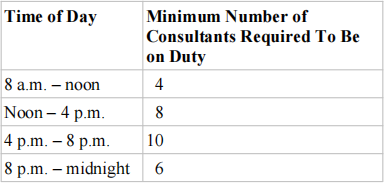
Two types of computer consultants can be hired: full-time and part-time. The full-time consultants work for eight consecutive hours in any of the following shifts: morning (8 a.m. – 4 p.m.), afternoon (noon – 8 p.m.), and evening (4 p.m. – midnight). Full-time consultants are paid $14 per hour.
Part-time consultants can be hired to work any of the four shifts listed in the table. Part-time consultants are paid $12 per hour. An additional requirement is that during every time period, there must be at least one full-time consultant on duty for every part-time consultant on duty. Determine a minimum-cost staffing plan for the center. How many full-time consultants and part-time consultants will be needed? What is the minimum cost?
5) Mercotic is a leader in slip-ring industry. A $750,000 order has just been received.
Unfortunately, Mercotic does not have enough wiring and harnessing capacity to fill the order by its due date. However, the company can subcontract any portion of this order to one of its competitors. Mercotic wants to determine the number of slip rings to make and number to buy to fill the customer order at the least possible cost. The wiring and harnessing capacities are 11,000 and 4,500 hours, respectively. All the necessary information is given in the table below.

a) How much of each model should Mercotic buy and make to minimize costs?
b) Suppose now that Mary, Mercotic’s CEO would like to make sure that the firm produces at least as many Model 2s as Model 3s. She believes that this will decrease costs. Do you agree with this claim?
c) Mary consults industrial and manufacturing engineers, and they suggest that with a new process, each model can be produced using half of their current harnessing requirements. If this new process costs $10,000, should Mercotic use it?
(Assume that Marc doesn’t require at least as many Model 2s and Model 3s.)
d) Mary suspects that only the relative costs of making and buying rather than the exact costs matter in the optimal solution. Specifically, she thinks that if the costs of making and buying increases by the same percentage, the optimal plan stays the same. Is she correct?
Extra Credit Exercises
To receive +0. 1 towards our Module Exercise 2, you must get each problem correct in its entirety.
1) Solve the following problem using iso-profit lines or level curves.
Min 2x1 + 3x2
S.t.
2x1 + x2 ≥ 3
4x1 + 5x2 ≥ 20
2x1 + 8x2 ≥ 16
5x1 + 6x2 ≤ 60
x1, x2 ≥ 0
2) A paint manufacturer, PCBCo, must determine how much paint should be produced in
the next four quarters. The firm estimates the demand for the next four quarters to be 40, 60, 75, and 25 in thousands of lbs. The firm must fully satisfy the demand in each quarter, i.e., no backlogging, In the beginning of period 1, PCBCo has an inventory of 10,000 lbs. The firm
( 1) has a production capacity of 40,000 lbs. each quarter with a per unit cost of $400 per thousand lbs using regular labor,
(2) may have workers work overtime where the per unit cost increases to $450 per thousand lbs.,
(3) incurs a holding cost of $20 per thousand lbs. at the end of a period.
How many lbs. of paint should PCBCo produce to satisfy demand while minimizing total production and inventory costs? (Hint: The inventory cost is based on the amount stored at the end of the period!)
3) Cargo Loading (Baker and Powell, 2013). You are in charge of loading cargo ships for International Cargo Company (ICC) at a major East Coast port. You have been asked to prepare a loading plan for an ICC freighter bound for Africa. An agricultural commodities dealer would like to transport the following products aboard this ship:
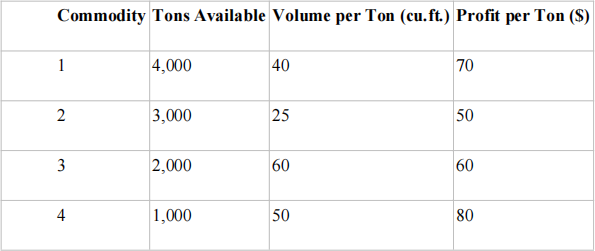
You can elect to load any or all of the available commodities. However, the ship has three cargo holds with the following capacity restrictions:
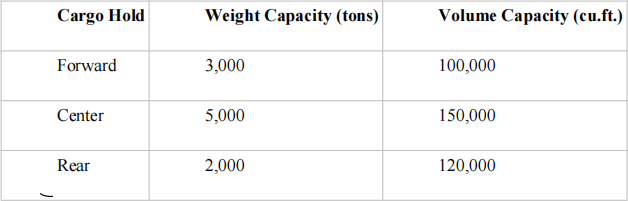
More than one type of commodity can be placed in the same cargo hold. However, because of balance considerations, the weight in the forward cargo hold must be within 10 percent of the weight in the rear cargo hold, and the center cargo hold must be between 40 percent and 60 percent of the total weight on board. Write the mathematical![]() formulation for the cargo loading problem.
formulation for the cargo loading problem. ![]()
4) Coordinating Advertising and Production (Baker and Powell, 2013). The Hawley Lighting Company manufactures four families of household lighting at its factory. The product families are table lamps, floor lamps, ceiling fixtures, and pendant lamps. The following table shows the average material costs for each of the products:

Each product is made in one of two production processes by purchasing components, assembling and testing the product, and, finally, packaging it for shipping. Table lamps and floor lamps go through the assembly and finishing process in Department 1, while ceiling fixtures and chandeliers go through the process in Department 2. Variable production costs and capacities (measured in units of product) are shown in the following table. Note that there are regular and overtime possibilities for each department.

Average selling prices for the four products are known, and estimates have been made of the market demand for each product at these prices. These figures are shown in the
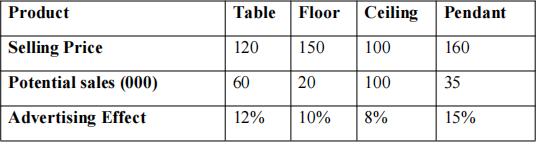
following table:
Sales levels can also be affected by advertising expenditures. Starting with the demand levels in the table, an increase of up to $10,000 in advertising raises the demand by the percent shown in the last row. An expenditure of less than $10,000 in advertising will lead to a proportional effect on demand. For example, an increase in advertising of $5,000 for table lamps would raise demand by 6 percent, or 3,600 units. However, there is a budget limit of $18,000 on the total amount to be spent on advertising among all four products. Create a production and advertising plan for this firm that maximizes profit.
a) What is an optimal output plan for the company?
b) For each department, what is the marginal value of additional overtime capacity? c) What is the marginal value of additional advertising dollars?
d) What is the marginal value of additional sales for each product?

