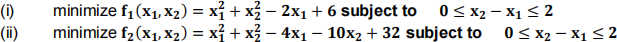关键词 > CIVE5024M&CIVE5971M
CIVE5024M & CIVE5971M Design Optimization
发布时间:2023-12-01
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Design Optimization
CIVE5024M & CIVE5971M Assignment
Due Friday 8th December 2023 at 16:00
1. (30 marks) The Potential Energy P(x1, x2) of a dynamic problem, which consists of two wheeled carts connected to each other is given by the equation below.
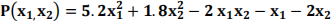
In order to determine the displacements (x1, x2) of the carts, the potential energy needs to be minimised. Minimize this function using the Nelder-Mead simplex method, starting with x0 = [x1 x2] = [2. 0 2. 0], an initial step size c=2, a = 1. 0, β = 0. 5, Y = 2. 0, p = 0. 5 and tol = 0.3.
Perform the Nelder_Mead search until the convergence criterion
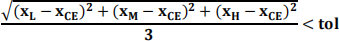
Your answer should contain all the numerical calculations in the various iterations of the search algorithm and afigure showing how the simplex changes during these iterations. You should provide a solution similar to those given in the Nelder-Mead simplex examples given on Minerva.
Give all your values of x1, x2 and f(x1, x2) to 4 decimal places.
2. (40 marks) The two bar truss micro-structure of Figure Q2.1 needs to have the highest possible stiffness to support a compressive force. This is to be achieved by minimising its compliance (C) given by equation (Q2.1). The truss is subject to three constraints, a limit on its maximum stress, given by equation (Q2.2) and constraints on the minimum height on the truss in millimetres given by x1 ≥ 2 and the cross sectional areas of the two bars x2 ≥ 0 in mm2. The optimisation problem is then defined below by these three equations.
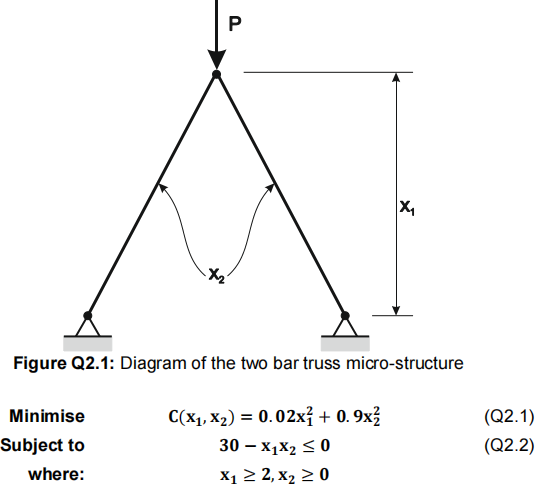
You are asked to:
(a) Write the problem in the standard Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) formulation. [5 marks]
(b) Define all of the necessary equations and cases that must be considered to solve the KKT problem of part (a) [5 marks]
(c) Solve the KKT to find the global minimum. Note that you will need to solve a set of non-linear simultaneous equations several times, using an appropriate software tool (Excell, Matlab etc.). You must show all your working and what the equations you solved were, together with screen shots of the spreadsheet or codes you used to solve the problems. [25 marks]
(d) Solve the optimisation problem graphically, using a suitable method. Provide a figure showing your solution and explain briefly how it shows the solution. [5 marks]
3 (30 marks)
(a) For the multiple constraint problem given below, use the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) method to determine the utopia point. (20 marks)
Your answer should contain all the standard KKT formulation including all necessary equations and cases that must be considered to determine the utopia point.
(c) Plot the Pareto front, showing the utopia point (4 marks)