关键词 > MATH3871/MATH5970
MATH3871/MATH5970 Bayesian Inference and Computation
发布时间:2021-09-17
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MATH3871/MATH5970
Bayesian Inference and Computation
Tutorial Problems 1
1. Frequentist Probability
Sam plays soccer on the weekends. Sam’s team has scored the following numbers of goals in recent games
2, 3, 1, 2, 1, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 2, 2, 3
What is the probability for Sam’s team to score 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 goals in a match?
2. Estimating the probability of a rare event
Suppose we want to study the probability of neonatal death after a particular surgery. We observe x = 0 previous deaths over n = 47 previous operations.
A reasonable model for this data is a binomial model (see Section 2.4.1 from Hoff (2010)).
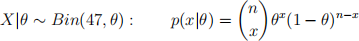
where
and
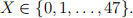
(a) Estimate the probability of death
. Can you provide an interval estimate of the probability of death?
(b) Given that probability, what is the prediction for a future operation?
3. Investments
According to a financial analyst researcher, 60% of the publicly-traded companies that increased their share price by more than 5% in the last three years replaced their CEOs during the period.
At the same time, only 35% of the companies that did not increase their share price by more than 5% in the same period replaced their CEOs. Knowing that the probability that the stock prices grow by more than 5% is 4%, find the probability that the shares of a company which fires its CEO will increase by more than 5%.
4. Coloured Balls

In a bag there are 6 balls of unknown colours. Three balls are drawn without replace-ment and are found to be red.
(a) Considering each colour to be equiprobable a priori, what is the probability that no red ball is left in the bag?
(b) Repeat the experiment, using a different choice of prior distribution. In what way does this change of prior affect the posterior probability of no red balls left in the bag?
5. Billiard ball
A billiard ball W is rolled on a line of length one, with a uniform probability of stopping anywhere. It stops at p. A second ball O is then rolled n times under the same assumptions and X denotes the number of times the ball O stopped on the left of W. Given X, what is the posterior distribution of p?
6. Sufficient Statistics - UGD
Consider
three binomial inde-pendent observations when the sample sizes
,
and
are known. Find two sufficient statistics.
7. Likelihood principle - UGD
While working on the audience share of a Netflix series
representing the part of the audience, an investigator found 919 viewers and 354 nonviewers. If no additional information is available on the experiment, define two possible experiments that may have led to the same observations.

