关键词 > VectorCalculus/Electromagnetics
Test 2 - Vector Calculus and Electromagnetics
发布时间:2023-10-18
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Test 2 - Vector Calculus and Electromagnetics - Sample
Instructions: Attempt all questions. There are 100 marks in total; marks awarded for each question are given in brackets. Write your responses in the space provided. If you need more room, you may use the additional blank sheet at the back of this test. When using extra space, clearly mark the question you are attempting.
This is an closed book test. A formula sheet is provided at the end. You are allowed to bring 4 double-sided A4 papers of your own notes. No other materials are allowed.
Time allowed: 50 minutes
Question 1: Dielectrics 14 marks
(a) Tick all correct statements
(i) For linear dielectric, the polarisation vector P is proportional to the applied electric field vector E.
(ii) The electric susceptibility of vacuum is 1.
(iii) The electric dipole moment is proportional to the charge and the distance between two positive and negative charge.
(iv) The electric dipole moment is normal the displacement vector from the neg- ative to the positive charge.
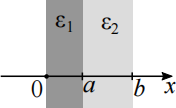
(b) A nonhomogeneous dielectric consists of two pieces of homogeneous linear dielec- tric with permittivity of ϵ1 and ϵ2 as shown in the diagram.
Applying a uniform electric field E = E0x(ˆ). At which location do we have non-zero polarisation charge? Briefly explain your answer.
Question 2: Capacitance and Energy 23 marks
![]() (a) The potential field in free space is given as V (x,y, z) =
(a) The potential field in free space is given as V (x,y, z) = ![]() V. Find the total energy stored within the region 0 ≤ x,y, z ≤ 1. Unit of length is metre.
V. Find the total energy stored within the region 0 ≤ x,y, z ≤ 1. Unit of length is metre.
(b) The permittivity between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor varies as ϵ(x) = [12]
ϵ0 e −αx , where x is the distance from one of the plates, and d is the distance between the plates. If the area of the plates is S, assuming that d < S, calculate the capacitance of this capacitor.
Question 3: Current and Magnetic Flux Density 23 marks
(a) Let the current density be [10]
J(r,ϕ,z) = 2r2 cos2 ϕr(ˆ) − rsin2ϕφ(ˆ) A/m2
Find the total current I crossing the surface r = 2, 1 ≤ z ≤ 3. Unit of length is metre.
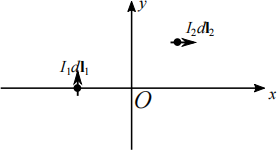
![]() (b) The figure below shows two current elements on xy-plane in free space (I1 , I2 > 0). Determine the direction of the magnetic flux density dB1 and dB2 at the origin due to each current element.
(b) The figure below shows two current elements on xy-plane in free space (I1 , I2 > 0). Determine the direction of the magnetic flux density dB1 and dB2 at the origin due to each current element.
![]() (c) Consider two surfaces defined as S1 : x2 + y2 ≤ 3, z = 1 and S2 : R = 2,θ ≤ π/3. Sketch these two surfaces. Compare the magnetic flux through S1 and S2 .
(c) Consider two surfaces defined as S1 : x2 + y2 ≤ 3, z = 1 and S2 : R = 2,θ ≤ π/3. Sketch these two surfaces. Compare the magnetic flux through S1 and S2 .
Question 4: Magnetic Force and Magnetic Moment 22 marks
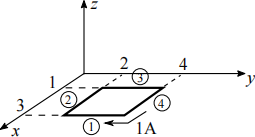
(a) The magnetic flux density in a region of free space is given as B(x,y, z) = [10]
( −3y,2x2 , 2) T.
Find the magnetic force on the current section ❖1 as shown in the figure below. The length unit is metre.
![]() (b) A charge Q > 0 has an initial velocity v (v > 0) in x(ˆ)-direction enters a uniform electric field and magnetic field, both in z(ˆ)-direction. What is the trajectory of this charge? Sketch the trajectory and explain your answer.
(b) A charge Q > 0 has an initial velocity v (v > 0) in x(ˆ)-direction enters a uniform electric field and magnetic field, both in z(ˆ)-direction. What is the trajectory of this charge? Sketch the trajectory and explain your answer.
Question 5: Ampere’s Law18 marks
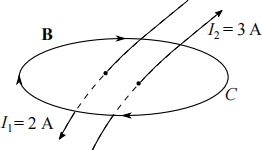
(a) For the following setup, calculate the line integral along the contour C of the magnetic flux density B due to the two currents. Note that the contour encloses both two line currents. Assume free-space condition.
![]() (b) A cylindrical current sheet of Js1 = 5z(ˆ) A/m are located at r1 = 2 m in the cylindrical coordinates. Calculate the surface current density Js2 required to be placed at r2 = 3 m such that the magnetic field is zero for r > 3 m. Assume free-space condition.
(b) A cylindrical current sheet of Js1 = 5z(ˆ) A/m are located at r1 = 2 m in the cylindrical coordinates. Calculate the surface current density Js2 required to be placed at r2 = 3 m such that the magnetic field is zero for r > 3 m. Assume free-space condition.

