关键词 > ESE4070/5070
ESE 4070/5070 Fall 2023 Midterm Exam
发布时间:2023-09-28
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ESE 4070/5070
Fall 2023
Midterm Exam. 165 points.
This midterm must be submitted on Canvas by 11:59 PM on Wednesday, September 27, 2023. Late submissions will not be considered. You are permitted to use the book,
class notes, class slides and the open Internet while completing this exam. You are also agreeing to abide by Penn’s Code of Academic Integrity – this exam is to be your work alone, no collaborating with your classmates or any other persons.
Question 1: For each, explain your reasoning briefly but clearly. No points for answers without reasoning. 5 points each (30 total).
a) List and explain one advantage of packet switching over circuit switching.
b) Give one example of what ICMP can be used for.
c) Why are ethernet switches beneficial?
d) A source host sends an IP packet of 1420 bytes out, but the destination host received 3 IP packets, each of less than or equal to 572 bytes. Explain briefly what
happened and why.
e) In packet switching networks, header bits are added to data bits to help with
forwarding packets. Since header is “overhead” (no useful data information), we could just send all data bits in one packet. What is one disadvantage this would bring?
f) In Ethernet MAC protocol, are collisions considered “expected events” (i.e. part of “normal behavior”) or “errors” (i.e. should not have happened)?
Question 2: Which of these is an advantage of Manchester encoding? Choose all that apply. (5 points)
a. Conserves network bandwidth
b. Embeds the clock signal into the data signal
c. Is compatible with NRZ encoding
d. Helps transmit long strings of zeros reliably
e. None of these
Question 3: Which form of delay is most influenced by geographic distance? (5 points)
a. Transmission
b. Propagation
c. Queueing
d. Processing
e. None of these
Question 4: Which parameters can DHCP assign to IPv4 clients? (5 points) a. IPv4 address
b. Default-gateway (router)
c. DNS server
d. Web browser home page
e. Time server
f. All of these
Question 5: Your computer sends out a DNS request over an Ethernet connection. (5 points each, 15 total)
a) What information is included in the first byte of the Ethernet frame’s payload? Circle the best answer:
a. TCP port
b. IP version
c. DNS transaction ID (first field of DNS request)
d. UDP source port
b) What number is in the protocol field of the IP header?
a. 17 (UDP)
b. 53 (DNS destination port number)
c. 1 (ICMP)
d. 4 (IPv4)
e. 4070 (your favorite class)
c) If you were to open Wireshark and examine the packet, what headers would you observe, from outermost to innermost?
Question 6: Check out the network shown below. There are four servers (top) connected to four clients (bottom) through a simple network. The network from top to bottom is a single, common middle link with a capacity of R = 200 Mb/s. The four paths from the servers have a transmission capacity of Rs = 10 Mb/s. Each of the four links to the clients has a capacity of Rc = 70 Mb/s. Answer the questions below (5 points each, 25 total):
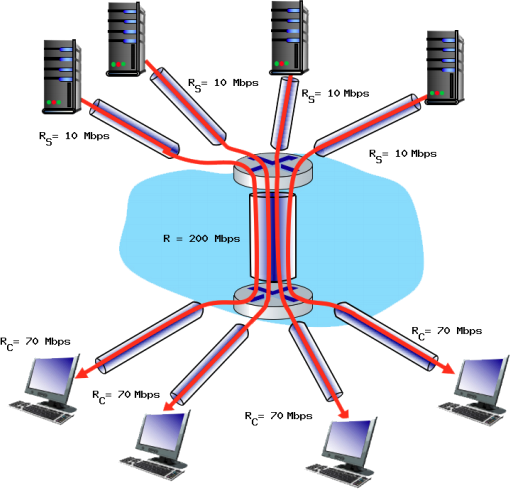
a) What is the maximum achievable end-end throughput (in Mbps) for each of four client-to-server pairs, assuming that the middle link is fairly shared (divides its transmission rate equally)?
b) Which link is the bottleneck link? Format as Rc, Rs, or R
c) Assuming that the servers are sending at the maximum rate possible, what are the link utilizations for the server links (RS)? Answer as a decimal
d) Assuming that the servers are sending at the maximum rate possible, what are the link utilizations for the client links (RC)? Answer as a decimal
e) Assuming that the servers are sending at the maximum rate possible, what is the link utilizations for the shared link (R)? Answer as a decimal
Question 7: A network showing IPv6-over-IPv4 tunneling is below. There are four IPv6 networks. There are IPv6-only, IPv4-only, and dual stack (v4/v6) routers. The dual stack routers build IPv6-over-IPv4 tunnels to each other.
Imagine a host (ending in :be96) in Subnet D wants to send an IPv6 packet to a computer (ending in :34bf) on Subnet B. And the path between the two hosts is D -> E - > d -> b -> c -> B. Answer the following questions. Questions 1-30 are 2 points each, question 31 is 10 points (70 points total).
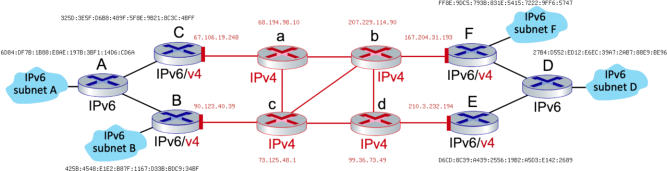
1. Is the datagram being forwarded from D to E an IPv4 or IPv6 datagram?
2. What is the source address of this D to E datagram?
3. What is the destination address of this D to E datagram?
4. Is this D to E datagram encapsulating another datagram? Yes or No.
5. Is the datagram being forwarded from E to d an IPv4 or IPv6 datagram?
6. What is the source address of this E to d datagram?
7. What is the destination address of this E to d datagram?
8. Is this E to d datagram encapsulating another datagram? Yes or No.
9. What is the source address of this encapsulated datagram?
10. What is the destination address of this encapsulated datagram?
11. Is the datagram being forwarded from d to b an IPv4 or IPv6 datagram?
12. What is the source address of this d to b datagram?
13. What is the destination address of this d to b datagram?
14. Is this d to b datagram encapsulating another datagram? Yes or No.
15. What is the source address of this encapsulated datagram?
16. What is the destination address of this encapsulated datagram?
17. Is the datagram being forwarded from b to c an IPv4 or IPv6 datagram?
18. What is the source address of this b to c datagram?
19. What is the destination address of this b to c datagram?
20. Is this b to c datagram encapsulating another datagram? Yes or No.
21. What is the source address of this encapsulated datagram?
22. What is the destination address of this encapsulated datagram?
23. Is the datagram being forwarded from c to B an IPv4 or IPv6 datagram?
24. What is the source address of this c to B datagram?
25. What is the destination address of this c to B datagram?
26. Is this c to B datagram encapsulating another datagram? Yes or No.
27. What is the source address of this encapsulated datagram?
28. What is the destination address of this encapsulated datagram?
29. What router is the 'tunnel entrance'? Give the router's letter
30. What router is the 'tunnel exit'? Give the router's letter
31. Which protocol encapsulates the other, IPv4 or IPv6? What is the advantage of this architecture? What might be a disadvantage of this architecture?
Question 8: Early in the course we learned about some history of the Internet and the architectural principles that make up much of the Internet’s design and philosophy.
Write a paragraph or two about the first time you used an application on the Internet – how old were you and what did you do with it? Does that service or application still exist? Then write a few sentences about what a young person’s first engagement with the Internet will be like 10 or 20 years from now – what services might exist, how might future generations be introduced to the network, and what kinds of problems and opportunities will exist? Feel free to speculate! (10 points)

