关键词 > MATH2070/2970
MATH2070/2970: Optimisation and Financial Mathematics
发布时间:2021-09-09
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
School of Mathematics and Statistics
Assignment
MATH2070/2970: Optimisation and Financial Mathematics
Semester 2, 2021
1. Consider the following linear programming problem
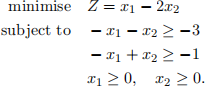
(a) Write the problem in standard form.
(b) Solve the problem in standard form graphically. Also,
● Introduce appropriate slack or surplus variables and define the boundaries of the feasible region in your graphical representation.
● Indicate the shortest path to optimality.
(c) Solve the problem manually using the simplex algorithm. Determine the optimal solution
and the optimal value
.
Explain every step you make. In particular:
● How do you choose certain values to enter the basis? Explain why.
● How do you choose which variables should leave the basis? Explain why.
● How do you decide when to stop? Explain why.
2. Consider the following linear programming problem
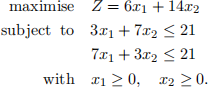
Solve the problem manually using the simplex algorithm. Determine the optimal solution 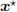 and the optimal value
and the optimal value 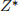 . Explain every step you make. In particular,
. Explain every step you make. In particular,
● Record which variables enter and leave the basis at each step.
● Give a complete characterisation of the optimal solution(s).
3. (MATH2070 only.) Consider the following optimization problem
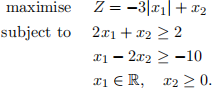
(a) Is this problem an LP problem in its current form? Explain your answer.
(b) Convert this problem to an (equivalent) LP problem of the following form:
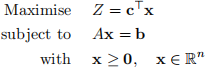
where
and A is an m × n matrix, for some n and m.
Explain every step you make. In particular, define every variable that you introduce and explain why it is needed.
4. A tea company sells tea under a “premium label” and an “economy label”. Both are blended from three basic grades of tea:
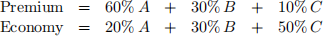
The market prices are $1000/tonne for premium and $750/tonne for economy. Due to the limited supply, the company can only purchase up to 100 tonnes of grade A at a cost of $800/tonne. The cost of grade B is $600/tonne and the cost of grade C is $400/tonne. To meet the demand, the total production of the two blends must be at least 200 tonnes.
How much of each blend should they produce to maximise their profit (not gross but net re-turns)? Formulate an LP problem to determine this. Solve the LP using two phase simplex algorithm.
Remember to define all the variables clearly and explain every step.
5. (MATH2970 only.) A best approximate solution to an inconsistent set of m equations in n unknowns,
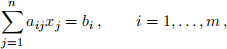
can be found by minimising the sum of the absolute errors,
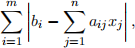
with respect to xk, k = 1, . . . , n. This L1-approximation optimisation problem is equivalent to the following LP problem with n + m decision variables xj, j = 1, . . . , n, and ei, i = 1, . . . , m.
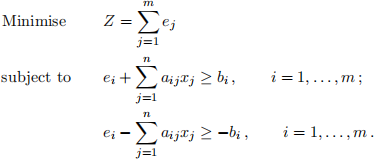
(a) Write down the dual problem using dual variables yi, i = 1, . . . , m, for the first m con-straints and wi, i = 1, . . . , m, for the last m constraints. Show by eliminating the wi that the dual problem can be simplified to
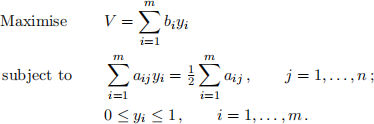
(b) The result in part(a) can be used to fit a straight line of the form y = ax + b to the five points (−2, −3), (−1, 2), (1, 5), (3, 10), (5, 14) by minimising the sum of the absolute errors at the five points (i.e. use L1 curve-fitting). Formulate the simplified dual LP problem of Part (a) for this curve-fitting problem.
Note: you are not required to solve the LP that you formulated.

