关键词 > STAT318/462
STAT 318/462: Data Mining Assignment 1
发布时间:2023-08-14
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
STAT 318/462: Data Mining
Assignment 1
Due Date: 23.59pm, 18th March, 2023
Please submit your assignment as a pdf and your code as a .r or .Rmd files on LEARN.
You may do the assignment by yourself or with one other person from the same cohort (300-level students cannot work with 400-level students). If you hand in a joint assignment, you will each be given the same mark. Marks will be lost for unexplained, poorly presented and incomplete answers. Whenever you are asked to do computations with data, feel free to do them any way that is convenient. If you use R (recommended), please provide your code. All figures and plots must be clearly labelled.
1. (6 marks) Consider a binary classification problem Y ∈ {0, 1} with one predictor X. The prior probability of being in class 0 is Pr(Y = 0) = π0 = 0.69 and the density function for X in class 0 is a standard normal
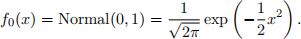
The density function for X in class 1 is also normal, but with µ = 1 and σ 2 = 0.5
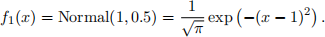
(a) Plot π0f0(x) and π1f1(x) in the same figure.
(b) Find the Bayes decision boundary (Hint: π0f0(x) = π1f1(x) on the boundary).
(c) Using Bayes classifier, classify the observation X = 3. Justify your prediction.
(d) What is the probability that an observation with X = 2 is in class 1?
2. (8 marks) In this question, you will fit kNN regression models to the Auto data set to predict Y = mpg using X = horsepower. This data has been divided into training and testing sets: AutoTrain.csv and AutoTest.csv (download these sets from LEARN). The kNN() R function on Learn should be used to answer this question (you need to run the kNN code before calling the function).
(a) Without any programming find the value of the training MSE for the kNN when k = 1 (justify your answer). Argue which is larger, the training MSE or the testing MSE, again for the case k = 1.
(b) Perform kNN regression with k = 2, 5, 10, 20, 30, 50 and 100, (learning from the training data) and compute the training and testing MSE for each value of k.
(c) Which value of k performed best? Explain.
(d) Plot the training data, testing data and the best kNN model in the same figure. (The points() function is useful to plot the kNN model because it is discontinuous.)
(e) Describe the bias-variance trade-off for kNN regression.
3. (2 marks) Suppose we collect data for a group of students that have taken STAT318 with variables X1 = hours spent studying per week, X2 = number of classes attended and
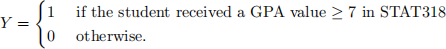
We fit a logistic regression model and find the estimated coefficients to be βˆ 0 = −16, βˆ 1 = 1.4 and βˆ 2 = 0.3.
(a) Estimate the probability of a student getting a GPA value ≥ 7 in STAT318 if they study for 5 hours per week and attend all 36 classes.
(b) If a student attends 18 classes, how many hours do they need to study per week to have a 50% chance of getting a GPA value ≥ 7 in STAT318?
4. (10 marks) In this question, you will fit a logistic regression model to predict the probability of a banknote being forged using the Banknote data set. This data has been divided into training and testing sets: BankTrain.csv and BankTest.csv (download these sets from LEAN). The response variable is y (the fifth column), where y = 1 denotes a forged banknote and y = 0 denotes a genuine banknote. Although this data set has four predictors, you will be using x1 and x3 to fit your model1 .
(a) Perform multiple logistic regression using the training data. Comment on the model obtained.
(b) Suppose we classify observations using
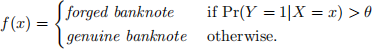
i. Plot the training data (using a different symbol for each class) and the decision boundary for θ = 0.5 on the same figure.
ii. Using θ = 0.5, compute the confusion matrix for the testing set and comment on your output.
iii. Compute confusion matrices for the testing set using new and different θ: θ1 = 0.3 and θ2 = 0.6. Comment on your output. Describe a situation when the θ1 = 0.3 model may be the preferred model.

