关键词 > CIVE5024M/CIVE5971M
CIVE5024M/CIVE5971M Design Optimisation January 2021
发布时间:2023-08-03
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
CIVE5024M/CIVE5971M
Design Optimisation
January 2021
1. An engineer is required to schedule the manufacture of two different car parts. Each part
requires three operations, each done on a separate machine: turning, milling and grinding. The time available per lot for the two parts on each machine, together with the maximum time
available for use of each machine and the profit margins for each lots of parts produced is
given in Table Q1, where each lot consists of 10 units of each part. This can be formulated as the maximization linear programming (LP) problem of equation Q1.

You are asked to:
(a) Determine the maximum profit (z) and the number of units of parts that produces this profit. [14 marks]
(b) Due to changes in the cost of electricity required to run the three machines, the profit per lot for each part has now changed to £40.10/lot for part 1, and £65.40/lot for part 2.What, if any, has been the effect of this change? [11 marks]
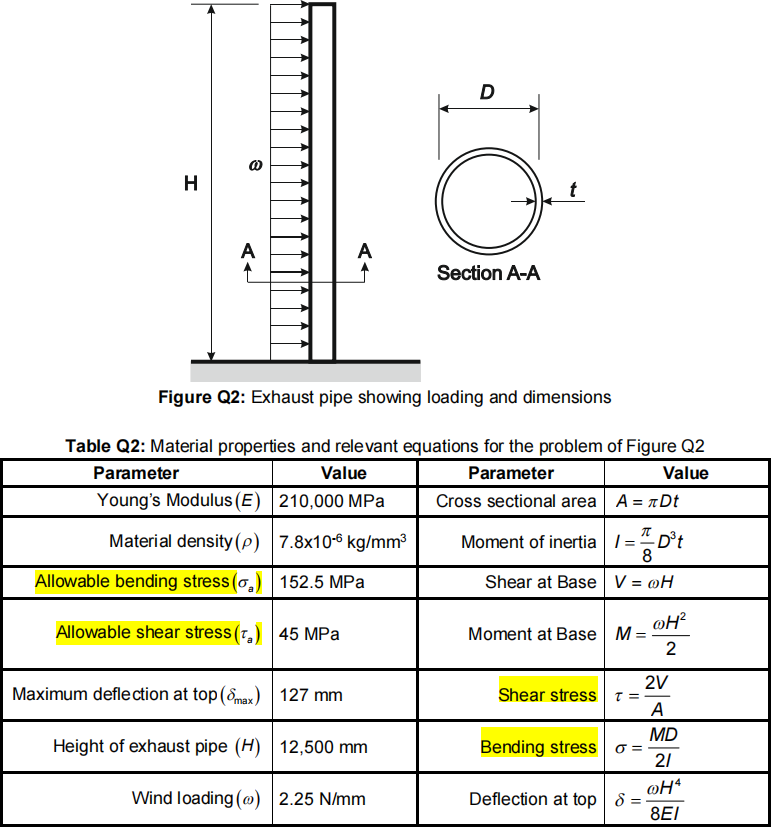
2. A hollowed exhaust pipe needs to be designed that will allow gasses to be expelled above a building. The height of the pipe is given as H (mm). It will be made from a uniform hollow circular tube with a mean diameter (D) and a wall thickness (t). The exhaust pipe must not fail when experiencing high winds. Minimise the mass of the pipe. For design purposes, you can treated it as a cantilever that is subjected to a uniform lateral wind load w(N/mm), as shown in Figure Q2. The exhaust pipe must not fail in bending or shear and the deflection at the top should not exceed 127mm. The ratio of mean diameter to thickness must not exceed 60. All relevant information and equations are given in Table Q2. The range of values for (D) and (t) are 150 £ D £ 650 mm and 2 £ t £ 15 mm. Please note that all values should be used as given as they are in the correct units.
You are asked to:
(c) Formulate the optimum design problem. [14 marks]
(d) Solve the optimization problem using the graphical method using only these 11 values of the mean diameter {150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500, 550,600, 650}. [11 marks]
Problem description for questions 3 and 4
The covid-19 pandemic has forced people to depend on the online delivery of packages. A well-established online company is exploring the possibility of using a pneumatic cannon inside a van to deliver their packages safely to the front door of houses, as shown in Figure Q34.
Equation Q34.1 is used to calculate the horizontal distance (D) travelled by the package and equation Q34.2 is used to calculate maximum height (H) reached by the package with the angle (q) in the range (0 £q £ 90) . The height to the end of the pneumatic cannon where the package exits is h = 1.7m, the gravitational acceleration is g = 9.81 m/s2 and the projecting velocity from the pneumatic cannon is V = 12 m/s.
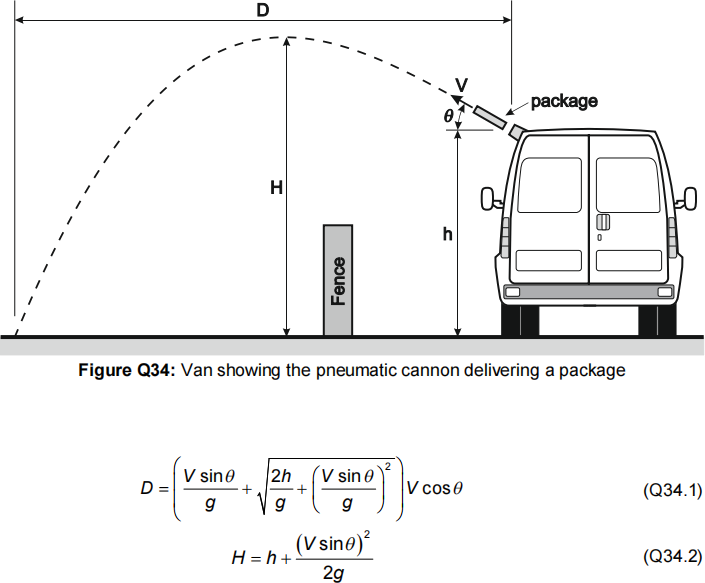
3. Use the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) method to find the maximum horizontal distance
(D) travelled by the parcel, given by equation Q34.1. The PSO parameters to use are given in Table Q3.1. The 25 random numbers required to be used to solve this problem are given in Table Q3.2 in the order they must be used. [25 marks]
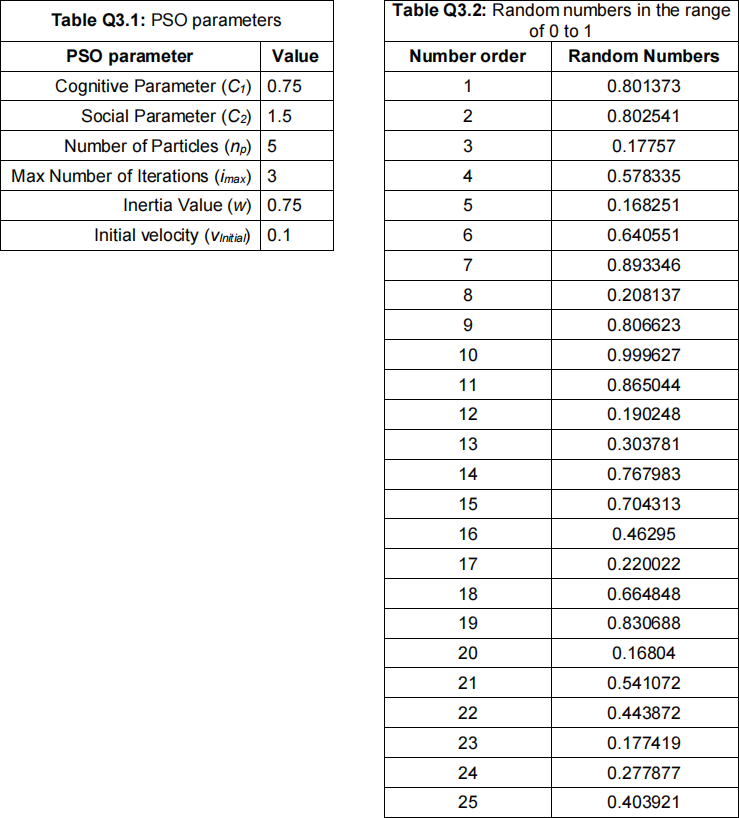
4. The driver of the van of Figure Q34 reached a delivery destination and has a dilemma. The front door is 12.5 metres from the van, but there is a 6-metre fence between the van and the door. In order to help the driver determine what angle to set the pneumatic cannon, you are asked to:
(a) Use three iterations of the Golden Section method to calculate the angle (q) in the range (0° £q £ 90°) for the package to travel over the 6-metre fence. To do this, minimize the square of the difference between equation Q34.2 and the 6-metre high fence, given by equation Q4.1. At this angle, will the package reach the door safely? [10 marks]
(b) Use three iterations of the Bisector method to calculate the angle (q) in the range
(45° £q £ 90° ) for the package to reach the front door. To do this, minimize the square of the difference between equation Q34.1 and the distance 12.5m, given by equation Q4.2. At this angle, will the package clear the 6-metre fence safely? [10 marks]
(c) Based on your answers to parts (a) and (b), explain which of the two methods used reaches a better result in three iterations? [5 marks]


