关键词 > CPEN/EECE481
CPEN/EECE 481, Summer 2023 Final Exam
发布时间:2023-06-29
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
CPEN/EECE 481, Summer 2023
Final Exam, 27/28 June 2023
1. (4 points) An electronic data storage firm can purchase a bank of servers for $450,000. After five years of use, the servers are expected to have a salvage value of $35,000. What will the server’s depreciation amount in year 5 be (rounded to the nearest dollar), assuming:
(a) They are classified as computer hardware, which is CCA Asset Class 50?
(b) Straight line depreciation?
(c) Sum-of-the-years’-digits depreciation?
(d) Double declining-balance depreciation?
2. (5 points) Consider three alternatives for a project: A, B, and Do Nothing.
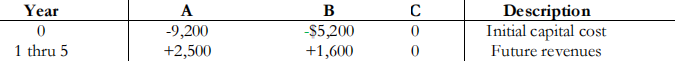
Assume a borrowing rate of 6% (use this as the discount rate).
(a) Calculate the NPW values for Options A and B, rounded to the nearest dollar.
(b) Calculate the IRRs for Options A and B, rounded to the nearest tenth of a percent.
(c) Calculate the incremental IRRs for options A and B.
(d) Which option would you recommend? Why?
(e) It may be possible to borrow money at a different borrowing interest rate. Construct a choice table for the three alternatives.
3. (4 points) Darrak must decide if a new solar energy generation system is a good investment. The infrastructure (capital) will be built immediately (year 0).
The system will cost $14 million to construct, and will last 3 years. It is expected to have a salvage value of $2 million at the end of the 3rd year. Revenues in year 1 will be $6.5 million, and operational costs in year 1 will be $1 million.
Revenues and future operating costs are expected to rise at 2% per year after year 1. The combined federal and provincial incremental tax rate is 30%. Use a CCA depreciation rate of 45% and a discount rate of 5% (reflecting the borrowing costs of the firm).
You may wish to use a table similar to that below to assist your analysis.
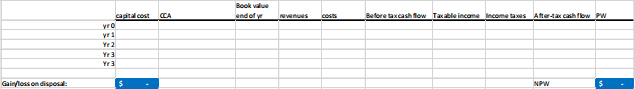
a) What is the gain or loss on disposal of the proposed investment (rounding to the nearest dollar)?
b) Determine the net present worth of the after-tax cash flow, rounding to the nearest dollar.
c) Should Darrak recommend that the project proceed?
4. (4 points) You must decide between two options: buying a home to live in, or continuing to rent. In either case, you are planning to retire in 20 years, convert all your savings and assets to cash, and move to the Dominican Republic.
You currently rent a place for $26,000 per year. Utilities are included. You expect your rent to rise by 2.5% every year.
A comparably sized home would cost $500,000 to purchase, including all relevant fees and taxes. You have saved $50,000. That money is earning 3% per year, and you expect that savings rate will continue if you leave the money there. If you buy the home, though, the $50,000 would have to be used as a deposit toward the purchase. You could get a mortgage loan for the rest of the purchase price with a fixed rate 6.0% interest rate. You would (unusually) make one (large) mortgage payment per year, and will pay back the entire loan over the 20 years. You anticipate that the home would rise in value by 3% every year. If you buy the home, you will need to pay your own utilities and property tax. These will cost $3,200 per year in the first year, and you anticipate that these costs will rise 5.5% every year. If you buy the home, you plan to sell the home after 20 years. You will pay 5% of your sale price for transaction fees (so, will receive 95% of the sales revenue).
Whichever option you choose, you will plan to withdraw all of your money at the end of the 20 years when you leave the country. Round all answers to the nearest dollar, or the tenth place (for percentages).
a) Calculate the annual mortgage loan repayment amount.
b) If you choose to purchase the house, how much will it be worth in 20 years when you sell it?
c) Calculate all cash flows in each of the 20 years under each scenario.
If you rent, what is the sum of undiscounted rent? What is the undiscounted value of the savings (which were left in the bank) when withdrawn in 20 years? What is the sum of all undiscounted cash flows?
If you buy, what is the undiscounted sum of all mortgage payments? What is the undiscounted sum of all utility payments? What is the undiscounted revenue from the sale of the house (after fees)? What is the sum of all undiscounted cash flows?
Which of these has lower undiscounted costs?
d) Choose a discount rate to apply. Why is the discount rate you have chosen appropriate?
e) Calculate the Net Present Worth of each option. Which option would leave you in better financial condition when you retire and move away: which option costs less?
f) At what mortgage borrowing rate would you be indifferent to the two options? Otherwise said, at what borrowing rate will the NPW for the two options be equal? Explain your methodology if you feel it will help.
5. (6 points) A firm is considering two possible capital asset purchases that could increase the firm’s revenues.
The table below outlines key parameters for the two options.
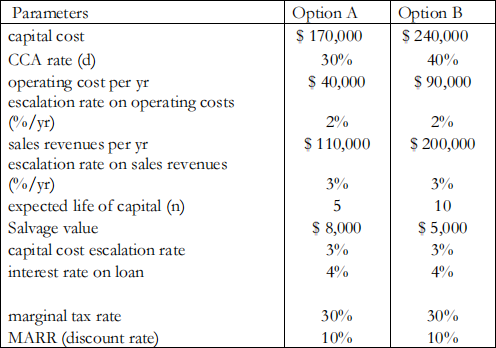
Analyses have been done for both of the options, in the attached Excel file for this problem.
Unfortunately, the analyst made 12 errors in the analysis. You must identify all of the errors, and describe why each one is an error. You do NOT have to fix the errors. Easy errors are worth fewer points than complex errors.
6 (4 points) Sales and profits for a new product are uncertain. The marketing department has made the
following independent sets of predictions:
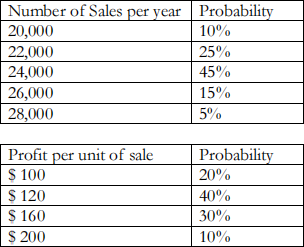
(a) Construct a table of probability distributions. Include the probability, total sales #s, profit per unit sold, and total profit for each possible outcome.
(b) Based on this distribution, calculate the expected value of total profits in dollars per year.
7. (3 points) You are interested in getting a credit card. You are offered the following two options.
A large national bank offers a credit card that costs $150 annually (as a fee), and has a borrowing interest rate of 12%. Alternatively, a local bank offers a credit card with no annual fee, a borrowing interest rate of 14%, and a 2% rebate on all gasoline and grocery purchases.
What steps would you take to analyze your options? What data or other information would you need to choose an option?
8. (4 points) The year is 2022. The provincial highway department is analyzing the reconstruction of a mountain road to Tofino. The vehicle traffic increases each year; hence the benefits to the motoring public also increase. Based on a traffic count, the benefits are projected as follows:

The reconstructed pavement will cost $230,000 if it is installed in 2024. If it is installed in a future year, the cost will be higher: construction costs are expected to rise 7% per year. It will have a 15-year useful life. In each potential situation where you are considering beginning the project, the construction will always occur in one year, and the benefits will begin the following year. Assume a 5% discount rate. The reconstruction, if done at all, must be operational no later than 2030 (so, the last possible year of construction is 2029). Based on NPW analysis, should the project be done, and if so, in what year should it be constructed?
9. (3 points) In the fleet purchase options analysis tool covered in class, one of the costs included was the ‘lost interest on capital funds’ . What does this refer to, and why would it be included in such an analysis? What key concepts covered in the course does it inclusion illustrate? Explain why and how.

