关键词 > STAT3001/7301
STAT 3001/7301 Mathematical Statistics Tutorial Sheet 9 2023
发布时间:2023-06-12
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
STAT 3001/7301 Mathematical Statistics
Tutorial Sheet 9
2023
1. IQ scores can be modelled by a normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation 15. A person with an IQ score of 130 or above is considered as gifted. Candidates can take a standardised IQ test to estimate their IQ score. It is believed that scores vary each time a candidate take the test and that these scores is normally distributed with standard deviation 10. A candidate scored 135 in the standardised IQ test. We wanted to test whether the candidate can be classified as gifted.
(a) Find the 95% credible interval of the IQ score of the candidate.
(b) Test the hypothesis, basing your decision on the posterior odds.
(c) Calculate the corresponding Bayes factor.
2. Consider a coin flipping experiment where we flip the coin n times, so that
X1 ,X2 , . . . Xn ∼ iidBer(θ) and θ denote the probability of getting a head. We wanted to test H0 : θ = 0.5 against H1 : θ ![]() 0.5, assuming a Beta prior under H1 (i.e. θ|H1 ∼ Beta(α,β)). Calculate the Bayes factor for H0 relative to H1 .
0.5, assuming a Beta prior under H1 (i.e. θ|H1 ∼ Beta(α,β)). Calculate the Bayes factor for H0 relative to H1 .
3. Consider the data center example at the end of Lecture 34 (Week 12 Lecture 3). Temperature gauges are installed in the data center to monitor the temperature of the equipment. An alarm will sound when it senses a temperature gauge exceeds a specified threshold. This can be represented by the Bayesian network in Figure 1, where the variables are: A (alarm sounds), AF (alarm faulty), GF (gauge faulty), G (gauge reading), and T (actual temperature).
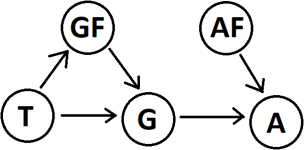
Figure 1: Bayesian network of the data center
(a) Suppose the gauge can only report temperature as either normal or high. For
simplicity, we will also classify the actual temperature as either normal or high. It the gauge is not faulty, then the probability it will report the correct temperature is p, whereas this probability is q when the gauge is faulty. Deduce the table of conditional probabilities associated with the node G.
(b) Suppose that the alarm always function properly when it is not faulty. If it is
faulty, then it does not sound. Deduce the table of conditional probabilities associated with the node A.
(c) Now suppose that both the alarm and gauge are not faulty. The alarm sounds. Deduce an expression for the probability that the temperature is high given this situation. To simplify notation, you may let g be the probability that the gauge is not faulty given the temperature is high, h be the probability that the gauge is not faulty given the temperature is normal, and t be the probability that the temperature is high.

