关键词 > ECON6001/6701
ECON6001/6701: Final S1 2022
发布时间:2023-05-29
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECON6001/6701: Final S1 2022
1 Short Questions (45 points)
Group Q1 (4 points)
1. Consider the following tree.
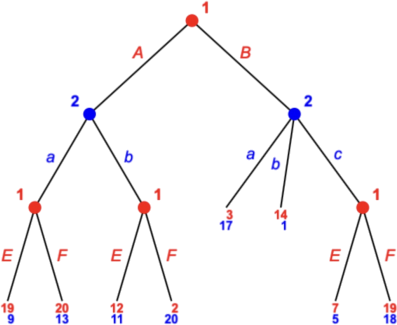
Player 1 has __ strategies and player 2 has __ strategies.
2. Consider the following tree.
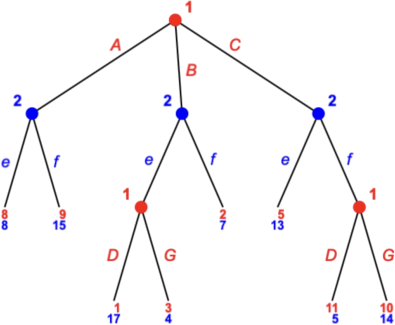
Player 1 has __ strategies and player 2 has __ strategies.
Group Q2 (7 points)
1. Consider the following tree.
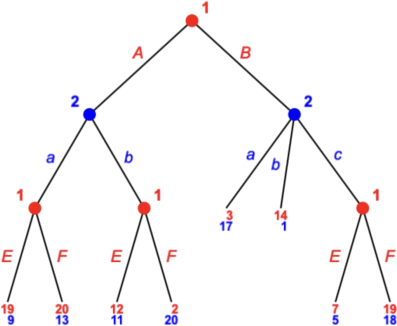
What is SPNE of this game? You have to provide strategy for each player. The answer without the properly formulated strategy will give you 0 points.
2. Consider the following tree.
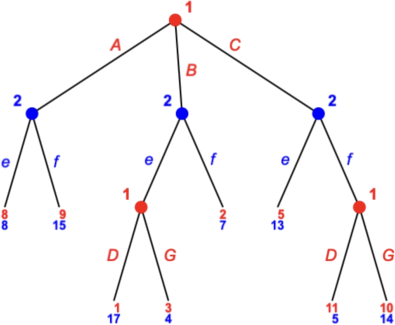
What is SPNE of this game? You have to provide strategy for each player. The answer without the properly formulated strategy will give you 0 points.
Group Q3 (8 points)
1. Consider Stackelberg competition model. Demand is Q = 240 − 2P . Firm 1 moves first. Firm 1’s marginal cost is 6 and Firm 2’s marginal cost is 4. The quantity produced by Firm 1 is __.
2. Consider Stackelberg competition model. Demand is Q = 120 − 4P . Firm 1 moves first. Firm 1’s
Group Q4 (3 points)
1. Which returns to scale does technology F (K, L) =^5KL + min(3K, 2L) exhibit?
(a) IRS
(b) CRS
(c) DRS
(d) Not defined
2. Which returns to scale does technology F(K, L) =^5KL + min(5K, 5L) exhibit?
(a) IRS
(b) CRS
(c) DRS
(d) Not defined
Group Q5 (5 points)
1. Suppose there are two consumers with u1 (x) = lnx + 2 and u2 (x) = 3 lnx. Consumers’ wealth is w1 = 50 and w2 = 100. Given these utilities and wealth, which of the consumers will be more risk-averse?
(a) Consumer 1
(b) Consumer 2
(c) Both consumers are identically risk-averse
(d) Consumers’ risk aversion is not comparable
(e) Not enough information to answer the question
2. Suppose there are two consumers with u1 (x) = ^5x and u2 (x) = ^x + 3. Consumers’ wealth is w1 = 200 and w2 = 100. Given these utilities and wealth, which of the consumers will be more risk-averse?
(a) Consumer 1
(b) Consumer 2
(c) Both consumers are identically risk-averse
(d) Consumers’ risk aversion is not comparable
(e) Not enough information to answer the question
Group Q6 (4 points)
1. A firm has access to the following technologies: F1 (K, L) = 3K+ L and F2 (K, L, Z) = K +9L+2Z . Then the aggregate technology is __. Provide your answer in the form: 5K + 5L + 5Z without spaces.
2. A firm has access to the following technologies: F1 (K, L, Z) = 2K + 2L + 5Z and F2 (K, Z) = 3K + 4Z . Then the aggregate technology is __. Provide your answer in the form: 5K + 5L + 5Z without spaces.
![]() Group Q7 (8 points)
Group Q7 (8 points)
1. Suppose the expenditure function is e(px , py , u) = u(2p(p)2北y + 3py ). Then sxx of the Slutsky matrix at px = 4, py = 2 and u = 1 is __.
2. Suppose the expenditure function is e(px , py , u) = u(p(p)3北2y + 5py ). Then sxx of the Slutsky matrix at px = 1, py = 1 and u = 1 is __.
Group Q8 (6 points)
True/False questions, each 1.5pt.
1. A utility representing a continuous preference must be continuous.
2. Quasi-concave utility implies downward-sloping ICs.
3. ICs can intersect if preference is not convex.
4. SEU consumer’s choice must satisfy SARSEU, but does not have to satisfy WARP.
2 Long Answer Questions (55 points)
Group Q9 (23 points)
Consider the following game in normal form.
1. (15 pts) Derive best responses for both players considering mixed strategies. (Hint: you might want to simplify the matrix first.)
2. (8 pts) Find all MSNE (including pure).
Version 1:
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
E |
1, 2 |
3, 3 |
5, 4 |
2, 2 |
|
F |
0, 4 |
2, 7 |
2, 1 |
8, 6 |
|
G |
1, 2 |
2, 1 |
1, 2 |
7, |
Version 2:
|
|
A |
B |
C |
|
D |
2, 2 |
6, 8 |
0, 7 |
|
E |
4, 5 |
1, 2 |
2, 1 |
|
F |
3, 3 |
7, 1 |
1, 2 |
|
G |
2, 1 |
4, 0 |
2, 1 |
Group Q10 (32 points)
1. Suppose production technology is F (K, L, H) = 2H + ln K + 5 ln L. Derive the long-run cost function. Note that the problem has corner solutions. If you don’t consider them, you will be able to score not more than 75% of points.
2. Suppose production technology is F (K, L, H) = 9H + ln K + 2 ln L. Derive the long-run cost function. Note that the problem has corner solutions. If you don’t consider them, you will be able to score not more than 75% of points.

