Econ 438 Problem Set #2
Winners and Losers
from Globalization
Problem Set #2: April 15th
You may discuss this problem set with your classmates, but everything you turn in must be your own work.
Label all figures clearly.
1. This question is about the specific factors model.
The world consists of two countries, Scranton and Pawnee (*), that can produce two goods, paper products (p) and recreation services (r). The production functions and labor resource constraints are given by,
Scranton,
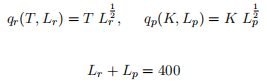
Pawnee,
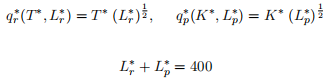
Finally, each country is endowed with the following stocks of land and capital,
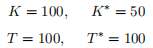
a. [5 pts] What is the only difference between these countries and what goods do you expect each country to export?
b. [10 pts] Suppose these countries are initially in autarky, and the prices in each country are given by,
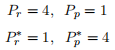
What is the allocation of labor in each country and how much of each good does each country produce?
c. [10 pts] Now suppose the countries open to trade, and world prices are given by,
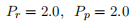
How much of each good does each country produce after opening up to trade and what does this imply about which goods are being exported by each country? Show your work.
d. [10 pts] Finally, which factors of production win and loose in each country?
2. This question is about vertical foreign direct investment and the fragmentation of supply chains across countries
Use the two-country model of vertical FDI we developed in class to answer the following questions. Assume that 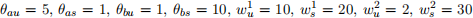 , and
, and 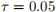 .
.
a. [15 pts] In Excel, create a column of
that vary from 0 to 0.30 by increments of 0.01. Create the following columns, where each row differs by the value of
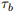
1. The cost of the final good in country 1 if a and b are both made in country 1.
2. The cost of the final good in country 1 if b is made in country 1, shipped to country 2 where a is made, and the final good is shipped to country 1.
3. The cost of the final good in country 2 if a and b are both made in country 2.
4. The cost of the final good in country 2 if b is made in country 1 and shipped to country 2 where a is made.
5. The cost of the final good in country 2 if a and b are both made in country 1 and the final good is shipped to country 2.
b. [5 pts] For what values of
is the best firm structure complete fragmentation? Explain
c. [5 pts] For what values of
is the best firm structure partial fragmentation? Explain
d. [5 pts] For what values of
is the best firm structure to export from country 1? Explain
e. [10 pts] In one graph, plot each of the 5 columns against
. Put
on the x-axis. Clearly label the graph.
3. [20 pts] Redo part a. from question 1, but let 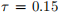 . Why is complete fragmentation no longer viable for any level of
. Why is complete fragmentation no longer viable for any level of 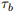 ? Explain
? Explain
2021-04-19