MF 728: Fixed Income
MF 728: Fixed Income
Professors Eugene Sorets and Chris Kelliher
Spring 2021
Problem set # 4
Due: Thursday, March 11th, by 2pm.
1. Swaption Pricing and Risk Management under the SABR Model:
Consider the following table of normal swaption volatilities and corresponding par swap rates:
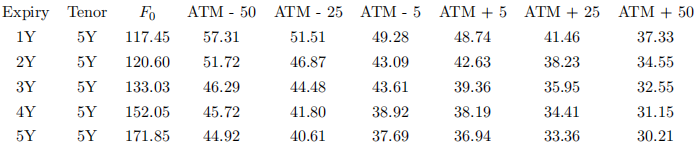
NOTE: All numbers in the table are reported in bps.
(a) Calculate the constant instantaneous forward rate for each swap that will lead to the par swap rates listed. You may use a different instantaneous forward rate for each swap and are not required to go through an entire bootstrapping exercise.
(b) Using the rates obtained above, calculate the current annuity value for each swap in the above table.
(c) Calculate a table of premiums for each swaption in the table using the Bachelier pricing formula and the annuities computed above.
(d) For each option expiry, find the set of SABR parameters that best matches the quoted normal volatilities. Utilize the asymptotic approximation formula to calculate the normal volatility for a given set of SABR parameters and look for a solution that minimizes the distance between market and model volatilities.
(e) Comment on the relationship of the calibrated parameters as a function of expiry.
(f) Using these calibrated SABR parameters, calculate the price and normal volatility of swaptions with strikes equal to ATM - 75 and ATM + 75.
(g) Calculate the equivalent Black volatilities for each option in the table above.
(h) Calculate the delta of each options under Black’s model.
(i) Estimate a SABR smile adjusted delta for each option by calculating the expected implied shift in the volatility, 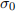 for a given shift in
for a given shift in 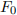 . Use this to create a shift of
. Use this to create a shift of 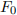 and
and 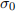 and use this shift to approximate delta. Compare the delta you obtain using this methodology to the delta you obtained via Black’s model. Comment on any differences you observe.
and use this shift to approximate delta. Compare the delta you obtain using this methodology to the delta you obtained via Black’s model. Comment on any differences you observe.
2021-03-11