Economics 580 Assignment #5: Practice Questions
Economics 580
Assignment #5: Practice Questions
I. Consider two firms, 1 and 2, producing differentiated products. The demands for the two products are symmetric and given by
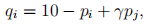
for 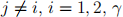 is a demand parameter measuring diversion ratio and the degree of product differentiation, and
is a demand parameter measuring diversion ratio and the degree of product differentiation, and 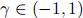 . The marginal costs of production for both firms are 0.
. The marginal costs of production for both firms are 0.
1. Suppose that the two firms compete by simultaneously choosing their prices. Determine the Bertrand-Nash equilibrium prices,
, and firm profits.
2. Suppose that the two firms choose their prices to maximize their joint profits (through price-fixing collusive agreements or through a merger). Determine the optimal prices
, and firm profits.
3. Compare your answers in the above two settings. When will the joint-profit maximizing prices be greater (and lower) than the independent/competitive prices (respectively)? Explain briefly your answers.
4. Now, suppose the two firms play a 2 by 2 matrix game in which each player chooses one of the two price levels
. Compute the payoffs in the matrix and determine the Nash equilibrium of the static game. For calculation simplicity, in this question assume
.
5. Explain what would happen if the two firms with a discount factor δ play the above matrix game repeatedly (infinitely many times). For what level of the discount factor will the firms sustain the collusive outcome using a trigger strategy? Again, assume
.
II. Consider two firms, 1 and 2, producing differentiated products. The demands for the two products are symmetric and given by
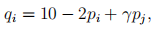
for 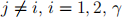 is a demand parameter measuring diversion ratio and the degree of product differentiation, and
is a demand parameter measuring diversion ratio and the degree of product differentiation, and 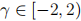 . The marginal costs of production for both firms are $1. Answer the following three questions for each of the following values of
. The marginal costs of production for both firms are $1. Answer the following three questions for each of the following values of 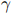 = 0, 1, — 1, and — 2, respectively.
= 0, 1, — 1, and — 2, respectively.
1. Suppose that the two firms compete by simultaneously choosing their prices. Determine the Bertrand-Nash equilibrium prices, and firm profits.
2. Suppose that the two firms choose their prices to maximize their joint profits (through price-fixing collusive agreements or through a merger). Determine the optimal prices, and firm profits.
3. Compare the outcomes from the above two settings.
III. Consider two firms, 1 and 2, producing differentiated products. The demands for the two products are symmetric and given by
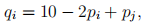
for 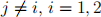 . The marginal cost of production for firm 1 is $1 and for firm 2 is 0. Answer the following three questions.
. The marginal cost of production for firm 1 is $1 and for firm 2 is 0. Answer the following three questions.
1. Suppose that the two firms compete by simultaneously choosing their prices. Determine the Bertrand-Nash equilibrium prices, and firm profits.
2. Suppose that the two firms choose their prices to maximize their joint profits (through price-fixing collusive agreements or through a merger). Determine the optimal prices, and firm profits.
3. Compare the outcomes from the above two settings.
IV. Consider two firms, 1 and 2, producing differentiated products. The demands for the two products are asymmetric and given by
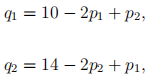
The marginal cost of production for both firms are 0. Answer the following three questions.
1. Suppose that the two firms compete by simultaneously choosing their prices. Determine the Bertrand-Nash equilibrium prices, and firm profits.
2. Suppose that the two firms choose their prices to maximize their joint profits (through price-fixing collusive agreements or through a merger). Determine the optimal prices, and firm profits.
3. Compare the outcomes from the above two settings.
2021-03-10