Math 178B Midterm
1. (15 points) Recall the Sickness-Death Model:
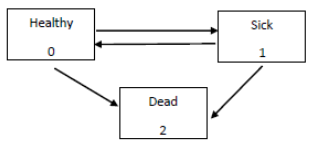
A policyholder of age 55 purchases a 10-year term insurance with the following conditions.
• A lump sum of 100, 000 is payable immediately upon death.
• As long as the policyholder is in the healthy state, a yearly premium rate of P will be continuously paid.
• As long as the policyholder is in the sick state, a yearly benefit with a rate of 5P will be continuously paid.
• The multiple state transition forces and the term structure are in accordance with tables D.7 and D.8.
Based on the given conditions, calculate P.
2. (15 points) Consider the following multiple state model.
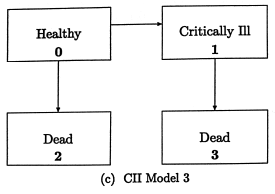
The policyholder is a healthy, 50 year old individual. If the policyholder su↵ers from a critical illness (state 1), the policy pays a lump sum of 10, 000 at the end of the month of diagnosis, plus an additional 1, 000 at the end of each subsequent month while the life survives. A benefit of 40, 000 is paid at the end of month of death, if the life dies after the disability diagnosis. The policy pays 50, 000 at the end of the month of death, if the life dies without su↵ering a disability.
The premiums are payable monthly while in State 0. A 5% annual e↵ective interest rate is assumed, which is used to calculate the following EPV’s.
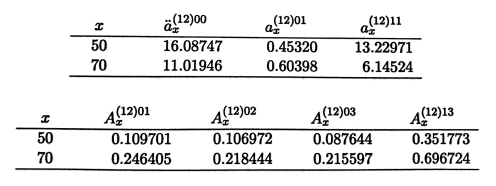
The monthly premiums are calculated w.r.t. the Equivalence Principle and found out to be P = 79.72. Using this piece of information calculate the the policy values at t = 20, 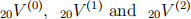 .
.
3. (20 points) Considering a company’s (Cabbage Corp.) financial situation, we use the multiple state model with three states: (0) solvent, (1) bankrupt, (2) liquidated. All the nonzero forces of transition are constant and are reported as follows: 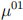 = 0.02,
= 0.02, 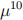 = 0.06 and
= 0.06 and 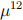 = 0.1.
= 0.1.
Calculate the probability that the company currently, at the start of the year, bankrupt will be solvent at the end of one year, using Kolmogorov’s forward equations and a step size of h = 0.5.
4. (20 points) Consider the following part of a multiple decrement table:
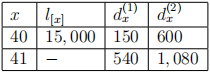
Assuming that each separate independent decrement has the UDD assumption (but not the whole multiple decrement model), calculate 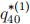 and
and 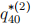 .
.
5. (10 points) Balin, (x), and Dwalin, (y) are two independent lives. 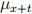 = 5t and
= 5t and 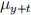 = t, for any t > 0. Calculate the probability that Balin dies within one year, and this happens before the future lifetime of Dwalin.
= t, for any t > 0. Calculate the probability that Balin dies within one year, and this happens before the future lifetime of Dwalin.
6. (20 points) Beren and Luthien, both aged 65, purchase a contract providing the following benefits:
(i) An annuity-due of S per year while both are alive, reducing to 0.6S per year after the death of Beren as long as Luthien is alive and reducing to 0.7S per year after the death of Luthien as long as Beren is alive.
(ii) A life insurance benefit of 100, 000 payable at the end of the year of death of Beren, whether or not Luthien is alive.
You are also given:
• Future lifetimes are independent.
• The mortality of each life follows the Standard Ultimate Life Table.
• i = 0.05
• There is a single premium for this contract in the amount of 1, 000, 000, payable at the start of the contract.
Calculate S.
2021-02-07