CS5281 Internet Application Development
CS5281
Internet Application Development
GENERAL INFORMATION
■ Lecturer:
● Dr. Kenneth Lee ([email protected])■ Examination 50% (2 hours)
● Appendix like partial syntax/command list will be provideo■ Group Project 30%
● Phase 1 assessment - Design, HTML, CSS
● Phase 2 assessment - also includes JavaScript and PHP (demonstration in the last class)■ Quiz 15% (1 hour, prelim date: Week9 lecture, to be confirmed)
■ Tutorial Exercises 5%
REFERENCE TEXT
■ We do not stick to a single textbook, but rather we'll focus on the power point slides and possibly web resources.
■ Students who want a reference book may refer to:
● "HTML5 & CSS3 Video QuickStart Guide. 9th Edition" by Elizabeth Castro and Bruce Hyslop,Peachpit Press, 2020"
● "JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide, 5th Edition" by John Pollock, 2019
● Or online resources like W3School(http://www.w3school.com)


TOPICS
■ Introduction to Internet, Internet Application Architecture
■ Client Side Technologies:
● HTML - How to define structure of page
● CSS - How to define the format/appearance of page
● JavaScript - Add logic to page (e.g. data validation)
● Brief introduction to libraries like JQuery■ Server Side Technologies:
● PHP - Dynamic page generation with file/DB/form data.■ Introduction to other topics (e.g. AJAX, mobile) if time allows.
INTERNET APPLICATION ARCHITECTURE
■ Overview
■ Browser
■ Servers, Web & Others
■ Client Server System
■ Scripting
OVERVIEW
■ Any program that uses Internet technologies (e.g.socket APIs of TCP/IP) can be regarded as IAs
■ Recently, Web systems are the main stream IA systems, advantages:
● Standard user interface
● Can link to existing DBMS and legacy systems
● Highly scalable
● Distributed and component based
● Could be assessed by both desktop and mobile devices■ A Typical Web System Setup
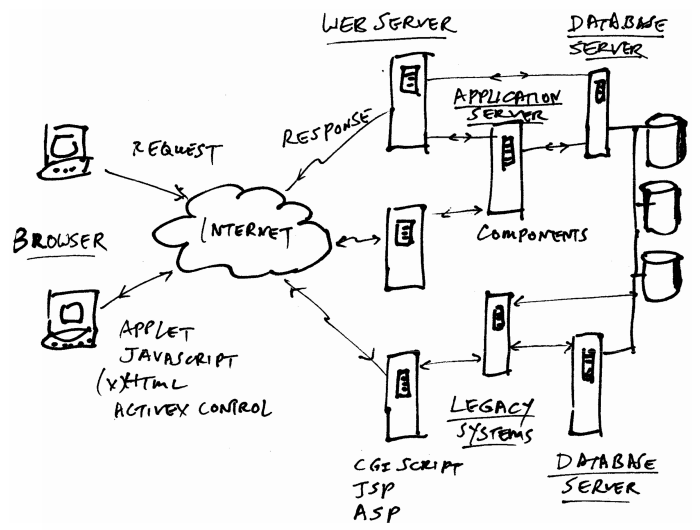
CLIENT SERVER SYSTEMS
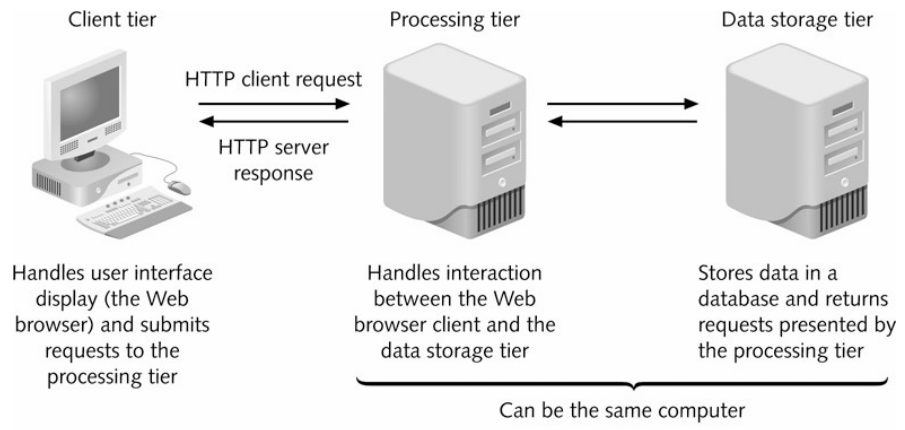
● 1st tier (presentation service):
● always implemented on a client computer, handling nterface only, eq. Browser, HTML/DHTML, client side script, APPLET
● 2nd tier (business service -middleware):
● implements application logic and business rules usually in the same machine as Web server, eg. server side script, COM+, Java Bean, etc.
● 3rd tier (data service):
● includes database server and components used to access the database, eg. SQL server, ADO, JDBC/ODBC. JDO, etc.
Web browsers
■ The web browser is the presentation layer of the system
■ Information is retrieved from web server by sending HTTP request
■ HTTP request is sent from browsers and HTTP response is delivered by servers
■ Upon receiving the response, the browser renders and displays the HTML on the screen
■ interprets and runs script (Scriptlet) & executes APPLET or ActiveX Control
■ There are many variations of web browser available
● Lynx (text-based, more than 20 years old)
● Internet Explorer, Edge
● Opera
● Firefox
● Chrome...etc

■ Compatibility (display, scripting) is the problem of web development with different browsers.
■ Also need to consider screen size if the service also targets mobile platforms.
SERVERS, WEB & OTHERS
■ Web Server, a server program:
● Run by web provider/host but not typical user
● monitor the HTTP port (default 80) for user request
● delivers the page, runs CGI scripts/JSP/ASP or activates components in Application Servers
● multi-threaded /task■ Common Products:
● Microsoft IIS, Apache, Sun ONE, Tomcat etc.

■ Database Server:
● just a DBMS such as Sybase, SQL Server, DB2, Oracle etc.
● could reside in another machine from the Web server■ Application Server:
● a general term for the machine hosting programs or other resources that can be activated by the Web server
● usually host the components (DCOM, EJB etc.)
● other resources can be images or video streams
SCRIPTING
■ Scripts
● command languages e.g. Unix Shell script, Windows batch file, Javascript & VBScript, usually executed by nterpretation (script engine)■ Client-Side Scripting
● scripts are embedded in the HTML and sent to the browser
● executed in the client side (browser)
● mainly used to enhance user interface handling: data validation, drop down manual, animation etc.
● Usually no access to local file (until recently).
● Becoming more and more mature and partially take over the rasks of APPLET / Flash / Activex Control■ Server-Side Scripting
● executed in the server side (Web Server)scripts are embedded in the textual file, executed first to roduce result (usually HTML also) which are then sent to the browser
● mainly used to produce dynamic page content
● also used to activate other components or access database
● many different scripting languages : Perl, PHP, JSP, ASP, etc.
● In the old days, client side (e.g. Javascript) uses a different language from the server (e.g. PHP), but recently, there're attempts on using the same language. (e.g. Node.JS)

● Don't need to learn a new language
● Can possibly reuse code (e.g. verify user data)
■ Instead of coding all of the logic yourself, for some tasks, you could send the request to another machine and have the problem solved for you. Example:
● Google Map Geocoding (Map address to longitude/latitude)
● Store a file onto cloud storage (e.g. Google Drive)
● Get the weather report of a city
● ...etc.
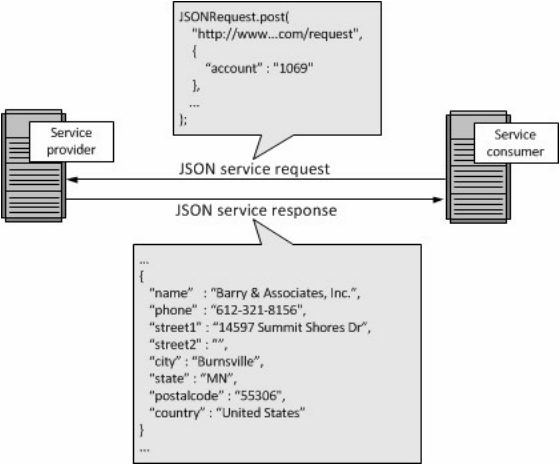
■ Could be coded in any programming language (though Javascript is common for client)
■ Information (e.g. temperature, address) is usually sent in the form of XML (extensible Markup Language) or JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)
■ Because of limited time, we do not officially cover XML/JSON in our course. The figure below intends to give you a feeling of how XML/ SON look like:

http://www.service-architecture.com/articles/web-servic.services explained.html
2021-01-25