Econ 204 Practice MT 1
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Econ 204 Practice MT 1
Part I: Multiple Choice Questions
1) In 2005, DAMA's exports were $30 billion, imports $40 billion, and real GDP $200 billion. DAMA had a trade ________ equal to ________ ofGDP in 2005.
A) surplus; 5 percent
B) deficit; 5 percent
C) surplus; 10 percent
D) deficit; 10 percent
2) The difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics is that
A) microeconomics looks at supply and demand for goods, while macroeconomics looks at supply and demand for services.
B) microeconomics looks at prices, while macroeconomics looks at inflation.
C) microeconomics looks at individual consumers and firms, while macroeconomics looks at national totals.
D) microeconomics looks at national issues, while macroeconomics looks at global issues.
3) The classical approach to macroeconomics assumes that
A) wages, but not prices, adjust quickly to balance quantities supplied and demanded in markets.
B) wages and prices adjust quickly to balance quantities supplied and demanded in markets.
C) prices, but not wages, adjust quickly to balance quantities supplied and demanded in markets.
D) neither wages nor prices adjust quickly to balance quantities supplied and demanded in markets.
4) How did Keynes propose to solve the problem of high unemployment?
A) have the government increase its demand for goods and services
B) increase the growth rate ofthe money supply
C) allow wages to decline so that firms will want to hire more workers
D) put on wage and price controls so that wages won't rise and firms won't have to lay people offto cut costs
5) Assume that the municipal government of Lethbridge, Alberta, has taxes of $500, government purchases of $350, transfer payments of $150, and interest expenses of $50. The government budget would
A) show a surplus of $100.
B) show a surplus of $50.
C) be in balance with neither a surplus nor a deficit.
D) show a deficit of $50.
6) If a Canadian construction company built a road in Kuwait, this activity would be
A) excluded from Canadian GNP.
B) fully included in Canadian GDP.
C) included in Canadian GNP only for that portion that was attributable to Canadian capital and labour.
D) included in Canadian GDP but not Canadian GNP.
7) Nations such as Egypt and Turkey have wide differences between GNP and GDP because both countries
A) have a high level of imports and exports relative to GNP.
B) have a large portion of their GNP produced by multinational corporations.
C) have a large number of citizens working abroad.
D) purchase large amounts of military wares from other countries.
8) National saving equals private saving plus government saving, which in turns equals
A) GDP + NFP - C - G.
B) C + S + T.
C) GDP + C + G.
D) GDP + NFP.
9) If national savings in an economy is equal to $50 billion, exports are $10 billion, imports are $5 billion, and net factor payments from abroad is -$2 billion, total investment will be
A) $45 billion.
B) $47 billion.
C) $57 billion.
D) $74 billion.
10) The real wage is measured by
A) the difference between the nominal wage rate and the inflation rate.
B) the difference between the nominal wage rate the interest rate.
C) the ratio of nominal wage and price level.
D) the wage rate divided by the inflation rate.
11) An increase in the real wage will cause an individual to increase his or her supply of labour if
A) the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
B) the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
C) the substitution effect is equal to the income effect.
D) the substitution effect is negative and the income effect is positive.
12) Which one of the following is true?
A) The marginal product of capital is positive but declining as the capital stock increases.
B) The marginal product of capital is positive and increasing as the capital stock increases.
C) The marginal product of capital is negative and declining as the capital stock increases.
D) The marginal product of capital is negative but rising as the capital stock increases.
13) Cyclical unemployment arises when
A) unskilled or low-skilled workers find it difficult to obtain desirable, long-term jobs.
B) labour must be reallocated from industries that are shrinking to areas that are growing.
C) workers must search for suitable jobs and firms must search for suitable workers.
D) output and employment are below full-employment levels.
14) A rise in wealth reduces labour supply. What happens to current employment and the real wage rate?
A) Both employment and the real wage rate would increase.
B) Both employment and the real wage rate would decrease.
C) Employment would increase and the real wage would decrease.
D) Employment would decrease and the real wage would increase.
15) Zowie! Surfboards has the following production function:
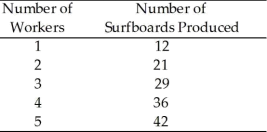
If surfboards sold for $30 and the nominal wage rate was $200, how many workers would the
firm employ?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
16) The marginal product of labour
A) is measured by the slope of the production function relating capital to employment.
B) is larger when the labour supply is relatively larger.
C) is smaller when the labour supply is relatively smaller.
D) decreases as the number of workers already employed increases.
17) A higher real interest rate will
A) increase the profitability ofnew investment.
B) decrease lending of funds from firms to other economic agents.
C) reduce the desired investment of all firms.
D) reduce the desired investment of only those firms that have to borrow.
18) If consumers foresee future taxes completely, a reduction in taxes this year that is accompanied by an offsetting increase in future taxes would cause
A) a rightward shift in the saving curve and a rightward shift in the investment curve.
B) a shift in neither the saving nor the investment curve.
C) a leftward shift in the saving curve, but no shift in the investment curve.
D) no shift in the saving curve, but a rightward shift in the investment curve.
19) Most people would prefer
A) higher current consumption relative to future consumption.
B) higher future consumption relative to current consumption.
C) to smooth consumption over their lifetime.
D) to match current consumption to current income.
20) Suppose the interest rate is 2 percent, the capital depreciation rate is 5 percent, and the price of a new capital is $100. What is the user cost of capital?
A) $5
B) $2
C) $3
D) $7
Part II Long answers questions
Question 1 - Macroeconomic information for the economy of Anchovy is given below:
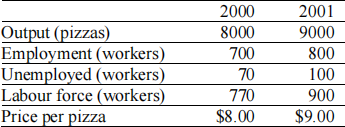
a. What was the growth rate of average labour productivity in Anchovy between 2000 and 2001? (4 marks)
Average labour productivity: 2000: 8000/700 = 80/7; 2001: 9000/800 = 90/8;
growth rate = [(90/8)/(80/7)] - 1 = -.016 = -1.6%
b. What was the inflation rate in Anchovy between 2000 and 2001? (3 marks)
Inflation rate: (9/8) - 1 = .125 = 12.5%
c. What was the unemployment rate in 2000? In 2001? (3 marks)
Unemployment rates: 2000: 70/770 = .091 = 9.1%; 2001: 100/900 = .111 = 11.1%
Question 2 - The country of Myrule has produced the following quantity ofgauges and potatoes, with the price of each listed in dollar terms:
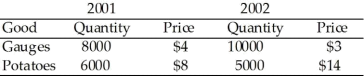
a. Using 2001 as the base year, what are the price indexes for 2001 and 2002? (3 marks)
2002 price index = base-year output at current prices/base-year output at base- year prices = [(8000 × 3) + (6000 × 14)] / [(8000 × 4) + (6000 × 8)] = 108,000 / 80,000 = 1.35
b. What is the inflation rate using this index?
Inflation rate = [(1.35/1) - 1] × 100% = 35%
c. What is the percent change in real output using this index?
Nominal GNP (2001) = (8000 × 4) + (6000 × 8) = 80,000
Nominal GNP (2002) = (10,000 × 3) + (5000 × 14) = 100,000
Real GNP (2001) = nominal GNP (2001) = 80,000
Real GNP (2002) = nominal GNP (2002)/price index = 100,000/1.35 = 74,074 Real output growth = [(74,074/80,000) - 1] × 100% = -7.4%
Question 3 Suppose that the production function is Y = 2![]() 0.25
0.25![]() 0.75 . The capital stock is K = 50. The labor supply curve is NS = 50[(1-t)w]2 , where w is the real wage, t is the tax rate on labor income, and hence (1-t)w is the after-tax real wage rate.
0.75 . The capital stock is K = 50. The labor supply curve is NS = 50[(1-t)w]2 , where w is the real wage, t is the tax rate on labor income, and hence (1-t)w is the after-tax real wage rate.
a) Assume that the tax rate on labor income, t, equals zero. Find the equation ofthe labor demand curve. Calculate the equilibrium levels ofthe real wage and employment, the level of full employment output, and the total after-tax wage income ofworkers. (5 marks)
Since w = MPN = 1.5![]()
![]() .
. ![]()
![]() −
−![]() .
. ![]() ;
; ![]() −
−![]() .
. ![]() =
= ![]() .
. ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . / w ; so N = (
. / w ; so N = (![]() .
. ![]() )
) ![]() /
/![]()
![]()
![]() , so N = 5.0625 K/
, so N = 5.0625 K/ ![]()
![]() . When K = 05, N = 253.125/
. When K = 05, N = 253.125/ ![]()
![]()
If t = 0.0, then NS = 50w2. Setting labour demand equal to labour supply gives 253.125/w4 = 50w2, so w6 = 5.0625, or w = 1.3103. Then NS = 50 (1.3103)2 = 85.85. [Check: N = 253.125/1.31034 = 85.85] Y = 2(![]() )
)![]() .
. ![]() N0.75 = 5.318(85.85)0.75 = 150. The total
N0.75 = 5.318(85.85)0.75 = 150. The total
after-tax wage income of workers is (1−t) w NS = 1.3103 x 85.85 = 112.5.
b) Calculate the rate ofreturn on capital? (2 marks)
Y = NW + RK; 150 = 112 + 50R; R = 0.76
c) Repeat part (a) under the assumption that the tax rate on labor income, t, equals 0.3. (5 marks)
If t = 0.3, then NS = 50 [(1 − 0.3) w]2 = 35w2. The marginal product of labour is MPN = 4 / N0.25, so N = 50[(1 − 0.3) x 4 / N0.25]2, so N3/2 = 392, so N = 53.56. Then 2(![]() )
)![]() .
. ![]() N0.75 = 5.318(53.56)0.75 = 105.28. Then w = 4 / 53.560.25 = 1.48. The
N0.75 = 5.318(53.56)0.75 = 105.28. Then w = 4 / 53.560.25 = 1.48. The
total after-tax wage income of workers is (1−t) w NS = 0.7 x 1.48 x 53.56 =
55.48. Note that there is a big decline in output and income, although the
wage is higher.
d) Suppose that a minimum wage ofw = 1.75 is imposed. If the tax rate on labor income, t, equals zero, what are the resulting values of employment and the real wage? Does the introduction ofthe minimum wage increase the total income ofworkers, taken as a group? (3 marks)
A minimum wage of 1.75 is binding if the tax rate is zero. Then N = 253.125/ ![]() .
. ![]()
![]() = 27, NS = 50 x 1.752 = 153.125. Unemployment is (153.125 – 27) 126.125. Income ofworkers is
= 27, NS = 50 x 1.752 = 153.125. Unemployment is (153.125 – 27) 126.125. Income ofworkers is
wN = 1.75 x 27 = 47.25, which is lower than without a minimum wage,
because employment has declined so much.
2022-02-15