MGT6152 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MGT6152
MANAGEMENT SCHOOL
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
SECTION A COMPULSORY: ANSWER QUESTIONS ONE AND TWO
Question One
Task One
Your colleague has produced a routine profitability analysis of the three factories of
WWP Ltd for the last month, as follows:
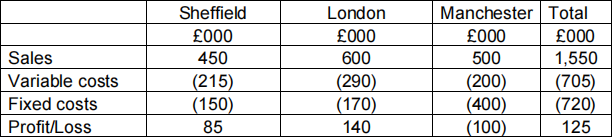
Required:
a) Prepare a detailed, differential cost calculation to show whether the Manchester factory should be closed. Assume that £200,000 of Manchester fixed costs and all Manchester variable costs are avoidable, and if the Manchester factory is closed, £200,000 of Manchester’s fixed costs are unavoidable. (10 marks)
b) Outline factors that might be relevant to the decision to close or continue the Manchester factory. (6 marks)
Task Two
Marco plc manufactures product FG which has a selling price of £80. The following forecast has been made for the coming year:
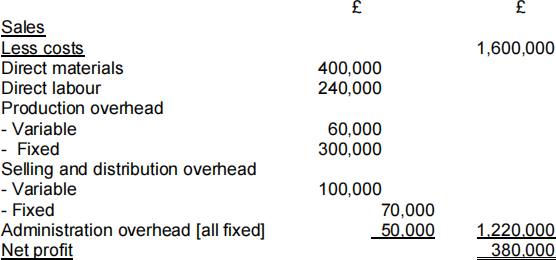
Required
(a) Calculate the breakeven point and margin of safety in sales volume and value. (Use the contribution per unit to do this.) (5 marks)
(b) Ascertain the profit or loss, which would be achieved if 11,000 units were sold. (2 marks)
(c) Calculate the number of units to be sold to make a profit of £300,000 per year. (2 marks)
(Total 25 marks)
Question Two
Task One
FG Ltd manufactures a range of products including A, B and C. Planned production for the three months to 31 March 2019 is A = 5,000 units, B = 4,000 units; and C=3,500 units. The following information is available concerning the unit production costs and revenues for each product

The raw material costs £80 per kilo, and it has now been ascertained that while 32,000 kilos are required to produce budgeted output, only 29,500 kilos will be available in the three months to 31 March 2019.
Fixed overheads amount to £200,000 per month.
Required:
(a) Prepare a revised production budget that will produce the maximum net profit for the three months to 31 March 2019 and calculate the profit for the same period. (10 marks)
(b) Calculate the shortfall in contribution imposed by the constraint on raw materials, the maximum contribution in the absence of a raw material constraint, and how many additional kilos of raw materials are required. (6 marks)
Task Two
Sheffield Ltd, a subsidiary of BFJ plc, makes two products, Machine part X and Machine part Y. The monthly budget for the two products is as follows:
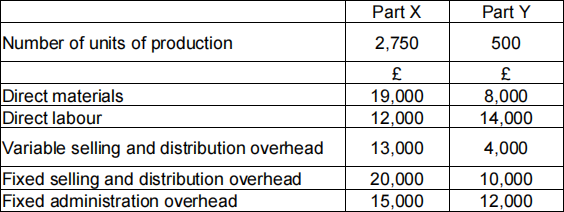
Sheffield Ltd has the opportunity to purchase each of the two products externally from WEZ Productions Ltd at the following prices:
Machine part X £18 each
Machine part Y £50 each
Required:
(a) A recommendation, supported by calculations, as to which product or products, if any, Sheffield Ltd should continue to manufacture, and which should be “bought in” from WEZ Ltd. (5 marks)
(b) As a management accountant, explain to the production manager of Sheffield Ltd why marginal costing is considered to be useful for short-term decision making but not for stock valuation. (4 marks)
(Total 25 marks)
SECTION B: ANSWER ONE QUESTION FROM THIS SECTION
Question Three
The following information relates to forecasts of activity for Baku plc:
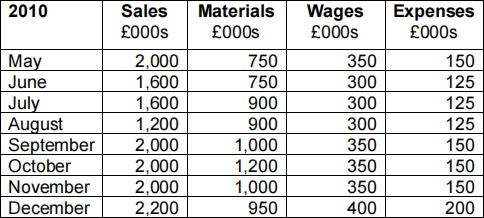
1. One quarter of sales are on credit and customers are allowed one month in which to pay.
2. Wages are paid as they fall due. Suppliers of materials grant one month’s credit and suppliers of items of expenses allow two month’s credit.
3. From the capital budget it is known that a payment of £8,000,000 for new machinery is due to be made in November.
4. The proceeds from a loan, amounting to £5,000,000, will be received in October.
5. The expected cash balance at 1 July 2016 is £1,000,000.
6. Baku plc currently does not have a bank overdraft facility.
Required:
(a) Prepare a Cash Budget for the six months to 31 December 2016, by month and in total. (Total 13 marks)
(b) Discuss the significant features in the Cash Budget which you have prepared for Baku plc. (Total 12 marks)
(Total 25 marks)
Question Four
The following information was provided for products A and Y:
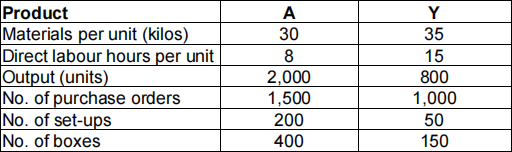

Cost of material £4 per kilo
Direct wage rate £8 per hour
Required:
(a) Use the labour hour-based overhead absorption rate to calculate the unit cost for
each of the two products. (4 marks)
(b) Use the Activity Based Costing approach to calculate the unit cost for each of the two products. (Present your answers to 2 decimal places). (14 marks)
(c) Comment on the results of (a) and (b). (7 marks)
(Total 25 marks)
SECTION C: ANSWER ONE QUESTION FROM THIS SECTION
Question Five
Critically discuss, using your words, the balanced scorecard concept as a performance measurement and management system, also with reference to academic literature.
(Total 25 marks)
Question Six
Critically discuss, using your words, the Just in Time concept, how it is expected to reduce cost and eliminate waste from business operations and its implications on management accounting, also with reference to academic literature.
(Total 25 marks)
2022-01-29