Econ 2160A EXAMPLE EXAM QUESTIONS FOR CHAPTERS 19-21
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Econ 2160A
EXAMPLE EXAM QUESTIONS FOR CHAPTERS 19-21
Fall 2021
The following are example test questions covering Chapters 19-21. There is an answer key included at the end of the document.
Your Final Exam will be cumulative (Ch 1-3 and 14-21). Please see the Test 1 and Test 2 modules as well as your actual Test 1 and Test 2 for example questions related to Chapters 1-3 and 14-18. These examples questions for Chapters 19-21 are only meant to give you an idea of the types of questions that might appear on your test from these chapters. You should NOT limit your studies to these topics. Your final exam can cover any topics from the course. If you need clarification as to what has been covered, please see the Reading List sections of the modules in Course Content.
CHAPTER 19:
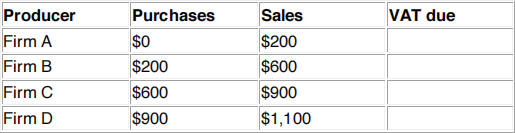
1. The table below outlines the purchases and sales at each stage in the production and sale of widgets. Fill in the last column of the table indicating the value-added tax due by each producer. Assume a tax rate of 15% and assume that Firm B is tax exempt.
2. From a lifetime view, consumption taxes are generally considered
a) regressive.
b) progressive.
c) proportional.
d) multiplicative.
Please use the information below to answer questions 3 through 5.
David saves $3,000 of his Year 1 income to spend in Year 2. The interest rate is 12 percent, the tax rate that applies to interest income is 25 percent, and the sales tax rate is 10 percent. David spends all of his available funds in Year 2.
3. How much will David pay in taxes on his interest income in Year 2? [Please present your answer in Year 2 dollars, not present value/Year 1 dollars.]
4. Rounded to the nearest dollar, how much will David pay in sales taxes in Year 2? [Please present your answer in Year 2 dollars, not present value/Year 1 dollars.]
5. If David increases his consumption in Year 1 and therefore decreases his saving for Year 2, what will happen to his present value lifetime tax burden?
a) It will increase.
b) It will decrease.
c) It will stay the same.
CHAPTER 20:
6. Suppose Mrs. Davina's home has an assessed value of $350,000. She originally paid $290,000 to purchase the home and holds a mortgage of $200,000 on the home. The residential property tax rate in Mrs. Davina's municipality is 2 percent. What does Mrs. Davina owe in property taxes annually?
7. In the traditional view, the supply curve of structures is
a) upward sloping.
b) downward sloping.
c) horizontal.
d) vertical.
CHAPTER 21:
8. Before applying the corporate tax rate, firms may deduct
a) wage payments.
b) interest payments.
c) depreciation allowances.
d) all of the above
9. Consider a corporate tax system that uses the declining-balance method for determining depreciation for tax purposes. Assume that the applicable rate is 40 percent, and the tax life of the asset is 3 years. If a corporation purchases a depreciable asset for $10,000, what depreciation deduction is allowed in Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3?
10.Capital Computer Corporation takes out a $10,000 loan to finance the purchase of new physical capital. It must repay the loan in full with interest in one year. The interest rate is 10 percent and the applicable corporate tax rate is 30 percent. What is the present value savings from the deductibility of the interest payment from Capital Computer Corporation’s taxes? Please round your answer to the nearest dollar.
ANSWER KEY:
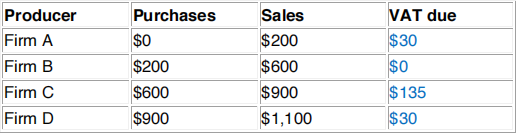
1.
2. C
3. David will pay $90 in taxes on his interest income in Year 2.
4. David will pay $297 in sales taxes in Year 2.
5. B
6. $7,000
7. C
8. D
9. Year 1: $4,000
Year 2: $2,400
Year 3: $3,600
10.$273
2021-12-15