Level M Mathematical Finance (20443) Additional Task
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Level M Mathematical Finance (20443)
Additional Task
Question 1:
The Black-Scholes equation for a European put P (S, t) can be trans- formed into the diffusion equation
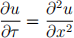
using the transformations S = Eex , t = T _ 2τ/σ2 and
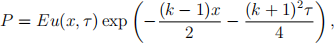
where the constant k = 2r/σ2 is determined by the volatility σ and the risk free interest rate r. The initial condition is given by u = u0 (x) at τ = 0, where
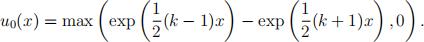
The boundary conditions are
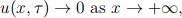
and
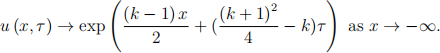
Let the problem (1)-(4) be solved numerically by a finite difference method. A computational grid used for numerical solution of (1)-(4) is generated in the domain [x一 , x+] × [0, τmax] with the grid step size δx and time step size δτ .
Students are required to independently investigate the topics of stαó]1]ty and c。)"ě¥。ě)cě with regards to
finite difference methods used to solve the initial boundary-value diffusion problem in order to answer the following questions:
(a) What is a conditionally stable finite difference method when the diffu- sion problem is solved?
(b) Let an explicit finite difference method be used for numerical solution of the problem (1)-(4). The user starts computation on a grid with the grid step size δx = 0.2 and the time step size defined as
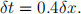
The user compares the result of the computation with the exact solution available to him and he decides to decrease the grid step size δx by a factor of two to compute a more accurate numerical solution. The time step size is also redefined for the new value of δx according to (5). The user intends to repeat this procedure (i.e. halving the grid step size δx and redefining the time step δt accordingly) as many times as required for the numerical solution to converge to the exact solution within the prescribed tolerance. Will the numerical solution converge to the exact solution of the problem (1)-(4) as a result of the above- mentioned procedure? Explain your answer.
(c) What is an unconditionally stable finite difference method when the diffusion problem is solved?
(d) Formulate an implicit finite difference method for numerical solution of the problem (1)-(4). What are the appropriate discrete initial and boundary conditions for u(x, τ )? Will the numerical solution obtained as a result of the computational procedure explained in (b) converge to the exact solution of the problem (1)-(4) when the implicit finite difference method is employed? Explain your answer.
(Hint: Among other sources of information, you may wish to have a look at references [1] and [2] in your investigation of the problem.)
References:
[1 ] R. D. Richtmyer and K. W. Morton (1967) Difference methods for initial-value problems. New York - London : Interscience.
[2 ]G. D. Smith (1978) Numerical solution of partial differential equations : finite difference methods. Oxford : Clarendon Press.
Question 2:
The trinomial method is a simple extension of the binomial method. In the trinomial method, we denote the value of the underlying asset S at time t = tk as Sk with the value of S at time t = tk+1 = tk + δt denoted as Sk+1 . We assume that Sk+1 can take three different possible values given the known value of Sk :
● an up-step with Sk+1 = uSk with probablility pu ,
● a middle-step with Sk+1 = mSk with probability pm ,
● a down-step with Sk+1 = dSk with probability pd .
The most common parameter values are 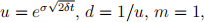
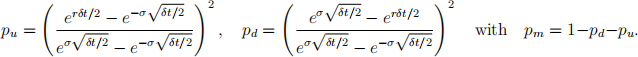
Consider the case of a call on a put compound option V (S, t). The com- pound option expires at time t = T1 = 1 with exercise price E1 = 15 with the put option expiring at time t = T2 = 3 with exercise price E2 = 110. The value of the underlying at time t = 0 is S(0) = 100. The risk free interest rate is r = 0.1, the volatility is σ = 0.5 and δt = 1.
(a) Draw an appropriate trinomial tree for this problem, clearly stating
how you choose to identify each node.
(b) Calculate the numerical value of the parameters (u, m, d, pu , pm , pd ).
(c) What restrictions are required on the time step δt to ensure that the trinomial method is valid?
(d) Perform three steps of the trinomial in order to determine the value of the compound option at time t = 0.
2021-12-15