MATH 377 Financial and Actuarial Modelling in R MOCK FINAL EXAM - II
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MATH 377
MOCK FINAL EXAM - II
Financial and Actuarial Modelling in R
1. Consider the following joint distribution for the returns on two stocks, A and B:
|
Probability |
Return on Stock A (RA ) |
Return on Stock B (RB ) |
|
0.3 |
-10% |
5% |
|
0.2 |
20% |
15% |
|
0.3 |
10% |
-5% |
|
0.2 |
30% |
20% |
(a) Find the mean and standard deviation of a portfolio such that the weight of stock A is 43% and the weight of stock B is 57%. [5 marks]
(b) Write an R program that plots the opportunity set available to any investor. [3 marks]
(c) Write an R program to plot the capital market line if the risk-free rate is 4%. [3 marks]
(d) Write an R program to find the minimum variance portfolio. What is the expected return of this portfolio? [3 marks]
2.
(a) The price of a stock is currently 15. Over each of the next four 2-month periods, it is expected to increase by 5% or decrease by 4%. The risk- free interest rate is 3.5% per annum with monthly compounding. Write an R program to find the initial price of an 8-month derivative that pays off −min(0.5 · (S(T))2 − 100, 0) [6 marks]
(b) Consider a European Call option over a stock with a current price of S(0) = 200 and volatility of 0.33. If the risk-free interest rate with quarterly com- pounding is 7% per annum, the strike price is 188, and the time to maturity of the option is 6 months:
(i) Find the price of the option using the Black-Scholes formula. [3 marks]
(ii) Find the Greeks for the option. [2 marks]
(iii) Plot rho (ρ) against the initial stock price for S(0) ranging from 100 to 300. [3 marks]
3.
(a) Let X = (X1 , X2 ) be abivariate normal distributed random vector with mean vector µ = (5, 3) and covariance matrix

(i) Compute r(X1 > 3, 0 ≤ X2 < 4). [3 marks]
(ii) Generate a sample of size 2500 from X to approximate the 5% quantile of X1(2) |X2 |. [2 marks]
(b) Consider an arithmetic Brownian motion with a drift of 0.75 and volatility of 0.12:
(i) Perform 5000 simulations of this process to approximate the probability that the process is below 3 at time 4. [3 marks]
(ii) Compare the above result with the corresponding theoretical probabil- ity. [2 marks]
4. Consider the collective risk model
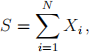
where N is Poisson distributed with mean λ = 2.5.
(a) Let X be a discrete random variable with density function given by fX (1) = fX (2) = 0.2 and fX (4) = fX (6) = 0.3. Find P(S ≤ 0.2E(S + 1)). [4 marks]
(b) Let X ∼ Weibull(2.5, 3.5). Recall that the density function of a Weibull(α , λ) distributed random variable is given by

(i) Plot the original distribution function of X along with its discretized version over (0, 10) using the upper discretization method with a step of 0.1. [4 marks]
(ii) Using the previous discretized version of X , find P(3 < S ≤ 8) via Panjer ’s recursion. [4 marks]
(iii) Simulate a sample of size 1000 from S to approximate the Coefficient of Variation (CV) of S. [4 marks]
5.
(a) Consider the classical surplus process

where N(t) is a Poisson process, with parameter λ representing the number of the claims and {Xi }i≥1 are i.i.d. random variables, independent of N(t). The density of the claim amounts is given by

Also, you are given that the intensity of the Poisson process is λ = 3, and the premium received per unit of time is c = 5.
(i) Write an R program to plot the exact ruin probability as a function of u ranging from 0 to 10. [4 marks]
(ii) Find an upper bound of the ruin probability for u = 2. [4 marks]
(b) Consider the above classical risk model under excess-of-loss reinsurance. Sup- pose that the relative security loading of the company in a reinsurance-free environment is θ = 15% and that the relative security loading under excess-of- loss reinsurance is θh = 30%. Write an R program to plot the risk adjustment coefficient as a function of the retention limit m ranging from 1 to 6. [8 marks]
2024-05-28