Econ 422 Monetary Economics
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Econ 422 Monetary Economics
Assignment 3
1. Explain the intuition how forward guidance works in the positive model of inflation by comparing the second best and the third best.
2. An important way of implementing monetary policy is for the central bank to control the overnight rate. Write down an equation, and then use it to explain why it is not necessary for the central bank to control any other longer-term interest rates.
3. The economy has infinite horizons with 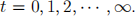 A measure one of agents each live forever. All agents are identical. At the beginning of time, each agent is endowed with a tree and
A measure one of agents each live forever. All agents are identical. At the beginning of time, each agent is endowed with a tree and 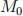 units of money, but no bonds. A tree yields output
units of money, but no bonds. A tree yields output 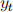 at the beginning of period t. Output is perishable, while trees are durable. Normalize the number of shares per tree to one. All transactions are in terms of goods. Let
at the beginning of period t. Output is perishable, while trees are durable. Normalize the number of shares per tree to one. All transactions are in terms of goods. Let 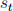 be the share of trees an agent holds at the beginning of period t and
be the share of trees an agent holds at the beginning of period t and 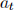 be the price per share of a tree after dividend payments.
be the price per share of a tree after dividend payments.
The government in this economy takes prices as given and spends 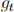 in period t, where
in period t, where 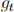 is exogenously given and is in per-capita terms. The government levies a lump-sum tax
is exogenously given and is in per-capita terms. The government levies a lump-sum tax 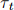 in period t. Moreover, the government issues
in period t. Moreover, the government issues 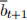 units of one-period bonds and
units of one-period bonds and 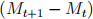 units of money in period t. The price of the one-period bond is
units of money in period t. The price of the one-period bond is 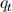 and one unit of bonds pays one unit of goods in period t+1. Note that
and one unit of bonds pays one unit of goods in period t+1. Note that 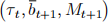 are the government's choices in period t.
are the government's choices in period t.
Let 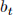 be the amount of bonds an agent holds at the beginning of period t and
be the amount of bonds an agent holds at the beginning of period t and 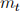 the amount of money holdings. Note that asset prices
the amount of money holdings. Note that asset prices 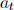 and
and 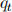 are in terms of goods. The nominal price of goods is denoted by
are in terms of goods. The nominal price of goods is denoted by 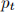 . An agent's intertemporal utility function is:
. An agent's intertemporal utility function is:
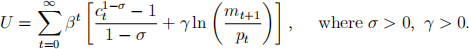
where 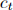 is the agent's consumption in period t and
is the agent's consumption in period t and 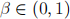 is the discount factor.
is the discount factor.
(a) Set up the representative agent's dynamic programming problem.
(b) Derive the first-order conditions.
(c) Derive the envelope conditions. Then combine the first-order conditions and envelope conditions to obtain the optimality conditions.
(d) Define the competitive equilibrium.
(e) Solve for equilibrium price
.
(f) Suppose that one-period nominal bonds are issued in every period t. Each unit of such bonds is sold for Qt units of money and pays one unit of money when it matures. Derive the equation that links the nominal interest rate to the real interest rate and the infiation rate.
(g) Show that money is both neutral and super-neutral. Also show that the Quan-tity Theory of Money holds in this economy.
(h) Let σ = 1. Derive the expression for the welfare benefit of switching inflation from
to
, where
<
.
(i) Calibrate the model using the following information from data: (i) government spending is 20% of GDP; (ii) real interest rate is 2%; (iii) inflation rate is roughly 2%; and (iv) income velocity of money is y=x = 1:5. Solve for the welfare benefit relative to GDP associated from reducing inflation from 2% to 1.5%.
2021-11-09