MIDTERM 2 GENERAL PHYSICS I
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MIDTERM 2 GENERAL PHYSICS I
Tuesday, January 2, 2024
Total Score: 100
Time Duration: 120 minutes (2 hrs.)
Exams Guidelines
All the students are directed to follow the instructions below for attempting the exam.
1. While attempting the numerical problems, please follow the general instructions as follows, which means you’ll definitely lose marks if you’ll not follow this way.
i. Given Data You must write the values of the parameters given in the numerical under the heading of “Given data”. 2 Marks
ii. To Find You must mention what is being asked to find under the heading of “To find”. 1 Mark
iii. Formula Applied You have to write the formula through which you can find the answer under the heading of “Formula applied”. 1 Mark
iv. Calculations All the calculations must be done under the heading of “Calculations”. 6 Marks
2. Try to elaborate the answers through equations and figures where needed.
3. Time is fixed so no student would be given extra time to solve the paper. Therefore, manage your time carefully.
Part-I Short Questions 20 Marks
1. Define the term “equilibrium”. Write down different types of equilibrium.
2. What do you know about deformation? Also describe the phenomenon of deformation in crystalline solids.
3. Explain what is meant by centripetal force and why it must be furnished to an object if the object is to follow a circular path?
4. Derive the expression of terminal velocity for an object moving in a fluid.
5. State and explain the law of conservation of angular momentum.
Part-II Numerical Problems 80 Marks
1. Calculate the angular momentum of a star of mass 2.0 × 1030kg and radius 7.0 × 105km. If it makes one complete rotation about its axis once in 20 days, what is its kinetic energy?
2. A wire 2.5m long and cross-section area 10−5m2 is stretched 1.5mm by a force of 100 N in the elastic region. Calculate
(i) the strain
(ii) Young's modulus
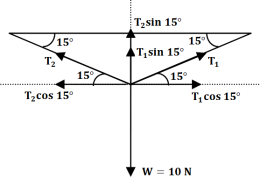
3. A load of 10 N is suspended from a clothes line. This distorts the line so that it makes an angle of 15* with horizontal at each end. Find the tension in the clothes line.
4. A 1.25cm diameter cylinder is subjected to a load of 2500kg. Calculate the stress on the bar in mega Pascal.
5. A 1000 kg car travelling with a speed of 144 km/h round the curve of radius 100 m. Find the necessary centripetal force.
6. A load is suspended by two cords as shown in the figure. Determine the maximum load that can be suspended at P, if the maximum breaking tension of the cord used is 50 N.

7. A tiny water droplet of radius 0.010cm descends through air from a high building. Calculate its terminal velocity. Given that η for air =19 × 10−6kg m−1 s −1 and density of the water ρ = 1000 kg m−3 .
8. A body of moment of inertia I = 0.80kg m2 about a fixed axis, rotates with a constant angular velocity of 100 rad s −1 . Calculate its angular momentum L and the torque to sustain this motion.
2024-03-16