ECN 311 Intermediate Mathematical Microeconomics Written Problem Set #4
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECN 311 Intermediate Mathematical Microeconomics.
Written Problem Set #4
Instructions:
§ This homework is due Monday 03/04/2023 at 11:55PM on Blackboard.
§ LATE ASSIGNMENTS OR EMAIL SUBMISSIONS ARE NOT ACCEPTED.
§ To be completed on your own.
§ By submitting this assignment, you acknowledge the pledge below:
I pledge that I will neither give nor receive any aid from any other person during this assignment, and that the work presented here is entirely my own.
No two assignments should be identical, and this includes identical solutions to those found on the internet. Any violation of the Academic Integrity Office rules will result in serious course sanctions (up to and including failure of the course). All violations will be reported to the Academic Integrity Office.
Blackboard Section (Total Points; 60 points).
Your answers must be submitted using the link on Blackboard. To receive full credit, we must receive the correct file where you must show all your work in obtaining numerical solutions, state the formulas used, and make clear your understanding of the concepts involved. Please use complete sentences and express your points clearly and fully. Use graphs whenever appropriate to help illustrate your points. Be sure to label your graphs. Make sure you submitted the correct file; no late assignments are accepted for any reason. Email submissions are disregarded.
1. Ann consumes two things: books (b) and chocolate (c). Ann’s uncompensated demand curve for books is: 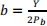 ; where ? is the number of books she reads per week; Y is her weekly income; and Pb is the price per book.
; where ? is the number of books she reads per week; Y is her weekly income; and Pb is the price per book.
a. With recent decreases in the price of books, does Ann reduce her consumption of books? Explain why or why not using the uncompensated demand function shown above. (Hint: use the partial derivative of demand with respect to price).
2. Pablo eats cakes and pies. His income is $20, and when cakes and pies both cost $1.00, Pablo consumes 4 cakes and 16 pies. But when the price of pies rises to $2.00, Pablo consumes 12 cakes and 4 pies.
a. Draw these optimal bundles and budget constraints on a diagram. Horizontal lines should describe consumption of pies.
b. Why does the budget constraint rotate as it does in response to the increase in the price of pies?
c. Trace the income and substitution effects on a separate diagram. Which is larger?
d. Are pies a normal or inferior good? How do you know? Are cakes a normal or an inferior good? How do you know?
3. True, False or uncertain; explain your answer. When income rises and the price of x falls, the consumer will always buy more units of x.
4. A consumer faces prices for fries and hamburgers of $1 each. Consumption of the two commodities at various weekly income levels are shown below.
a. Use the information to sketch the income-consumption line on a graph.
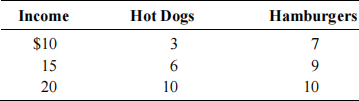
b. Draw the Engle curve for these two commodities.
c. What is the income elasticity of fries for this consumer as the price increases from $10 to $15.
5. Judi consumes steak and ramen noodles. When the price of ramen noodles decreases, Judi’s budget constraint rotates outward. Ramen noodles are considered an inferior good while steak is considered a normal good.
a. Determine the income and substitution effects in this case. Draw an approximation of these effects on a diagram.
b. How do income and substitution effects differ between normal and inferior goods?
6. Consider a consumer with indirect utility function 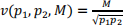
a. What is the consumer’s expenditure function?
b. What are the consumer’s Hicksian demand functions?
7. Suppose Matt's utility depends on the number of music tracks (x) and apps (y) on his phone. He spends his income (M) of 15 dollars per month on these goods. The price for x and y is 1.00. His utility function is U(x,y) = 4x0.8y0.2
His goal is to maximize his utility.
a. Set up the Lagrangian for this constrained maximization problem.
b. What are the necessary conditions for the optimum from the Lagrangian?
c. What is the optimal amount of music tracks and apps on his phone each month?
8. The uncompensated demand function for shoes is 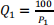 .
.
2024-03-05