Managerial Economics ARE 155 Midterm 2 Summer Session II 2023
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Managerial Economics ARE 155
Summer Session II 2023
Midterm 2, Thursday, August 31, 2023
Problem 1 (25 points):
Variable Cells
|
Cell |
Name |
Final Value |
Reduced Cost |
Objective Coefficient |
Allowable Increase |
Allowable Decrease |
|
$B$5 |
Amount Shipped XA1 |
300 |
0 |
8 |
1 |
1E+30 |
|
$C$5 |
Amount Shipped XA2 |
0 |
6 |
? |
1E+30 |
6 |
|
$D$5 |
Amount Shipped XB1 |
200 |
0 |
9 |
5 |
1 |
|
$E$5 |
Amount Shipped XB2 |
0 |
3 |
10 |
1E+30 |
3 |
|
$F$5 |
Amount Shipped XC1 |
0 |
5 |
14 |
1E+30 |
5 |
|
$G$5 |
Amount Shipped XC2 |
300 |
0 |
7 |
3 |
7 |
|
Constraints |
||||||
|
|
|
Final |
Shadow |
Constraint |
Allowable |
Allowable |
|
Cell |
Name |
Value |
Price |
R.H. Side |
Increase |
Decrease |
|
$H$10 |
Factory A Total LHS |
300 |
- 1 |
300 |
200 |
50 |
|
$H$11 |
Factory B Total LHS |
200 |
0 |
250 |
1E+30 |
50 |
|
$H$12 |
Factory C Total LHS |
300 |
0 |
325 |
1E+30 |
25 |
|
$H$13 |
Retail Center 1 Total LHS |
500 |
? |
500 |
50 |
200 |
|
$H$14 |
Retail Center 2 Total LHS |
300 |
7 |
300 |
25 |
300 |
(a) Suppose the cost of shipping from Factory C to Retail Outlet 2 decreases by $5 per unit. What will the change in TC be? (5 points)
(i) Test: AD = - 7, proposed ∆cC2 = - 5.
(ii) Past test: ∆TC = ∆cC2(xC2 * ) = - 5(300)
∆TC = - $1,500
(b) How much is Retail Center 2 willing to pay, in total, for an additional 30 units of x? (5 points)
(i) Test: AI = 25; proposed change = 30
(ii) Fail test, cannot comment on the ∆TC.
(c) Over what range of cB2 will the current answer remain optimal? (5 points)
7 ≤ cB2 ≤ Infinity
(d) How much does it cost to ship product x from Factory A to Retail Center 2? (5 points)
RCA2 = cA2 – (z2 – uA)
6 = cA2 – (7 – 1)
cA2 = 12
(e) How much is Retail Center 1 willing to pay for 1 unit of x? (5 points)
RCA1 = cA1 – (z1 + uA)
0 = 8 – (z1 – 1)
z1 = 9
Problem 2 (20 points):
max TR = 40x1 + 0x2
st 2x1 + 2x2 ≤ 50
4x1 = 88
x1, x2 ≥ 0
x1 and x2 are both integers
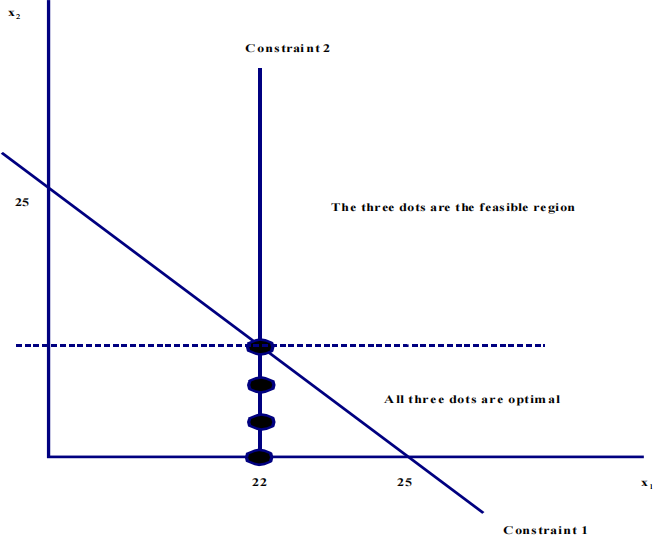
(a) On the graph below, you are to (i) highlight the feasible region and (ii) draw in the feasible region that shows the optimal point/s. (14 points).
(b) State or show on your graph all optimal solutions. You must (i) identify all optimal points and (ii) state the maximum TR value for each optimal point. (6 points).
There are 3 optimal points, all with a TR = 40*22 = $880
(x1, x2) (22, 0), (22, 1), (22, 2)
Problem 3 (20 points):
Pamela can get to work driving any of three possible routes. Her options are:
(i) Tennessee Street.
(ii) Back Roads.
(iii) Expressway.
The table below shows three states of nature: No traffic (no congestion), mild traffic (mild congestion), and severe traffic (severe congestion). The time travelled on each route for each state of nature is given, in minutes driving, in the table below.
|
Alternatives |
None |
Mild |
Severe |
|
Tennessee |
15 |
30 |
45 |
|
Back roads |
20 |
25 |
35 |
|
Expressway |
30 |
30 |
30 |
In the past 60 days, Pamela has encountered mild traffic on 18 days and severe traffic on 12 days. Assume that these past 60 days are typical of traffic conditions in general.
(a) Based on the expected time each route will require, which route should Pamela take? (8 points)
Prob(None) = 30/60 = 0.50
Prob(Mild) = 18/60 = 0.30
Prob(Severe) = 12/60 = 0.20
EMVT = 0.5(15) + 0.3(30) + 0.2(45) = 25.50
EMVBR = 24.50 (*)
EMVEXP = 30.00
(b) Pamela turns on her car radio which provide regular traffic conditions. On average, how much time can she save by listening to the radio, or, what is the EVPI? (14 points)
EVPI = EMV – EVWPI
EMV = 24.50 (from part (a)).
EVWPI = 0.5(15) + 0.3(25) + 0.2(30) = 21.00
EVWPI = 24.50 – 21.00 = 3.5
Multiple Choice (20 total points, 4 points per problem, only one correct answer):
1) States of nature
a) can describe uncontrollable natural events such as floods or freezing temperatures.
b) can be selected by the decision maker.
c) are not random events.
d) All of the alternatives are true.
2) The critical path
a) is any path that goes from the starting node to the completion node.
b) is a combination of all paths.
c) is the shortest path.
d) is the longest path.
3) Activities K, M and S immediately follow activity H, and their latest start times are 14, 18, and 11. The latest finish time for activity H
a) is 11.
b) is 14.
c) is 18.
d) cannot be determined.
4) If we are solving a 0- 1 integer programming problem, the constraint “x1 + x2 ≤ 1” is a constraint.
a) multiple-choice
b) mutually exclusive
c) conditional
d) corequisite
e) redundant
5) The difference between the transportation and assignment problems is that
a) total supply must equal total demand in the transportation problem
b) the number of origins must equal the number of destinations in the transportation problem
c) each supply and demand value is 1 in the assignment problem
d) there are many differences between the transportation and assignment problems
2024-03-03