ECON 2400D: Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory I
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECON 2400D: Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory I
Fall 2017
Midterm Test
1. –25 points– The representative consumer has the following utility function:
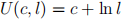
where c is the consumption good, l is the leisure hours. She has h hours of time available which she can allocate between work and leisure. For each hour of work, she earns w units of consumption good. She also earns π as dividend (profit) income, and pays T units of lump-sum taxes to the government. Both π and T are measured in consumption units. Thus, the consumer’s budget constraint is given:
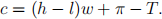
(a) Solve for c, and l that maximize the utility of the representative consumer.
(b) Determine the impact of an increase in the lump-sum taxes, T, on the consump-tion good, c, and leisure, l. Explain.
(c) Determine the impact of the increase in the wage rates, w, on the consumption good, c, and leisure, l. Explain.
2. –15 points– After a long recession, new labor market data reveals that the unemploy-ment rate is dropping. Discuss what might be happening in the labor market. Explain clearly.
3. –20 points– Consider two households in an economy. The household A is not em-ployed, and receives unemployment insurance benefit from the Canadian Government as he is searching for work. The household B is working as a contractor building a road for the Canadian Government in a remote town where nobody lives (or visits). Discuss whether the payments from the Government to either household are included in GDP calculation. Explain why they are (not) included, and state clearly any inconsistency in our GDP calculations in this example if there is any.
4. –20 points– Let the technology of the representative firm be given 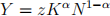 where 0 < α < 1.
where 0 < α < 1.
(a) Derive the condition for profit maximization.
(b) Calculate the profits of the firm.
(c) Suppose that the total factor productivity, z, for this firm increases. Determine the effect of this increase in z on the demand for labor.
(d) Suppose that the government introduces a subsidy on employment. The govern-ment pays s of consumption goods to the firm for each unit of labor it employs (0 < s < 1). Derive the condition for profit maximization with the new subsidy on employment. Determine the effect of this subsidy on the demand for labor, and calculate the firm’s profits.
5. –20 points– The representative consumer has the preferences such that she wants to consume c and l in fixed proportions:
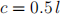
where c is the consumption good, l is the leisure hours. She has h hours of time available which she can allocate between work and leisure. For each hour of work, she earns w units of consumption good. She also earns π units of consumptions goods as dividend (profit) income. She pays a lump-sum tax of T units of consumption goods to the government.
(a) Write down the consumer’s budget constraint.
(b) Solve for c, and l that maximize the utility of the consumer.
(c) Suppose now that T increases. Determine the impact of the increase in T, on consumption, c, and leisure, l. Explain.
2021-10-29