CHEM224 2023 SI Session #16
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
CHEM224 2023 SI Session #16
Learning Objectives: By the end of this session, students should be able to:
● Describe aromaticity in heterocycles, and utilize this to identify basic lone pairs.
● Draw the mechanism of EAS, and use it to synthesize simple Benzene derivatives
Section 0: Review
1. What is required for a compound to be aromatic or antiaromatic? What is Huckel’s Rule?
2. Use MO theory to explain why Cyclooctatetraene is anti-aromatic if it is planar.
Section 1: Heterocycles
3. Predict if the following heterocycles are aromatic, nonaromatic or antiaromatic. Explain your answer using MO theory. In addition, explain which oxygen or nitrogen atoms will be more basic than water.
a. 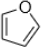
b. 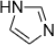
c. 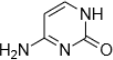
Section 2: EAS
4. Draw the mechanism of the following reaction. Explain why FeBr3 is used, and name, as well as draw, all resonance structures of the relevant intermediate.
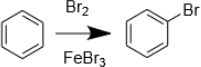
5. What reagents do we need to Chlorinate benzene instead? How about Iodination?
6. Explain what reagents we need to substitute a nitro group on benzene. Draw the mechanism of this substitution.
7. The product in (6) is treated with solid Zn in aqueous HCl. Draw the product of this reaction.
8. Explain what reagents we need to substitute a sulfonic acid onto benzene. Draw the mechanism of this substitution.
9. The product in (8) is treated with dilute sulfuric acid. Draw the product of this reaction, and the mechanism by which it occurs.
Section 3: Directed EAS Part 1
10. Draw the two possible products of the chlorination of toluene (methylbenzene). Explain which ring positions are favored, and which effect is responsible.
11. Draw the two possible products of thenitration of anisole (methoxybenzene). Explain which ring positions are favored, and which effect is responsible.
2024-01-23