CIVE5975 Foundation Engineering Example Exam Questions – Section A
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
CIVE5975 Foundation Engineering
Example Exam Questions - Section A
These questions are designed to examine your understanding of the basic principles of foundation engineering. On average, it should take you ten to twelve minutes to complete each question. This is feasible provided you have studied the subject in advance.
1. As part of the decommissioning of an offshore platform, it is necessary to remove the monopiles. It is proposed to seal the top of the monopile and apply air pressure inside the monopile. The monopile is a 10m long, 4m diameter steel tube with a wall thickness of 50mm. The base is 9m below the sea bed, which consists of 3m of very soft clay overlying a stiff clay. The undrained strength of the soft clay is 5kPa and its unit weight 15kN/m3 ; the strength of the stiff clay is 100kPa and the unit weight 18kN/m3. The top of the pile is 25m below the sea level. What is the maximum pressure is necessary to lift the pile out of the sea bed?
2. Calculate the additional long term settlement for a 5m wide by 10m long foundation at a formation level of 1m in a 2m thick layer of dense sand underlain by a 4m thick layer of firm to stiff clay. The clay is underlain by very dense sand. The upper sand layer has a unit weight of 20kN/m3 ; the clay layer has a coefficient of volume compressibility of 0.1m2/MN and unit weight of 18kN/m3. The load on the foundation is 5000kN and the foundation is 1m thick mass concrete. The ground water level is at 2m.
3. A monopile is being used to support a wind turbine which will be subject to wind forces. The monopile is driven into dense sand. Select the partial factors for the pile using Design Approach 1 of Eurocode 7 stating the reasons for your choice.
4. A site investigation reveals that a foundation is going to be placed on sand which has an average SPT value of 15. Determine the design values of the properties for the serviceability and ultimate limit states using Eurocode Design Approach 1.
5. Estimate the settlement after 25 years of a pad foundation which is two metres square. The permanent vertical load on the foundation is 2T, the fluctuating load is 0.5T and the formation level is 2m below ground level, the same level as the groundwater level. The alluvial sand, which extends below the zone of influence, is medium dense sand with a SPT blow count of 15. Ignore the weight of the foundation and backfill above the foundation.
6. The coefficient of volume compressibility of a clay layer is (0.1 - 0.001 x z) m2/MN [z is the depth below the ground surface]. The unit weight of the clay is 20kN/m3 and the groundwater level is at the surface. Calculate the settlement of the corner of a 10mwide by 20m long storage tank placed on top of the clay. The contact stress due to the storage tank is 36kPa.
7. A 350mm diameter cfa pile is 20m long. Calculate using Eurocode Design Approach 1 the capacity of the pile if the soil is clay with an undrained shear strength equal to the effective vertical stress. The unit weight of the clay is 20kN/m3. The groundwater level is at the ground surface.
8. Calculate the ultimate capacity using partial factors of a shallow foundation which is 10m long, 5m wide with the formation level at 1m below ground level. The ground water level is 3m below the ground surface and the pore pressure profile is hydrostatic. The soil is clay with undrained shear strength of 75kPa; the unit weight is 20kN/m3 .
9. A shallow foundation is 3m wide and 5m long. The formation level is at 1.5m below ground level in sand with an SPT N value of 15. At the time of the investigation the groundwater level was at 1m below ground level and the ground water level was hydrostatic. What is the maximum load that can be placed on the foundation?
10. Calculate the immediate settlement for a 5m wide by 10m long foundation in normally consolidated sand which has a SPT value of 12. The formation level of the foundation is 3m below ground level and the load on the foundation is 5000kN.
11. A 450mm diameter, 20m long reinforced concrete pile is driven into a stiff clay which has a shear strength profile [cu = 75 + 2.5 z kPa] where z is the depth below the surface. A surcharge of 15kPa is applied to the ground surface. Calculate the negative friction that will act as a result of this surcharge. Assume that the submerged unit weight of the clay is 10kPa.
12. A rectangular foundation, 10m long, 5mwide and 0.5m deep supports a vertical load of 5000T. The formation level is 1m below ground level, the same level as the water table. The soil consists of sand which has a unit weight of 18kN/m3 ; no cohesion and an angle of friction of 35o. Use Eurocode design approach 1 combination 1 to check that the foundation is safe.
13. Calculate the ultimate capacity using partial factors (Design Approach 1, Combination 1) of a caisson foundation which is 10m long, 5m wide with the formation level at 4m below ground level. The groundwater level is 3m below the ground surface and the pore pressure profile is hydrostatic. The soil is sand with an angle of friction of 35o, cohesion 5kPa and unit weight 20kN/m3 .
14. Large diameter offshore monopiles can be installed by water pressure created using a vacuum to remove all the water from within the pile. A 10m long, 4m diameter open ended steel pile sank 1m into the soft clay sea bed due to its own weight creating a seal. A vacuum was applied to the pile thus removing the seawater from the pile. The top of the pile is 25m below the sea level. Check if there is sufficient pressure to push the pile into the sea bed which consists of 3m of very soft clay overlying a stiff clay. The undrained strength of the soft clay is 5kPa and its unit weight 15kN/m3 ; the strength of the stiff clay is 100kPa and the unit weight 18kN/m3 .
15. Calculate the long term settlement for a 5m wide by 10m long foundation at a formation level of 1m in a firm to stiff clay which is underlain by very strong sandstone. The clay layer is 6m thick and has a coefficient of volume compressibility of 0.1m2/MN and unit weight of 18kN/m3. The load on the foundation is 5000kN and the foundation is 1m thick mass concrete. The ground water level is at 2m.
16. A 450mm diameter, 20m long reinforced concrete cfa pile is installed in sand. The angle of friction is 35o ; the unit weight 18kN/m3. The groundwater level is at 2m below ground level. Calculate the ultimate capacity of the pile.
17. Calculate the ultimate capacity using partial factors (Design Approach 1, Combination 1) of a bridge pier foundation that is 10m long, 3m wide with the formation level at 2m below the river bed. The depth of the river is 1m and the pore pressure profile is hydrostatic. The soil is sand with an angle of friction of 35o, cohesion 5kPa and unit weight 20kN/m3 .
18. A static test is to be carried out on a 400mm diameter compression pile. Four tension piles are to be used for reaction. The compression pile is 15m long and installed in stiff clay which has an undrained shear strength (= 50 + 2z) kPa where z is the depth below the ground surface. Calculate the maximum load on each tension pile.
19. An oil tank is to be tested by filling it with water but to prevent foundation failure, it is necessary to do it in stages. In this way some settlement can occur resulting in an increase in the stiffness of the clay before more water is added. The tank is 18m in diameter and 8m high. It is proposed to fill it in four stages, each stage being 2m of water. The soil consists of 15m of alluvial clay overlying a stiff clay. Assume the total settlement of a full tank is 100mm, calculate how long that would take assuming the coefficient of consolidation is 50m2/yr. Calculate how long it would take for 25mm of settlement to occur.
20. A 450mm diameter, 20m long reinforced concrete cfa pile is to be used as a raking pile , which is installed at 10o to the vertical in sand. The vertical load and horizontal load on the pile cap were 100kN and 300kN respectively. The cohesion is 5kPa; the angle of friction is 35o ; the unit weight 18kN/m3. The groundwater level is at 2m below ground level. Check whether the pile is
21. It has been decided to use preloading to consolidate a 10m thick layer of alluvial clay underlain by dense sand. The unit weight of the clay is 16kN/m3 , the compression index is 0.32 and the water content is 30%. The groundwater level is at the surface. The unit weight of the 4m high fill forming the preloading is 15kN/m3. Estimate the settlement of the clay layer.
22. Calculate the ultimate capacity using partial factors (Design Approach 1, Combination 2) of a caisson foundation, which is 10m long, 5m wide with the formation level at 4m below the seabed. The depth of the sea is 10m and the pore pressure profile is hydrostatic. The soil is sand with an angle of friction of 35o, cohesion 5kPa and unit weight 20kN/m3 .
23. As part of the decommissioning of an offshore platform, it is necessary to remove the monopiles. It is proposed to seal the top of the monopile and apply air pressure inside the monopile. The monopile is a 10m long, 4m diameter steel tube with a wall thickness of 50mm. The base is 9m below the seabed, which consists of 3m of very soft clay overlying a stiff clay. The undrained strength of the soft clay is 5kPa and its unit weight 15kN/m3 ; the strength of the stiff clay is 100kPa and the unit weight 18kN/m3. The top of the pile is 25m below the sea level. What is the minimum pressure necessary to lift the pile out of the seabed?
24. Calculate the additional long-term settlement for a 5m wide by 10m long foundation at a formation level of 1m in a 2m thick layer of dense sand underlain by a 4m thick layer of firm to stiff clay. The clay is underlain by very dense sand. The upper sand layer has a unit weight of 20kN/m3 ; the clay layer has a coefficient of volume compressibility of 0.1m2/MN and unit weight of 18kN/m3. The load on the foundation is 5000kN and the foundation is 1m thick mass concrete. The ground water level is at 2m.
25. A 450mm diameter, 20m long reinforced concrete cfa pile is installed in sand. The cohesion is 5kPa; the angle of friction is 35o ; the unit weight 18kN/m3. The groundwater level is at 2m below ground level. Calculate the working capacity of the pile using Design Approach 1, Combination 2.
26. A 3.5m long by 2.5m wide by 1.5m deep foundation carries a vertical load of 1300kN , which acts at 1.5m from the short edge of the foundation. The formation level, 1.5m below ground level, is in a uniform stiff clay with an undrained shear strength of 100kPa and a unit weight of 18kN/m3. Determine whether the foundation is adequate against bearing failure using Design Approach 1 Combination 2.
27. A 0.4m diameter cfa pile is drilled through 6m of soft clay into stiff clay. The soft clay has a unit weight of 16kN/m3 and shear strength of 15kPa; the relevant properties of the stiff clay are 19kN/m3 and 75kPa. The groundwater level was at 2m below ground level but due to excavations nearby, the ground water level was permanently lowered to 4m below ground level sometime after installation. The permanent vertical load on the pile is 50kN, calculate the minimum length of the pile using a global design factor of 2.
28. An approach embankment to a bridge is to be piled. Cfa piles will be drilled through the soil profile given in Table A3- 1. A geogrid will be placed across the top of the piles to transfer some of the embankment load onto the piles. The 5m high embankment is formed of compacted sand and gravel with a unit weight of 17kN/m3. Determine the maximum load on each of the 0.4m diameter piles if they are placed at 2m centres.
Table A3- 1 Soil profile and properties
|
Soil Type |
Depth to top of layer [m] |
Unit Weight [kN/m3] |
Undrained Shear Strength [kPa] |
Angle of Friction |
Cohesion [kPa] |
|
topsoil |
0.0 |
15 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Loose sand |
0.3 |
16 |
- |
30o- |
- |
|
Stiff clay |
5.0 |
18 |
100 |
- |
- |
Ground water profile: hydrostatic with phreatic surface at 1 m.
29. Calculate the time it takes for the foundation shown in Figure 29 to settle assuming that the coefficient of consolidation of the stiff clay is 1.5 m2/yr. At the time of construction the ground water level was 0.5m below ground level. It was permanently lowered to 0.8m during construction. What effect would this have on the long-term performance of the foundation?
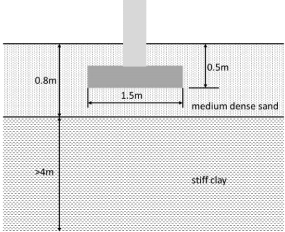
Figure 29 Cross section of foundation showing soil profile
30. Calculate the bearing capacity of a 4m by 3m pier foundation supporting a vertical load. The formation is 6m below ground level and the soil profile is given in Table 30. Use Design
Approach 1, Combination 2.
Table 30 Soil profile and properties
|
Soil Type |
Depth to top of layer [m] |
Unit Weight [kN/m3] |
Undrained Shear Strength [kPa] |
Standard Penetration Test |
Cohesion [kPa] |
|
topsoil |
0.0 |
15 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Dense sand |
0.3 |
18 |
- |
15 |
0 |
|
Firm clay |
2.0 |
17 |
50 |
- |
5 |
|
Dense sand |
3.0 |
18 |
- |
30 |
0 |
Ground water profile: hydrostatic with phreatic surface at 1 m.
31. Dynamic compaction was used to increase the density of a layer of loose sand and gravel. The original density of the 6m thick layer was 1600kg/m3 . Calculate the density after the compaction is complete if 12 x 103 Mg of sand and gravel is added over an area of 100m by 100m.
32. Dynamic compaction was used to increase the density of a layer of loose sand and gravel. The original density of the 6m thick layer was 1600kg/m3. Estimate the angle of friction after the compaction is complete if 12 x 103 Mg of sand and gravel is added over an area of 100m by 100m assuming the ground level is constant.
33. The ground level for a proposed industrial site is 5m above datum. The soil profile consists of 10m of dense sand overlying sandstone. The unit weight of the sand is 18kN/m3 and the modulus is 20MPa. The ground water level is 1m below the existing ground surface. Estimate the amount of settlement if the site level is raised by 2m using engineered fill which has a unit weight of 17kN/m3 .
34. It is proposed to use a vacuum to consolidate a layer of alluvial clay underlain by dense sand. The alluvial clay consists of a 1m crust overlying 2m of soft clay. The coefficient of volume change, mv, of the crust is 0.1m2/MN and that for the soft clay, 0.2m2/MN. Calculate the settlement of the alluvial clay.
35. Calculate the total load necessary to cause failure of a 1m diameter stone column in clay. The undrained shear strength of the clay is 15kPa. The column is 10 m long and is formed of gravel with an angle of friction of 35o. The unit weight of the normally consolidated clay is 16kN/m3 .
The phreatic surface is at ground level and the ground water profile is hydrostatic.
2024-01-15