MATH6153 Statistical Theory and Linear Models
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MATH6153
SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2018/19
Statistical Theory and Linear Models
1. [Total Marks 25] Let X1 and X2 be independent and identically distributed N (0, 1) random variables.
(a) [3 marks] Write down the joint probability density function of X = (X1 , X2 ).
(b) [10 marks] Find the joint probability density function of Y = (Y1 , Y2 ), where Y1 = X1 and Y2 = X2 /X1. Are Y1 and Y2 independent?
(c) [6 marks] Hence show that Y2 = X2 /X1 has a t distribution with 1 degree of freedom,with marginal p.d.f.
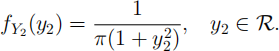
Hint: Use the fact that if g is an even function (satisfying g(y) = g(-y) for ally), then 1∞∞ g(y)dy = 2 10∞ g(y)dy.
(d) [3 marks] Write down how you could use X1 and X2 to construct a new random
variable Z χ2(2) (the chi-squared distribution with two degrees of freedom).
(e) [3 marks] Let X3 N (0, 1), independent of X1 and X2. Write down how you could use X1 , X2 and X3 to construct a new random variable W t2 (the t distribution with two degrees of freedom).
2. [Total Marks 25] Let x1 , . . . , xn be observations of X1 , . . . , Xn, which are
independent and identically distributed Poisson(λ) random variables, with probability function
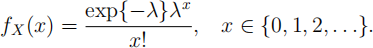
(a) [6 marks] Show the the maximum likelihood estimator of λ is
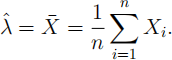
(b) [4 marks] Derive the asymptotic distribution of λ(ˆ) .
(c) [5 marks] Show that the moment generating function of X(-) is

You may use without proof the fact that the moment generating function of the Poisson(λ) distribution is mX (t) = expfλ(et — 1)g.
(d) [6 marks] Let φ = P (Xi = 0) = expf—λg. Write down the maximum likelihood
estimator φ(ˆ) of φ, and find the asymptotic distribution of φ(ˆ) .
(e) [4 marks] Using (c), find E(φ(ˆ)), and hence find the bias of φ(ˆ) as an estimator of φ .
3. [Total Marks 20] In a medical experiment, the number of the patients to whom a
medicine is effective among a selected population of m patients can often be
modelled by a Binomial distribution Binomial(m, p), whose probability function (p.f.)

where mis a known positive integer, but 0 < p < 1 is an unknown parameter. Suppose Y1 , Y2 , · · · , Yn are a random sample from the Binomial distribution Binomial(m, p). It is known that the maximum likelihood estimator of p is

and the expected (or Fisher) information I(p) = mn/[p(1 — p)].
Often we are concerned with the effective probability p. Suppose most experts
believe that p = 0.70, but there are some other experts who don’t agree with that and believe p = 0.50 only. You are asked to do a test of H0 : p = 0.70 against H1 : p = 0.50.
(i) [5 marks] By applying the Neyman-Pearson approach, show that the critical region for rejection of H0 in favour of H1 can be expressed as ˆ(p) cfor some suitable critical value c.
(ii) [5 marks] By applying the central limit theorem, give the large sample
distributions of ˆ(p)when H0 is true and when H1 is true, respectively.
(iii) [5 marks] Using the large sample distribution, derive an expression for the
probability of the Type I error, and hence find an expression for the critical value c given in part (i) in terms of mand n when the size of the testis α = 0.01. It is
given that Φ(2.326) = 0.99, where Φ( ·) denotes the cumulative density function of the standard normal distribution.
(iv) [5 marks] Derive an expression for the power of the test in part (iii),i.e., the
probability ofˆ(p) 三 cunder part (iii) when H1 is true. Hence show that in order for the power of the test to beat least 0.99, it is required that mn ≥ 125.
4. [Total Marks 15] Suppose that x1 , . . . , xn are independent observations of X , a Poisson distributed random variable with p.f.
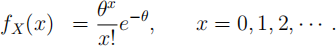
where θ is a positive parameter.
(a) [5 marks] Write down the likelihood function of θ. Hence write down a conjugate prior distribution for θ .
(b) [5 marks] Obtain the posterior distribution of θ under the conjugate prior
distribution. Find the parameters of this posterior distribution and write down expressions for the mean and variance of the posterior distribution.
(c) [5 marks] State the Bayes estimator of θ under the squared error loss function. Under what conditions are the maximum likelihood and the Bayes estimator equivalent?
5. [Total Marks 15] Suppose that y1 , y2 , . . . , yn are independent observations, with yi sampled from Yi:
Yi = β(1 + cos(xi )) + εi ,
with εi … N (0, σ2 ), for i = 1, . . . , n, where x1 , . . . , xn are known covariates, and β and σ2 > 0 are unknown parameters.
(a) [5 marks] Show that the least squares estimator of β that minimises the sum of squares, S(β) =:![]() [Yi — β(1 + cos(xi ))]2 , can be expressed as
[Yi — β(1 + cos(xi ))]2 , can be expressed as
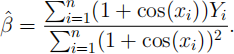
(b) [5 marks] Show that β(ˆ) is an unbiased estimator of β, i.e., E(β(ˆ)) = β, and
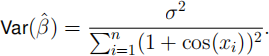
(c) [5 marks] Construct an unbiased estimator for σ2 based on the residual sum of
squares, S(β(ˆ)) =Σ![]() Yi - β(ˆ)(1 + cos(xi ))]2 , and state its distribution.
Yi - β(ˆ)(1 + cos(xi ))]2 , and state its distribution.
2024-01-09