MATH3085 Survival Models SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2020/21
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2020/21
MATH3085 Survival Models
1. [19 MARKS]
Suppose T is a survival random variable with probability density function

where θ > 0 and t > 0.
(a) Find the survival function of T. [2 MARKS]
(b) Find the hazard function of T. [1 MARK]
(c) Find the cumulative hazard function of T. [1 MARK]
(d) Find the expected lifetime. [6 MARKS]
Hint: Recall that the integral over (-1, 1) of the probability density function of the standard normal is equal to 1, i.e.

Let t1 , . . . , tn denote n independent and identically distributed observationsof T and let d1 , . . . , dn bedefined as

(e) Find an expression for the maximum likelihood estimate of θ . [5 MARKS]
Suppose n = 10 and there are eight observed failures with Σ![]() ti = 11.4 and Σ
ti = 11.4 and Σ![]() ti(2) = 23.2.
ti(2) = 23.2.
(f) Calculate the maximum likelihood estimate of θ for these data. [1 MARK] (g) Calculate an estimate of the time taken for the survival probability to decrease to 0.5. [3 MARKS]
2. [17 MARKS]
A group of rats were exposed to a carcinogen and the number of days to death due to cancer was recorded (as shown below). A + indicates a right censored observation.
95 142 156 163 198 198 204+ 232
232 232 232 232 250+ 250+ 250+ 250+
(a) Calculate the Kaplan-Meier estimate of the survival function of the random variable representing time to death due to cancer. [3 MARKS]
(b) Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the probability of a rat surviving beyond 100 days. [4 MARKS]
(c) Calculate the Nelson-Aalen estimate of the cumulative hazard function of the random variable representing time to death due to cancer. [3 MARKS]
(d) Transform your answer from part (c) to an estimate of the survival function. [2 MARKS]
(e) Sketch the estimates from parts (a) and (d) on a suitable set of axes (a very accurate sketch is not required, but you should label axes, identify the individual estimates and show any discontinuities clearly). Comment on the differences between the two estimates. [5 MARKS]
3. [18 MARKS]
(a) Data are available from a small portfolio of 7 electronic device insurance policies, and show, for two classes of policyholders (A and B), the time in months until a claim is made; the + indicates that the observation was right censored.
Class A: 10 5 13+
Class B: 7 21 17 19+
Suppose that a Cox proportional hazards model holds for these data where the hazard at time tis given by
h(t) = h0 (t) exp (βx) ,
where h0 (t) is the baseline hazard and x is a dummy variable such that

(i) Find the partial log-likelihood. [8 MARKS]
It can be shown that the partial likelihood is numerically maximised at βˆ = -1.16.
(ii) Test the hypothesis H0 : β = 0 against the alternative H1 : β ![]() 0 and report your conclusions. [6 MARKS]
0 and report your conclusions. [6 MARKS]
(b) A study was undertaken to assess a new treatment for arthritis. A sample of arthritis patients were randomised to either receive the new treatment or a
placebo. Additionally, their sex and arthritis type were also recorded. Patients were followed up and the time from treatment until pain disappeared was recorded.
Let x1 , x2 and x3 bedefined as follows.
x1 a dummy variable taking the value 1 if the patient received the new treatment and 0 otherwise;
x2 a dummy variable taking the value 1 if the patient is male and 0 otherwise;
x3 a dummy variable taking the value 1 if the patient has rheumathoid arthritis (RA) and 0 if they have ostheo-arthritis (OA).
A Cox proportional hazard model was fitted with the following form
h(t) = h0 (t) exp (β1x1 + β2x2 + β3x3 )
where h0 (t) denotes the baseline hazard of pain disappearing.
The study found the following results.
. The hazard of pain disappearing for males with RA who received the new
treatment was 2 times the hazard for males with OA who received the placebo treatment.
. For patients with RA, the hazard of pain disappearing for females who
received the new treatment was 3 times the hazard for males who received the placebo treatment.
. For patients who received the placebo treatment, the hazard of pain
disappearing for males with OS was three quarters of the hazard for females with RA.
Calculate the estimated values of β1 , β2 and β3. Based on the estimates alone, do you recommend the new treatment? [4 MARKS]
4. [15 MARKS]
Sleep is considered to consist of several layers or phases.
1. Awake (long);
2. Awake (short);
3. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep;
4. Deep (Non-rapid eye movement; NREM) sleep.
People move up and down the different phases several times during the night. It is not possible to move more than one phase of sleep instantaneously. For example, it is not possible to move from awake in the long form to REM sleep without moving to awake in the shortform first, and vice versa. The only exception to this is that you can become awake in the long form from any of the 3 other phases.
A study is undertaken to learn about the transitions between the different phases,
using a large group of volunteers. Each volunteer is invited into the study centre and given a bed. Once they fall asleep, by moving from awake (long) to awake (short),
sensors can determine which phase they are in at any given time. For each volunteer understudy, the number of transitions between each phase is recorded as well as the time in each phase. If a volunteer wakes up in the long form, they are removed from being monitored.
(a) Sketch a diagram showing the possible transitions between the phases considered in the study. [1 MARK]
(b) Use Kolmogorov’s forward equations to derive expressions for the rate of change of the transition probabilities to the awake (long form) from each of the other states. [8 MARKS]
During the study the total minutes in each phases is recorded along with the number of transitions between the phases. These are given in the table below
Minutes awake (shortform) 1350
Minutes awake (REM) 16790
Minutes awake (NREM) 4790
Number of transitions from awake (shortform) to REM 120
Number of transitions from REM to awake (shortform) 102
Number of transitions from REM to NREM 50
Number of transitions from NREM to REM 62
There were also a total of 25 people who were removed from being monitored due to waking up in the long form. Of these, prior to waking up in the long form, 20 were awake (short form), 4 were in REM sleep and 1 was in NREM sleep.
(c) Assuming transition intensities are constant over time, calculate maximum likelihood estimates for all unknown transition intensities. [4 MARKS]
(d) Is the assumption of constant transition intensities reasonable? Justify your answer. [2 MARKS]
5. [16 MARKS]
(a) A mortality investigation followed a sample of 50,000 people from their 60th
birthday until their death, or until they attained the age of 70 years. There were no withdrawals from the investigation for reasons other than death. The table below gives the number of people alive at various ages.

(i) Assuming uniform distribution of deaths within each two-year age group,
estimate the number of people who survive to exact age 65 and the probability that a life aged exactly 60 will die between the ages of 65 and 67. [4 MARKS]
(ii) Recalculate your answers to part (i) under constant force of mortality within each two-year age group. [4 MARKS]
(b) The mortality investigation discussed in part (a) began on the 1st January 2020 and ended on the 1st January 2021. Part of this investigation was particularly interested in the survival of people aged between 65 and 66 (last birthday). The following table gives the details of 10 lives involved in the investigation.

(i) Assuming a binomial model with a uniform distribution of deaths between the ages of 65 and 66, find an expression for the log-likelihood, maximisation of which gives the maximum likelihood estimate of death aged 65 (last birthday) given survival to exact age 65. [4 MARKS]
(ii) Find the alternative method of moments estimate based on the initial exposed to risk E6(0)5 and use this to estimate the force of mortality μ65:5 (under constant force of mortality). [2 MARKS]
(iii) Calculate an estimate of μ65:5 under a two-state model. [2 MARKS]
6. [15 MARKS]
(a) The mortality experience of the female population of a region of the United
Kingdom is to be compared with a set of standard mortality rates. The following is an extract from the results.
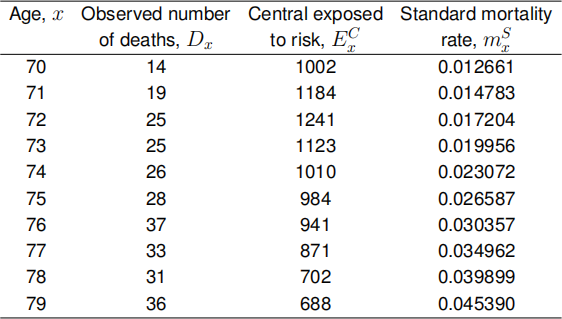
Test whether the data conform to the standard mortality rates using:
(i) A test of overall goodness of fit.
(ii) A test of systematic bias using the cumulative deviations test.
(iii) A test of systematic bias using the sign test (using the normal approximation to the distribution of the test statistic).
Comment on the prudence of carrying out all three tests above. [12 MARKS]
The following R code and output maybe useful
> qchisq(0.95,df=1:10)
[1] 3.841459 5.991465 7.814728 9.487729
[5] 11.070498 12.591587 14.067140 15.507313
(b) A large insurance company has performed graduation on the mortality
experience of part of its business, by using a (log-linear) Gompertz model with the following form
Dx Poisson(Ex(C)mx) where log mx = β0 + β1x + β2x2 .
The observed number of deaths, central exposed to risk and graduated rates for a series of ages is shown in the table below.
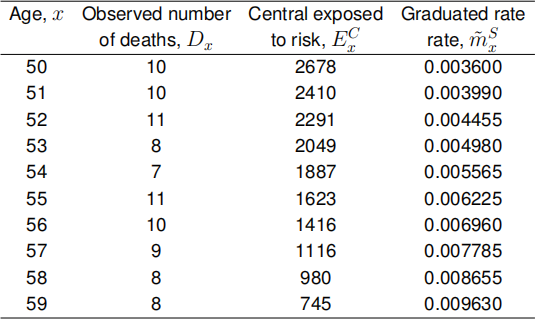
Test this graduation for overall goodness of fit. [3 MARKS]
2024-01-09