Jan 2022 EC220 Test
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Jan 2022 EC220 Test
January 31, 2023
1 A static game
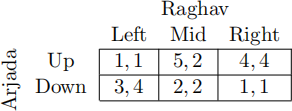
Iterated Elimination of Strictly Dominated Strategies...
A Deletes nothing, so that every proile of strategies is an IEE
B Deletes some strategies, leading to multiple IEEs
C Deletes some strategies, but the game does not have an IEE
D Deletes all but a single strategy for each player, leaving an IEE that is also the unique NE
E Deletes all but a single strategy for each player, leaving an IEE that is not a NE
F Deletes all but a single strategy for each player, leaving an IEE that is one of two or more NEs
G Deletes all strategies, so the game does not have an IEE
H Deletes nothing, so there is no IEE
C. Raghav’s mixed strategy :5L + :5R eliminates Mid, but that’s the end of the elimination sequence. As there are multiple strategy proiles left, there is no IEE.
2 Ininite Repetition
Suppose the following stage-game is ininitely repeated.
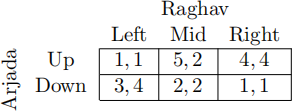
The payof vector (2; 3)...
A Is not a feasible payof vector.
B Is a feasible payof vector, but is never an SPNE payof vector.
C Is an SPNE payof vector if δ is high enough enough, but cannot be attained with Nash Reversion equilibrium strategies.
D Is an SPNE payof vector if δ is high enough, and can be attained with Nash Reversion equilibrium strategies.
A. The vector (2; 3) is not in the feasible set.
3 Information Sets
Let’s describe a game. First, Nature chooses if Agustin the bear is hungry or not. Agustin observes whether he is hungry or not, but Nick the salmon does not. Then, Agustin chooses whether to sunbathe, dive, or kayak. Nick observes Agustin’s choice, and then decides whether to swim, jump, or leave. Then, the game is over.
How many information sets does each animal have?
A Agustin has one information set, and Nick has one information set.
B Agustin has one information set, and Nick has two information sets.
C Agustin has one information set, and Nick has three information sets.
D Agustin has two information sets, and Nick has one information set.
E Agustin has two information sets, and Nick has two information sets.
F Agustin has two information sets, and Nick has three information sets.
G Agustin has two information sets, and Nick has six information sets.
H Agustin has three information sets, and Nick has two information sets. I Agustin has three information sets, and Nick has three information sets.
J Agustin has three information sets, and Nick has six information sets.
K Agustin has six information sets, and Nick has two information sets. L Agustin has six information sets, and Nick has three information sets.
M Agustin has six information sets, and Nick has six information sets.
F. Agustin has two information sets - corresponding to whether he is hungry or not. Nick has three information sets - corresponding to what he has observed Nick do.
4 The Ice Cream Market
Sinem and Dimitri produce ice cream in the market. Sinem knows if the weather will be warm or cold tomorrow, but Dimitri does not; the common prior puts equal prob- abilities on warm and cold weather. Sinem and Dimitri decide how much to produce simultaneously. If the weather is hot tomorrow, the price is 6 - 2Q, where Q is the sum of the quantities they produce; whereas if the weather is cold, the price is 3 - Q. An ice cream maker’s proits equal the quantity it produces, times the price; both Sinem and Dimitri wish to maximize their own proits.
In the unique BNE, how much does Sinem produce when the weather will be hot, and how much does Sinem produce when the weather will be cold?
A (0:5; 0:5)
B (1/3; 4/3)
C (1; 2)
D (2/3; 4/3)
E (1; 1)
F (1; 1:5)
G (1:5; 2)
H (3/5; 5/3)
I None of the above
E. Actually, Sinem’s type does nothing to incentives!
2024-01-06