Building physics Third call – 10/02/23 – exercises
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Building physics
Third call – 10/02/23 – exercises
Exercise 1 (2 pts)
A closed, adiabatic system is divided in two subsystems by a separator. The first subsystem has a volume of 0.01 m3 and contains 1 mol of monoatomic gas at the temperature of 400 K. The second subsystem, containing 2 mol of the same gas, is at the same pressure of the first, but its volume is three times the one of the first subsystem. If the separator is removed, calculate the equilibrium temperature and the variation of entropy of the system.
(533.3 K; 1.08 J/K)
Exercise 2 (2 pts)
A mixer is used to regulate the temperature of the water leaving the heating system of a building by properly mixing a stream at 60 °C with a stream at 20 °C. Calculate the flow rate from the two branches if the resulting flow rate is 1000 kg/h and its temperature 35 °C.
(625 kg/h; 375 kg/h)
Exercise 3 (2 pts)
A mass flow rate of 10 kg/s of saturated liquid at the pressure of 2000 kPa enters a heat exchanger where it reaches a superheated state at 500 °C. The heating power to complete the process is provided by a stream of flue gases (specific heat = 1.1 kJ/(kg K)) entering the heat exchanger at 1100 °C and leaving at 300 °C. Calculate the mass flow rate of the flue gases.
(29.09 kg/s)
Exercise 4 (2 pts)
A volumetric flowrate equal to 1000 m3/h at 30 °C and 20% of relative humidity is humidified by injecting liquid water until its dew point temperature reaches 10 °C. Calculate the mass flow rate of water required by the process.
(0.76 g/s)
Exercise 5 (2 pts)
The circulation pump of a heating system of a building is used to increase the pressure of a stream of 5000 liters per hour of water (ρ = 1000 kg/m3) from the pressure of 1.5 bar to 5 bar. Calculate the mechanical power required to run the pump if its isentropic efficiency is 60%.
(0.81 kW)
Exercise 6 (2 pts)
Consider a steel pipe (λ = 80 W/(m K)) of length 10 m, internal diameter 200 mm and thickness 5 mm. Water circulates inside the pipe at a temperature of 10 °C. To decrease heat losses, the pipe is insulated with a layer of material with thermal conductivity λ = 0.09 W/(m K) and thickness 40 mm. Calculate the heat loss of the pipe considering an ambient temperature of 35 °C and external heat transfer coefficient of 8 W/(m2 K).
(353 W)
Exercise 7 (2 pts)
Calculate the mean radiant temperature of a person standing in a rectangular room with the following characteristics:
- Floor temperature and view factor between person and floor: 25 °C and 0.25, respectively.
- Ceiling temperature and view factor between person and ceiling: 20 °C and 0.25, respectively.
- Right-hand side wall temperature and view factor between person and right-hand side wall: 17 °C and 0.1, respectively.
- Left-hand side wall temperature and view factor between person and left-hand side wall: 17 °C and 0.1, respectively.
- Front wall temperature and view factor between person and front wall: 18 °C and 0.2, respectively.
- Back wall temperature and view factor between person and back wall: 18 °C and 0.1, respectively.
(20.05 °C)
Exercise 8 (2 pts)
Calculate, using the proposed correlations and selecting the most appropriate air properties, the heat transfer coefficient by convection on the external wall of a building exposed to a wind parallel to the surface with a velocity of 10 m/s. Assume 5 °C as the temperature of the external air, 20 °C the temperature of the indoor environment and 10 m the characteristic length.

(19.7 W/(m2 K))
SECOND PART
Exercise (8 pts)
Consider a wall with the stratigraphy reported in the table below. The external operating temperature, the relative humidity and the convective-radiative heat transfer coefficient are 0 °C, 90% and 25 W/(m2 K) for the outdoor environment and 22 °C, 50% and 8 W/(m2 K) for the indoor environment.
Calculate:
[1] the U-value of the wall;
[2] the indoor and outdoor surface temperatures;
[3] the presence of interstitial condensation;
[4] the mass of condensate produced per m2 of surface due to interstitial condensation in one day.
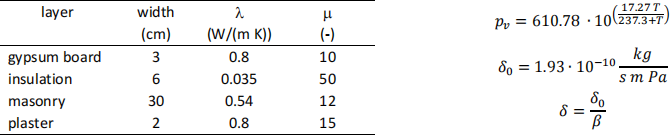
(0.40 W/(m2 K); 20.9 °C; 0.35 °C; YES; 0.624 g/(day m2))
2024-01-06