PHAY0029 MODERN ASPECTS OF DRUG DISCOVERY 2019
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MSc DRUG DISCOVERY AND DEVELOPMENT
MSc DRUG DISCOVERY AND PHARMA MANAGEMENT
MRES
PHAY0029
MODERN ASPECTS OF DRUG DISCOVERY
JANUARY 2019
SECTION A
DRUG DISCOVERY CASE STUDIES
1. Answer ALL parts of the question
a) With reference to the therapies available at the time, explain how James Black intended to revolutionize the treatment of coronary heart disease. (20 % of marks)
b) The structures of adrenaline, atenolol and betaxolol are shown. Describe the steps involved in Black’s discovery of propranolol and the subsequent development of these β1 selective antagonists. In your answer say which of atenolol and betaxolol are likely to cause drowsiness in patients and explain why. (60 % of marks)
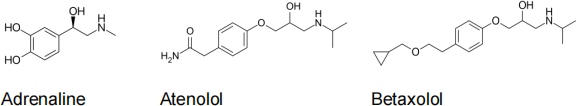
c) Since Black’s original discoveries, how much do you think G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have maintained prominence as drug targets? Justify your opinion with some evidence. (20 % of marks)
2. Compare and contrast the various approaches taken for the discovery of
inhibitors for angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) and for renin. Include in your answer some examples of the inhibitors that were identified and indicate reasons why some inhibitors were more successful in the clinic than others. (100 % of marks)
SECTION B
TECHNIQUES IN DRUG DISCOVERY
3. Answer BOTH parts of the question.
In the laboratory you have used ethanol to extract compounds from a plant material. Biological assays testing the crude ethanol extract have shown positive results. However, in order to take this research forward you need to identify the active compounds in the extract.
a) Discuss why capillary electrophoresis could be a useful technique for separating compounds in the plant extract. (20 % of marks)
Further research suggests that the major compounds of interest in the plant extract are polyphenols including the two illustrated below:
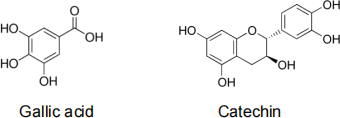
You therefore decide to carry out mass spectrometry in order to confirm the presence of these compounds in your crude extract. You use electrospray ionisation coupled to an ion trap mass spectrometer in negative ion mode.
b) Describe these techniques and, assuming there is no fragmentation, indicate the mass of the peaks you would expect to see on the obtained spectra for the above compounds. (80 % of marks)
4. Answer ALL parts of the question.
Single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) is used in many contexts in structure- based drug discovery.
a) Explain why you might use XRD crystallographic methods to describe a target ligand binding pocket for future drug discovery efforts. Explore what effects data resolution, disorder and mobility might have on the level of atomic detail derived from such experiments. (40 % of marks)
b) Illustrate with the aid of diagrams, the experimental set-up used in single crystal X-ray diffraction experiments, explaining aspects of sample preparation, basic data collection geometry and equipment. (40 % of marks)
c) Describe one type of electron density map used in crystallography and explain how it is used. (20 % of marks)
SECTION C
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY AND NEW TECHNOLOGY
5. When discussing the issues and challenges facing the pharma industry,
Professor Nigel Ratcliff stated the following: “There is a huge need for mind- set changes” . Discuss this statement in terms of the challenges facing the industry and how the industry should respond. (100 % of marks)
6. Your company is planning to develop an active travel vaccine against the Zika virus. Using examples of other vaccines discuss the strategy or strategies you believe the company should take. In your answer describe the characteristics of an ideal travel vaccine. (100 % of marks)
2024-01-05