Building physics Second call – 27/01/23 – exercises
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Building physics
Second call – 27/01/23 – exercises
Exercise 1 (2 pts)
A heat engine receives 1000 W of energy from a source at 700 K and produces 600 W of work, while discharging heat to a low temperature sink at 300 K. Calculate the efficiency of the engine and determine whether it is acceptable based on the second law of thermodynamics.
(0.6 → not possible because higher than the Carnot efficiency)
Exercise 2 (2 pts)
A closed system contains 2 mol of helium (ideal monoatomic gas with molar mass of 4 g/mol) at 400 °C and 2 bar. Calculate the final temperature and the exchanged work when a heat of 2000 J is provided to the system along an isobaric transformation.
(721.3 K ;800 J)
Exercise 3 (2 pts)
A mass flow rate of 100 kg/s of steam enters a turbine at the temperature of 300 °C and a pressure of 2 MPa. Calculate the isentropic efficiency of the turbine and the exchanged work knowing that the outlet pressure is 10 kPa and the vapor quality at the outlet is 0.85.
(0.907; 77.91 MW)
Exercise 4 (2 pts)
A volumetric flowrate equal to 1000 m3/h at 30 °C and 60% of relative humidity is cooled down to a temperature of 15 °C. Calculate the cooling power required and the mass flow rate of condensate produced.
(9.22 kW; 1.72 g/s)
Exercise 5 (2 pts)
A wall characterized by a U-value of 0.8 W/(m2 K) separates an indoor ambient at 20 °C and with 70% as relative humidity from the outdoor environment at - 10 °C. Determine whether there is surface condensation on the internal wall and in correspondence of a thermal bridge due to the presence of a pillar, where the heat flux is two times the one of the wall. Consider 7 W/(m2 K) as heat transfer coefficient on the indoor surface.
(no condensation; yes condensation)
Exercise 6 (2 pts)
Calculate the layer of insulation which is necessary to add to the wall with the given stratigraphy in order to meet the requirements of a building regulation which imposes a U-value lower than 0.21 W/(m2K). Assume a thermal conductivity for the insulation equal to 0.038 W/(m K) and heat transfer coefficient of 25 and 10 for the outdoor and indoor surfaces respectively.
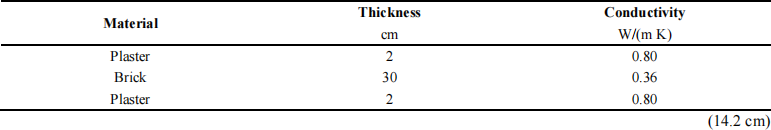
Exercise 7 (2 pts)
A cavity filled with air is made of two flat walls at the temperatures of 20 °C and 80 °C respectively. Calculate the heat transfer between the two walls by convection and radiation, knowing that the heat transfer coefficient by convection is 1.2 W/(m2 K), and that both walls have an emissivity of 0.7.
(72 W/m2; 249.4 W/m2; 321.4 W/m2)
Exercise 8 (2 pts)
An underfloor with a surface temperature of 30 °C is used to heat a room where the air is at 20 °C. Determine the heat transfer coefficient by convection between the air and the floor’s surface using the proposed correlation. Choose the correct properties and consider 1 m as characteristic length for the floor.
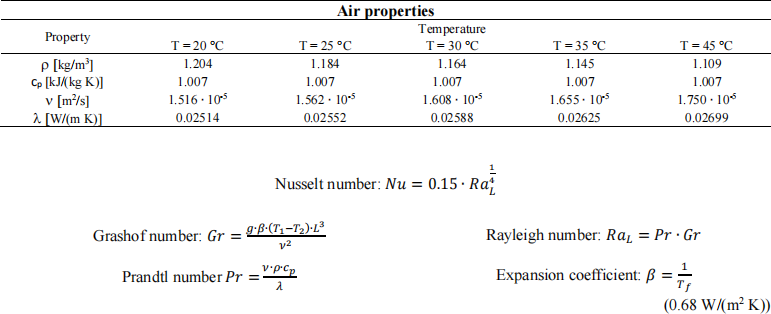
SECOND PART
The underfloor heating system of a building is connected to an air-source heat pump, which provides an heating capacity of 4 kW with a COP of 4 when the outdoor air temperature is -3 °C. Calculate:
- the mass flow rate of water delivered to the underfloor heating system if the temperature difference between supply and return is 6 °C;
- the electric power required to power the heat pump and heat duty at the evaporator;
- the refrigerant mass flow rate, knowing that the enthalpy of the refrigerant (R134a) at the outlet of the compressor is equal to 290 kJ/kg and the condensing pressure is 10 bar;
- the isentropic efficiency of the compressor considering that the evaporation temperature is 3 °C lower than the outdoor air temperature.
(0.159 kg/s; 1 kW; 3 kW; 0.022 kg/s; 0.70)
2024-01-05