BUSI4470 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
BUSI4470
BUSINESS SCHOOL
A LEVEL 4 MODULE, AUTUMN SEMESTER SAMPLE PAPER
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING
Time allowed TWO Hours
SECTION A
Candidates must answer this question
Question 1 Burberry
Burberry is a British luxury fashion house. The company is listed on the London Stock Exchange and has its headquarters in London.
The annual report states, “Burberry’s Capital allocation Framework is used to prioritise the use of cash generated by the Group. The framework addresses the investment needs of the business, regular dividend payments and additional returns to shareholders. The framework also seeks to maintain an appropriate capital structure for the business and a strong balance sheet”.
The company uses IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) to prepare its financial statements. Extracts from the Financial Statements 2018 are presented below.

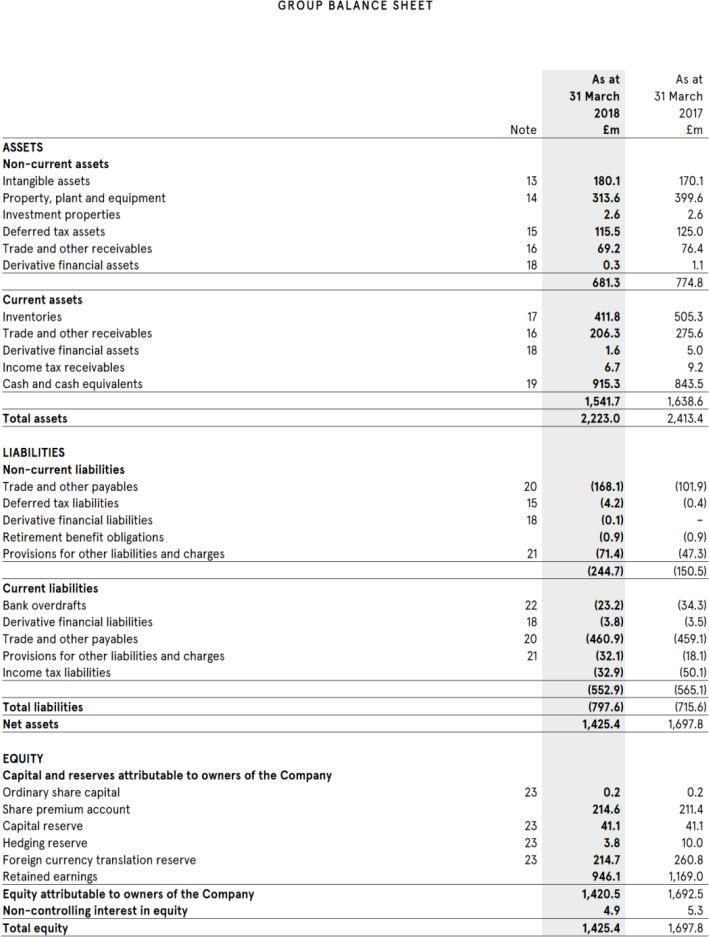
For this question, you are provided the following industry average ratios:
|
i |
Gross Profit Margin |
65% |
|
ii |
Return on Capital Employed |
30% |
|
iii |
Trade and other payable days |
120 |
|
iv |
Current Ratio |
1.8:1 |
|
v |
Gearing |
18% |
|
vi |
Asset Turnover |
1.7 Times |
Required:
(a) Using analytical tools, carry out a comparative analysis of Burberry’s accounts for 2017 and 2018. (15 marks)
(b) Identify two key stakeholder groups for Burberry and prepare a brief report for them explaining Burberry’s position as compared to the industry. (5 marks)
[Total 20 marks]
SECTION B
Candidates must answer this question
Question 2 Dida Ltd.
The company directors of Dida Ltd, have decided to pilot an activity based costing (ABC) system at one of its factories. The finance controller at the factory produces the following list of activities and estimates of the relevant quantities involved for the 2014 financial year.
|
Activity |
|
Expected Qty. |
Total cost of activity (£) |
|
Machining Finishing (labour) Materials ordering Materials issues Machine set-up |
|
6,000 12,000 186 120 70 |
148,200 136,440 12, 183 11,592 19,915 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following information for two products, C and D was also produced
Product C Product D
Prime cost (per unit) £28.50 £32.70
Machine hours* 2,500 3,500
Labour hours 7,200 4,800
Number of orders 124 62
Number of issues 70 50
Number of hours used in set-up 26 44
*One unit of C uses 1 machine hour, whereas one unit of D uses 1.4 machine hours. Based on 1 machine hour per unit, completed production for product C is 2500 units. Completed production for product D, based on 1.4 machine hours per unit, is also 2500 units.
Required
a) Calculate the unit cost for product C and D using machine hours as a basis for allocating the overhead. (10 marks)
b) “Although Activity Based Costing (ABC) has been applied in a large number of organisations throughout the world, it is not necessarily appropriate for all organisations. It appears to have been most successful where:
1. Indirect costs are a high proportion of total costs.....
2. There is a diverse range of products or services provided....
3. There is intense competition and a more accurate costing system is needed...”
(Bruce Bowhill 2008: 141)
In light of the quote above, critically evaluate the appropriateness, or not, of ABC in current western practice. You may refer to your answer in part a to aid your evaluation. (15 marks)
c) Briefly explain two key attributes that management accountants should possess. (5 marks)
SECTION C
Candidates must answer both questions from this section
Question 3:
Financial statement frauds are often associated with audit failures (Cullinan, 2004).
Define ‘audit failure’ and discuss potential causes for audit failures.
[25 marks]
Question 4:
In their article, titled, “You owe it to yourself: The financially literate manager”, Brown et al (2006) argue that financial literacy helps business managers to function efficiently at work because they are able to evaluate the information needed to make decisions that have financial ramifications or consequences.
Brown, R. B., Saunders, M.N.K., and Beresford, R. (2006). You owe it to yourself: The financially literate manager. Accounting Forum 30 (2006) 179 - 191
You are required to critically analyse the importance and the extent of financial literacy for business managers.
[25 marks]
2023-12-28