ME 104 Thermodynamics [F23] Homework Assignment 6
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ME 104 Thermodynamics [F23]
Homework Assignment 6
[Due MON 10/09]
Text: Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, Y. Çengel and M. Boles, McGraw-Hill, 10th Edition, 2024. The link to the book is provided on the course site.
Problem 1: [5–51] Steam flows steadily through an adiabatic turbine. The inlet conditions of the steam are 4 MPa, 500°C, and 80 m/s, and the exit conditions are 30 kPa, 92 percent quality, and 50 m/s. The mass flow rate of the steam is 12 kg/s. Determine (a) the change in kinetic energy, (b) the power output, and (c) the turbine inlet area.
Problem 2: [5–89] Hot exhaust gases of an internal combustion engine are to be used to produce saturated water vapor at 2 MPa pressure. The exhaust gases enter the heat exchanger at 400°C at a rate of 32 kg/min while water enters at 15°C. The heat exchanger is not well insulated, and it is estimated that 10 percent of heat given up by the exhaust gases is lost to the surroundings. If the mass flow rate of the exhaust gases is 15 times that of the water, determine the temperature of the exhaust gases at the heat exchanger exit and the rate of heat transfer to the water. Use the constant specific heat properties of air for the exhaust gases.
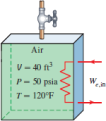
Problem 3: [5–124E] An insulated 40-ft3 rigid tank contains air at 50 psia and 120°F. A valve connected to the tank is now opened, and air is allowed to escape until the pressure inside drops to 25 psia. The air temperature during this process is kept constant by an electric resistance heater placed in the tank. Determine the electrical work done during this process.
Problem 4: [5–132] A balloon initially contains 40 m3 of helium gas at atmospheric conditions of 100 kPa and 17°C. The balloon is connected by a valve to a large reservoir that supplies helium gas at 125 kPa and 25°C. Now the valve is opened, and helium is allowed to enter the balloon until pressure equilibrium with the helium at the supply line is reached. The material of the balloon is such that its volume increases linearly with pressure. If no heat transfer takes place during this process, determine the final temperature in the balloon.

2023-12-28