CHEM0028: CONCEPTS IN COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY 2023
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
B.Sc. DEGREE 2023
M.Sci. DEGREE 2023
CHEM0028: CONCEPTS IN COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY Coursework
Credit value: 15
Deadline: 16:00 GMT
2 February 2024
Candidates should attempt ALL questions. Each section is marked out of 30.
Your submission must be word-processed, using the settings below.
A4 paper
Minimum margins 1.25 cm (0.5 inch)
Minimum font size: 10 pt
Single Spaced
No cover sheet is required.
Work must be submitted as three separate files on Moodle.
Start each section on a new page. The page limit for EACH section is 2 pages, including any figures and references. The figures in this paper can be included in your work without further reference. Work beyond 2 pages on any question will not be marked. Any additional sources beyond the course notes and reading must be referenced.
SECTION A
This question related to the material from Dr Rivera on molecular mechanics. You may answer this section in handwritten format, but do not exceed 2 pages.
1) A forcefield is being parameterised for glycolaldehyde depicted below:
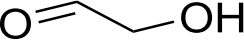
Scheme 1
Name each kind of bond, bond angle, and torsional angle that needs to be considered for this parameterisation. [7 marks]
2) This molecule is modelled using periodic boundary conditions with lattice vectors:
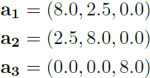
Two conformers are considered which are identical except for their dihedral  angle: the cis and trans conformers. The program writes their Cartesian coordinates in ˚Angstroms as such:
angle: the cis and trans conformers. The program writes their Cartesian coordinates in ˚Angstroms as such:
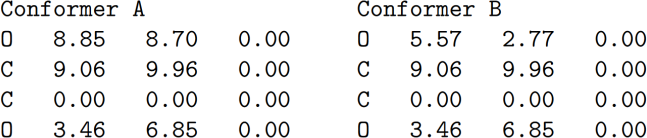
a) For each atom, write the coordinates of the periodic image closest to the origin. [6 marks]
b) Identify which conformer is cis, which is trans. You may distinguish between them solely based on the O-O distance. [4 marks]
c) We use the following torsional potential for  :
:
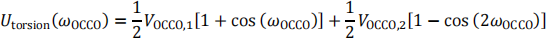
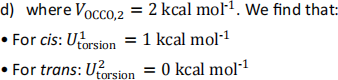
A third conformer is simulated at uto(3)rsion = 2 kcal mol-1. Find the  angle for the third conformer in degrees in the range [-180◦,180◦]. There are multiple solutions, but you only need to give one. You may use the following cos(2x) = 2cos2(x) − 1. [10 marks]
angle for the third conformer in degrees in the range [-180◦,180◦]. There are multiple solutions, but you only need to give one. You may use the following cos(2x) = 2cos2(x) − 1. [10 marks]
3) A master student successfully simulates the molecular dynamics of glycolaldehyde in a solvent. They then want to repeat the calculation at a constant higher temperature, but their results don’t make sense. Their supervisor suggests the following changes:
• Make the timestep shorter.
• Change the bond stretch potential from harmonic to Morse.
• Change from the Verlet algorithm to the Velocity Verlet algorithm.
Explain why each of these pieces of advice would be helpful to model dynamics at a constant high temperature. [3 marks]
SECTION B
This question related to the material from Dr Heleon Quantum Methods.
Part 1
The Born-Oppenheimer Hamiltonian can be written as
He = Te + veN + vee
Where Te is the kinetic energy of the electrons
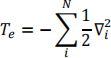
veN is the interaction between each electron and each nucleus
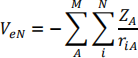
where the summations are over i = 1, … ,N electrons and A = 1, … ,M nuclei, and vee is the interaction between electrons
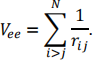
There is also the repulsion between nuclei
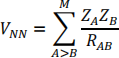
which is added in at the end of the calculation.
Considering Te, veN, vee and vNN, state with brief reasoning which of these terms (if any) need not be considered for the following systems:
a) H2+
b) H2
c) A single Lithium atom [6 marks]
Part 2
Comment on the suitability of Restricted Hartree-Fock (RHF) for description of the dissociation of molecules. For the case of H2 in a minimal basis, would you expect configuration interaction singles (CIS) to significantly improve on a conventional RHF calculation? What about a configuration interaction singles and doubles (CISD) calculation? [7 marks]
Part 3
The intense blue colour of lapis lazuli is due to the trisulphur radical anion S3•- . Describe how you might computationally find the bond angle and bond length of S3•- . How might you estimate computationally the energy required to oxidize S32- to S3•-? Briefly discuss an advantage and disadvantage of the methods you propose. [8 marks]
Part 4
Pariser-Parr-Pople (PPP) theory can be considered a modification of Hückel theory which retains the neglect of differential overlap (NDO) assumption and a simplified one-electron Hamiltonian but includes electron-electron repulsion and therefore accounts for Coulomb and exchange effects. For the purposes of this question you may assume that the one-electron Hamiltonian elements hij area if i =j, β if i and j are nearest neighbours and zero otherwise, where a and β are constants as in Hückel theory, and that only the π electrons are treated explicitly. To what extent would you expect PPP theory to improve upon Hückel theory for the following properties? Briefly justify your answer:
a) Geometry optimization
b) Simulation of UV-vis absorption spectra
c) Vibronic effects [9 marks]
SECTION C
This question related to the material from Dr Crespo-Otero on hybrid methods and excited states.
The photochemistry of protonated Schiff bases in retinal is of great interest because they are part of rhodopsins, which are important for vision. The 2,4-pentadiene-iminium cation (PSB3) is widely used as a model system for retinal protonated Schiff bases. The photochemical process involves cis-trans photoisomerisation around the central double bond, which occurs through aS1-S0 conical intersection. To model this process accurately, it is important to include double excitations. An investigation of the excited state dynamics of PSB3 in water was performed using an additive QM/MM hybrid scheme and electrostatic embedding. The QM region comprised the PSB3 model at CASSCF[6,6]/6-31G* level of theory and the MM region included 300 water molecules simulated using the OPLSAA force field.
Scheme 2
Scheme 2
a.) Explain why electrostatic embedding was used in these simulations and how the QM/MM interactions are calculated in this scheme. [4 marks]
b.) Calculate the number of additional one-electron terms included in the electrostatic embedding Hamiltonian. [7 marks]
c.) If instead of water n-hexane is considered as a solvent, would it appropriate to perform the simulations employing mechanical embedding? Compare with respect to the simulations in water. Provide a concise rationale. [3 marks]
d.) Could you briefly mention and justify a strategy to improve the description of the photochemistry of PSB3? [2 marks]
e.) The CASSCF active space comprised 6 electrons distributed across 6 π orbitals (3 π and 3 π*). Justify the selection of this specific active space. [3 marks]
f.) For a CASSCF[6,6] active space, draw a diagram for a single-excited and a double excited configuration. Only consider the electrons and orbitals in the active space. [6 marks]
g.) Would be TDDFT a good methodology to investigate the photoisomerisation of PSB3.
Briefly explain. [2 marks]
h.) Do you need to go beyond the Born-Oppenheimer approximation to describe the photochemistry of PBSB3? Explain. [3 marks]
2023-12-26